










11 Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensor Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for gyroscopic (gyro) sensors as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 11 gyroscopic (gyro) sensor manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked gyroscopic (gyro) sensor companies as of April, 2024: 1.Epson Europe Electronics GmbH, 2.Innalabs, 3.Analog Devices, Inc..
Table of Contents
What Is a Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensor?
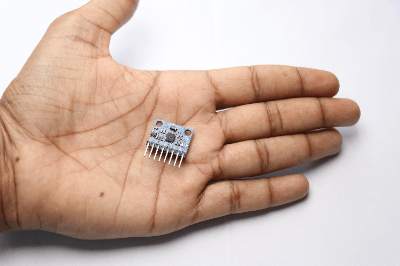 A gyroscopic (gyro) sensor is a sensor used to detect angular velocity.
A gyroscopic (gyro) sensor is a sensor used to detect angular velocity.
It is also called a gyroscope. Angular velocity refers to the physical quantity of rotation of an object per unit of time, and is an indispensable sensor in today's industrial machinery products, where advanced and accurate control is required.
Gyro sensors are heavily used in fields such as robotics, aircraft, and automobile body control, where feedback control must take into account minute rotations.
Uses of Gyroscopic Sensors
Gyro sensors are used in a wide range of applications in the control of smartphones, digital cameras, gaming devices, space industry, aviation, automobiles, and industrial robots.
Specific applications of gyro sensors are as follows:
- Image stabilization of smartphones and digital cameras
- Walking control of biped robots
- Measurement and control of aircraft position
- Measurement of user movement and position in VR games
Gyro sensors have different characteristics depending on the product, such as size and heat and vibration tolerance. Therefore, the accuracy of the control of the device using the gyro sensor and the environment in which it will be used must be taken into consideration when selecting a gyro sensor.
Principle of Gyroscopic Sensors
Gyro sensors are typically classified into the vibration type, which functions according to the Coriolis force, and the optical type, which functions according to the Sagnac effect of light.
1. Vibrating Gyroscopic Sensor
The Coriolis force used in vibrating gyro sensors is the fictitious force acting on an object located in a rotating frame of reference with respect to an inertial frame.
Vibration gyro sensors can be further classified into piezoelectric and capacitive types.
- Piezoelectric Method
This method measures the voltage value generated in a rotating transducer as a physical quantity corresponding to the Coriolis force. - Capacitance Method
The Coriolis force during rotation generates a difference in the capacitance between the left and right sensing electrodes of the resonator, and the angular velocity is calculated by measuring the Coriolis force from the difference in capacitance.
The relationship between the Coriolis force and angular velocity can be expressed by the following equation.
ω=F/2mv (ω: angular velocity, F: Coriolis force, m: mass of object, v: velocity of movement)
2. Optical Gyroscopic Sensor
The Sagnac effect used in optical gyroscopic sensors is the principle stating that if the optical path through which light passes is in motion, the length of the optical path will increase. This physical phenomenon occurs because the speed of light is always constant. In an optical gyroscopic sensor, the light path lengthens as the orbiting light itself rotates, and the angular velocity can be calculated by measuring the phase difference caused by the lengthening.
Other Information on Gyroscopic Sensors
1. Gyroscopic Sensor Compensation Methods
Drift Correction
There are multiple factors that can cause errors in the output of Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensors. One of the most important such factors is drift, which refers to the drift of the zero point, which is originally given as the initial value, resulting in a gradual shift of the initial value and a larger detection error.
Internal factors that cause drift include DC component fluctuations (low-frequency fluctuations) and high-frequency noise effects; DC component fluctuations are called bias instability and high-frequency noise is called angular random walk. Bias instability depends on the stability of the supply voltage, which can be improved by reviewing the power supply.
Angular Random Walk Correction
The correction method for angular random walk is a matter of each company's know-how, but a commonly used correction method is to use a Kalman filter.
The Kalman filter is a method for estimating the most appropriate system state based on the previous information and the currently acquired data. It can be rephrased as a problem of estimating the original state of a variable that changes with time, based on the past information and the currently acquired information. It is important to treat the measured values and the variables themselves as if they are subject to noise.
2. Difference Between a Gyroscopic Sensor and an Accelerometer
Gyroscopic sensors are similar to accelerometers. Although they are sometimes confused, they are completely different.
As the name suggests, acceleration sensors are designed to detect acceleration. They use inertial forces to measure changes in the speed at which an object is moving and outputs them as an electrical signal. Acceleration sensors are used in a wide range of applications because other types of information, such as the state of vibration of an object and the magnitude of impact, can also be obtained from acceleration. The basic structure is similar to that of a gyro sensor.
Gyros sensors, on the other hand, as mentioned above, are used to detect angular velocity. They use the Coriolis force to measure the motion (rotation) and changes in orientation and posture of an object and output them as electrical signals.
3. 3-, 6-, and 9-Axis Sensors
Recently, 3-axis and 6-axis sensors are often described as sensors that detect inertial force. Each corresponds to acceleration (3-axis) and angular velocity (6-axis) of forward/backward, left/right, and up/down, and as in-vehicle sensors, they are indispensable for ADAS and automatic driving technology, which are driving assistance systems for automobiles.
As an example, car navigation systems are equipped with both Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensors and Acceleration Sensors. By using Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensors to detect the direction of the car and Acceleration Sensors to detect the distance traveled, the current location can be displayed with high accuracy even in places where signal reception is difficult, such as inside a tunnel.
The three axes are represented by roll, pitch, and yaw, and these axes can be used to represent posture. Especially for roll and pitch, it is possible to compensate for the drift, which is a source of error, as a feedback circuit. Furthermore, as a different ref for drift correction, there is a current standard that uses a magnetometer sensor in addition to the 6-axis compatible sensor, in which case it is called a 9-axis compatible sensor.
4. MEMS Compatibility With a Gyroscopic Sensor
Gyro sensors are used to display and control the motion of rotating machinery. MEMS technology is used in the semiconductor industry, where it is based on thin-film microfabrication technology.
Gyroscopic sensors also differ from optical and mechanical sensors in that they are relatively easy to miniaturize and integrate, and because MEMS sensors are highly compatible with ASICs that enable relatively sophisticated control, they are built into many devices, including smartphones and other mobile devices.
Furthermore, gyro sensors have different detection ranges for angular velocity, depending on their application. For example, mobile devices such as smartphones require a range of 300 to 2000 DPS (degrees per second, rotation angle per second), while automotive devices such as car navigation systems require a range of 100 to 500 DPS.
Therefore, when selecting a sensor, one must consider how much detection range is sufficient based on the usage conditions of the device.
List of 11 Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensor Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- China
- Germany
- Ireland
- Japan
- Turkey
-
-

