All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for radiation thermometers as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 12 radiation thermometer manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked radiation thermometer companies as of March, 2026: 1.Banner Engineering Corporation, 2.Wintronics, Inc., 3.KELLER HCW GmbH.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Radiation Thermometers
Engaged in research on nitride semiconductor growth using the MBE method at Waseda University Graduate School. After graduating from graduate school in 2016, he joined a non-ferrous metal manufacturer.
Engaged in equipment maintenance and engineering work at metal smelting plants. Moved to a chemical manufacturer in 2022. Engaging in similar tasks.
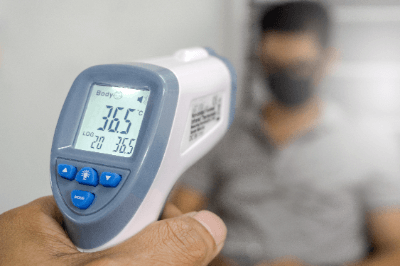 A radiation thermometer is a device that measures temperature by sensing infrared radiation emitted from a material.
A radiation thermometer is a device that measures temperature by sensing infrared radiation emitted from a material.
Since all substances emit infrared rays according to their temperature, this device measures temperature by detecting the amount of infrared rays. Although it cannot measure the temperature inside a material or the temperature of a gas, it can instantly measure temperature without touching the object.
The measurement range (spot diameter) and measuring distance are determined by the device, and the choice depends on the situation.
Radiation thermometers can measure temperatures at high speeds and without direct contact. Therefore, they are suitable for temperature measurement of moving or rotating objects or small heat capacity objects whose temperature changes with contact with the sensor.
They are used in a wide range of applications, including industrial processes and research fields.
Radiation thermometers are useful in the following cases:
All matter, including humans, emit infrared radiation. When you put the palm of your hand close to your cheek, you feel warmth because the skin of your hand detects the infrared radiation emitted from your cheek. In general, the higher the temperature of a substance, the greater the amount of infrared radiation emitted.
Radiation thermometers first collect the infrared radiation emitted from a substance onto a sensing element called a thermopile. The thermopile is a sensing element that emits an electrical signal from the absorbed infrared radiation.
In the thermopile, multiple thermocouples are connected in series with the warm junction facing the center, and an infrared absorbing film is placed at the center where the warm junction faces. Light collected by the lens hits only the warm junction, creating a temperature difference between the warm junction and the cold junction on the outside. This creates a voltage difference due to the Seebeck effect and enables temperature measurement.
Infrared radiation is part of the electromagnetic spectrum, and its frequency is between visible light and radio waves. Within this frequency range, only frequencies between 0.7 and 20 microns are used for practical temperature measurements.
Radiation thermometers are accurate to within ±1°C for general-purpose products. However, care must be taken to avoid measurement errors if the measurement conditions of the device are not properly followed during actual measurement. The following three conditions determine measurement accuracy.
Measurement Point
The measurement range (or spot diameter) varies according to the distance from the object to be measured. Generally, the measurement range increases when the measurement distance increases. Since the measurement distance and the measurement range vary depending on the type of radiation thermometer, these two conditions should be checked.
Temperature drift
If the ambient temperature of the radiation thermometer is changed abruptly, the measured value may change due to the temperature change. Therefore, keep the ambient temperature from changing abruptly.
Emissivity of the surface to be measured
Radiation thermometers measure temperature by measuring the intensity of infrared radiation emitted from the surface of an object. The intensity of the infrared radiation emitted from the object is determined not only by the temperature of the object, but also by a coefficient called emissivity. Therefore, emissivity correction is necessary when measuring temperature.
In recent years, due to increased hygiene awareness, more and more body temperatures are being measured with radiation thermometers. Generally, when measuring body temperature in cases where the external temperature is lower than the body temperature, the body temperature may be displayed lower due to the influence of the outside temperature.
On the other hand, in cases where the outside temperature is high, such as near a heater, a higher temperature may be indicated. When measuring body temperature, check the instruction manual for the radiation thermometer to ensure that the correct external environment is used.
Thermography is a non-contact temperature measuring device. Thermography is a device that visually displays the surface temperature of the entire measurement object in different shades of color for easy visualization. Specific examples of its use are shown below.
A radiation thermometer is used inside a thermal imaging camera.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Banner Engineering Corporation, established in 1966 and headquartered in Minneapolis, Minnesota, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial automation products. They offer an extensive range of sensors, including proximity sensors, photoelectric sensors, and limit switches, for detecting object presence, position, and speed. Additionally, Banner provides a different types of switches, such as pushbuttons, toggle switches, and rotary switches, to control electricity flow and offer system feedback. Their wide array of controls includes PLCs, HMIs, and motion controllers, enabling automation of industrial processes.