-
Analog Devices, Inc.
Gyroscopes
Manufacturer Overview
Incorporated in 1965, Analog Devices, Inc. designs, manufactures, tests, and markets integrated circuits (ICs), software, and subsystems that leverage analog, mixed-signal, and digital signal processing technologies. The company provides data converter products, power management and reference products for power conversion, driver monitoring, sequencing, and energy management applications in the automotive, communications, industrial, and high-end consumer markets. In addition, the company provides digital signal processing and system products for high-speed numeric calculations. It serves clients in the industrial, automotive, consumer, instrumentation, aerospace, and communications markets.
-
-
-
-

-
Shenzhen Rion Technology Co., Ltd.
GYRO
Manufacturer Overview
Shenzhen Rion Technology Co., Ltd., founded in 2008 and based in Shenzhen City, China, is a manufacturer of INS/GPS integrated navigation system, MEMS inclinometer and 3D compass. The company has a design and developing team in software and hardware. It provides tech-equipment and aerospace equipment, new energy, IOT and energy saving technology that are core parts of automation, intelligence, informationization and digitalization. These products find application in UAV, intelligent robot, oil drilling, coal mining, marine surveys and others. The company has won the AAA credit enterprise and has been awarded the quality credible brand in China's sensor industry.
-
-
-
-

-
Micro-Hybrid Electronic GmbH
Gyro sensors
Manufacturer Overview
Micro-Hybrid Electronic GmbH, established in 1992 and based in Hermsdorf, Germany, is a manufacturer of microelectronics and infrared sensors. It manufactures miniaturized and ceramic-based electronic circuits. It also specializes in manufacturing infrared sensors such as IR emitters, thermal IR detectors, pyroelectric IR detectors, gas sensors, and acceleration sensors. The manufactured products are equipped with several technologies like LTCC and SMD and chip and wire bonding technologies. Its manufactured products serve the industrial, medical technology, and mobility industries. Moreover, the company is involved in Research Cluster HIPS, KerMuSens, Thuringia-Invest, and GRW Joint task projects and has ISO / TS 16949:2009 certification.
-
-
-
-

-
SUMITOMO PRECISION PRODUCTS Co., Ltd.
MEMS Gyro & Systems
Manufacturer Overview
Sumitomo Precision Products Co. Ltd., established in 1961 and headquartered in Amagasaki, Japan, is a manufacturer of several products, including hydraulic controls, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, aerospace equipment, and environmental systems. It began manufacturing large heat exchangers in 1963, large propellers in 1967, and LNG vaporizers in 1969. In 1974, it began making ozone generators, and in 1988, it started manufacturing equipment for space applications. The company is ISO 14001 certified, and its product portfolio includes landing gear systems for commercial flights, high-temperature heat exchangers, coolant components for machine tools, LNG vaporizers, and silicon oxide sacrificial layer etching systems.
-
-
-
-

-
Epson Europe Electronics GmbH
Gyro / Gyro automotive

Manufacturer Overview
Epson Europe Electronics GmbH has been a manufacturer and supplier of electronic devices and components since 1989 and is based in Munich, Germany. The company's product portfolio includes quartz crystal devices, semiconductor devices, and sensing systems. The quartz crystals which are also known as timing devices are further subcategorized into crystal units, Oscillators, and real-time clock modules. The semiconductors have sues as Microcontroller, Display controllers, and for small network connecting, whereas the sensing systems provide solutions for accuracy, noise control, power consumption, and stability. These products have uses in Automotives, Industrial networking and healthcare, fitness, and energy control solutions.
-
-
-
-