Optex Fee Co., Ltd., was established in 2002 and based in Kyoto, Japan, is a manufacturer and supplier of factory automation sensors and solutions. The company offers an extensive and diversified product portfolio including photoelectric sensors, fiber-optic sensors, displacement sensors, non-contact thermometers, vision sensors, and other industrial automation products. These sensors and solutions play a pivotal role in enhancing manufacturing processes across a spectrum of industries, including automotive, electronics, and packaging.

HORIBA RADIO LABORATORY was established in Japan in 1945 and has spent the last three-quarters of a century growing as an R&D company and engaged in international operations. HORIBA Scientific offers 200 years of experience developing high-performance scientific instruments and analytical solutions. The HORIBA Group of worldwide companies provides an extensive array of instruments and systems for applications ranging from automotive R&D, process and environmental monitoring, in-vitro medical diagnostics, semiconductor manufacturing, and metrology to a broad range of scientific R&D and QC measurements. Operating in Asia, Europe, and North and South America, HORIBA scientific develops solutions that go beyond just products.

RKC Instrument has been continually growing for over half a century and strives to be a solution provider of measurement and control systems. RKC supplies quality products and professional engineering services quickly and efficiently. RKC specializes in everything from limit and multiloop controllers to heater break alarms and temperature sensors. RKC has a website in Chinese, English, and Japanese and has sales networks across the globe. Based on the management concept of “Realization of the highest quality,” RKC Instrument has obtained the accreditation of ISO9001, the international standard for quality management systems.

SENSATEC Co. Ltd., established in 1988 and based in Kyoto, Japan, is a manufacturer and supplier of OEM sensors. The company specializes in crafting electronic detection and control devices, medical tools, and beauty equipment, including various sensors, A/D/D/A converters, and optical fiber data systems. Its diverse product range also includes cable and coil winding processing, and it provides support for metal mask manufacturing. The company also offers tailored designs emphasizing miniaturization and handles everything from standard strips to soldering and assembly.

Sensortherm GmbH, established in 2001 and located in Steinbach, Hessen, Germany, is a manufacturer specializing in infrared temperature measurement devices which was acquired by Nynomic AG in 2019. The company’s products include its Einfarbenpyrometer single-color pyrometer for non-contact temperature measurement, its Highspeedpyrometer for rapid temperature measurement in laser processing applications, and its Quotientenpyrometer for comparing radiation intensity at multiple wavelengths to measure temperature. The company is ISO 9001:2015-certified, and serves clients in industrial manufacturing and research and development (R&D) operations.

Japan Sensor Corporation, founded in 1972, is a Japanese manufacturer based in Minato-ku, Tokyo, specializing in infrared measurement solutions. The company's product range includes fiber-type, fiber-less, and general-purpose infrared thermometers. These products feature quartz-permeable wavelengths, enabling measurement through glass, as well as the fastest response time of 0.001 seconds, facilitating rapid detection of temperature changes. Sensor heads, fiber cables, and temperature converters are also installed based on specific requirements. The company also offers indicating setters for infrared thermometers and emissivity meters.



Ranking as of March 2026
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Banner Engineering Corporation |
14.7%
|
| 2 | Wintronics, Inc. |
12.8%
|
| 3 | KELLER HCW GmbH |
11.9%
|
| 4 | Sensortherm GmbH |
10.1%
|
| 5 | Shinko Technos Co., Ltd. |
10.1%
|
| 6 | National Physical Laboratory |
8.3%
|
| 7 | Optex Fee |
8.3%
|
| 8 | Micro-Epsilon JAPAN K.K. |
6.4%
|
| 9 | SENSATEC Co., Ltd. |
6.4%
|
| 10 | Japan Sensor |
3.7%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the radiation thermometer page as of March 2026. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 Japan
Japan
|
4 | 50.0% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
2 | 25.0% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 12.5% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 12.5% |
72 products found
72 products
Sansei Electronics Co., Ltd.
510+ people viewing
■Typical usage examples ・Non-contact measurement of surface temperature or infrared radiation ・Temperature measurement of moving objects ・Contin...
Soki Co., Ltd.
700+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
We are selling the infrared radiation thermometer SK-8700Ⅱ, the best-selling infrared radiation thermometer. Although it is small and lightweight, ...
Yamazato Sangyo Co., Ltd.
730+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Digital radiation thermometer for ultra-thin glass surface measurement has high accuracy and stability with digital circuit and free temperature ra...
Asahiko Trading Co., Ltd.
490+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
■Summary The QRT1 quantum thermal PAR/temperature sensor consists of a QRT1 display unit and QTP1+ probe sensor combination. When used as a calibra...
Broadwatch Co., Ltd.
610+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Product information - Non-contact type, so you can rest assured about hygiene ・Large display and backlight for easy viewing ・With 2 modes, you c...
RKC INSTRUMENT
570+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
■Super heat resistance of 180℃ (sensor head) ・The sensor head can be installed in high-temperature atmospheres such as at the outlet of a heating ...
4 models listed
Soki Co., Ltd.
920+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
We are selling a waterproof radiation thermometer IR-310WP with a laser marker function that allows you to see the approximate measurement position...
Yamazato Sangyo Co., Ltd.
610+ people viewing
Last viewed: 22 hours ago
IS6/IGA6 IS6-TV/IGA6-TV is a fully digital radiation thermometer. Adopts a high-speed response of 120 μsec and a movable focus lens. The temperatur...
4 models listed
Sansei Electronics Co., Ltd.
580+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
■Typical usage examples ・Non-contact surface temperature measurement ・Temperature measurement of moving objects ・Remote measurement with small v...
Hakko Electric Co., Ltd.
480+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Summary The heat-sensitive part (sheath tip) is coated with Hylex coating, making it easier to absorb radiant heat. Suitable for controlling Hilex...
Yamazato Sangyo Co., Ltd.
420+ people viewing
IS12, IS12-S, IGA12, and IGA12-S are fully digital radiation thermometers. High-speed response (up to 1msec) and detection at short wavelengths all...
4 models listed
Muratec KDS Co., Ltd.
670+ people viewing
Last viewed: 15 hours ago
■Product overview/features ・For inspection of engine room and high temperature equipment ・PSC compliant product ・Easy operation just by pressing...
Yamazato Sangyo Co., Ltd.
470+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
IN5/5+ series is a digital radiation thermometer with fast response (fastest 10msec). With a detection wavelength of 5.14μm, it is suitable for tem...
3 models listed
Soki Co., Ltd.
1010+ people viewing
We are selling Sato Keiki Seisakusho's dustproof and waterproof radiation thermometer (Circle Thermo) SK-8950. It can be operated even with wet han...
Yamazato Sangyo Co., Ltd.
900+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
IN5+ series is a digital radiation thermometer with fast response (fastest 10msec). With a detection wavelength of 8 to 14 μm, it is possible to me...
3 models listed
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
510+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
Yamazato Sangyo Co., Ltd.
700+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
ISR6/ISR6-TV is a digital two-color radiation thermometer. Adopts a 2msec high-speed response and a movable focus lens. Metal and two-color measure...
2 models listed
Yamazato Sangyo Co., Ltd.
530+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
IGA6/23 and IGA6/23-TV are digital radiation thermometers. RS485 interface allows long distance communication with PC or PLC. ■Applications ・Meta...
2 models listed
Yamazato Sangyo Co., Ltd.
590+ people viewing
Last viewed: 41 minutes ago
IGAR6 is a digital two-color radiation thermometer. A wide range is achieved by automatic switching between single color and two colors (smart mode...
2 models listed
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
560+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
540+ people viewing
Last viewed: 22 hours ago
■Features ・Emissivity can be set (0.1 to 1.0). *K thermocouple temperature probe can be used with miniature omega connector specification.
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
750+ people viewing
Last viewed: 22 hours ago
■Features - Surface temperature measurement and internal temperature measurement by contact can be performed with one device. ・The maximum and min...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
560+ people viewing
■Features AD-5611A has a laser marker that allows you to locate the center of the measurement area.
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
530+ people viewing
■Features ・K thermocouple with miniature connector can be attached. ・A wide range of temperature measurements is possible.
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
490+ people viewing
■Features - Can quickly measure surface temperature. - Equipped with a 1-point laser marker that allows you to see the measurement point at a glanc...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
490+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features - Equipped with a laser marker to accurately measure measurement points. - Can quickly measure surface temperature. - Automatically holds...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
580+ people viewing
■Features - Comes with a USB port so you can connect it to a computer and manage data. ・Because it is a 2-point laser point, it is easy to see the...