-
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Gyro sensor
Manufacturer Overview
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (Murata Manufacturing) was founded in 1944 and is headquartered in Nagaokakyo, Japan. Murata Manufacturing designs, manufactures, and sells ceramic-based passive electronic components and solutions globally. The company operates through components, modules, and others segments, serving communications, mobility, industrial, healthcare, and personal electronics customers. They company's product offerings include noise suppression products, quartz devices,RFID devices, phase shifters, and wireless connectivity platforms. Services such as webinars and video library are also available for existing and potential customers alike.
-
-
-
-

-
Innalabs
Coriolis vibratory gyroscope
Manufacturer Overview
Innalabs, established in 2012 and based in Dublin, Ireland, is a manufacturer and supplier of inertial sensor technology. The product portfolio includes specific solutions for Coriolis vibratory gyroscopes and quartz servo accelerometers with high-accuracy navigation and stabilization. The products are used in various industries which include space, aerospace, land applications, marine, energy, transportation, and new technology markets. The company also offers world-class research, technial and development facilities with full product cycle solutions and inertial systems.
-
-
-
-

-
Texense
GYRN-S 3 Axis
Manufacturer Overview
Texense, founded in Nevers, France is a manufacturer of embedded sensors. The company's product portfolio includes Inertial Boxes, IR Temperature Sensors, Lean Angle Sensors, Miniature pressure sensors, and Pitot Sensors. Their products are used by international racing teams from F1, NASCAR, and Moto GP. The company serves markets including Automotive and Electric Vehicles, aviation and Electronics and IT. The company also provides services including global distribution, preventative maintenance, troubleshooting, repair and customer service.
-
-
-
-

-
STMicroelectronics
MEMS automotive sensor
Manufacturer Overview
ST Micro Electronics is a global semiconductor company serving customers with innovations to have a positive impact on people's lives. Their product line is micro electronic systems, such as switches, controllers, sensors and drivers. The main selling point of ST Micro Electronics is its provision of sustainable products, and introducing their electronics to create a more sustainable world. The company, as well as providing the electronic devices, also provides software and support, ensuring that all fields are covered to provide a fully provide a supported and strong relationship with their customer base. ST Micro Electronics believe that technology plays a key role in helping to solve environmental and social challenges, which is why their semiconductor technologies start with their employees, their customers and partners.
-
-
-
-

-
Dynalabs Mühendislik LTD
MEMS gyroscope / Inertial measurement unit
Company Overview
DynaLabs Mühendislik LTD, founded in 2013, and headquartered in Ankara, Turkey, is a manufacturer and a supplier of dynamic testing and measurement equipment. The company has an extensive MEMS accelerometer and gyroscope product lines that meet the automotive and aerospace industry's needs. Its product range includes capacitive accelerometers, piezoresistive accelerometers, gyroscopes, as well as inertial measurement units and permanent magnet shakers. The company's external amplifiers are designed to have integrated signal generators.
-
-
-
-

-
Imego AB
MEMS inertial sensors
-
-
Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensor Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of April 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Epson Europe Electronics GmbH |
16.7%
|
| 2 | Dynalabs Mühendislik LTD |
11.0%
|
| 3 | Innalabs |
11.0%
|
| 4 | Micro-Hybrid Electronic GmbH |
10.5%
|
| 5 | Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. |
10.0%
|
| 6 | Analog Devices, Inc. |
10.0%
|
| 7 | STMicroelectronics |
9.5%
|
| 8 | Shenzhen Rion Technology Co., Ltd. |
8.1%
|
| 9 | Texense |
4.8%
|
| 10 | SUMITOMO PRECISION PRODUCTS Co., Ltd. |
4.8%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the gyroscopic (gyro) sensor page as of April 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.: 77,581
- SUMITOMO PRECISION PRODUCTS Co., Ltd.: 1,779
- Micro-Hybrid Electronic GmbH: 250
Newly Established Company
- Dynalabs Mühendislik LTD: 2013 (11 years ago)
- Innalabs: 2012 (12 years ago)
- Shenzhen Rion Technology Co., Ltd.: 2008 (16 years ago)
Company with a History
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.: 1944 (80 years ago)
- Epson Europe Electronics GmbH: 1989 (35 years ago)
- Micro-Hybrid Electronic GmbH: 1992 (32 years ago)
Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensor Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
Global Distribution of Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensor Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 Germany
Germany
|
2 | 25.0% |
 Japan
Japan
|
2 | 25.0% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
1 | 12.5% |
 China
China
|
1 | 12.5% |
 Ireland
Ireland
|
1 | 12.5% |
 Turkey
Turkey
|
1 | 12.5% |
List of Gyroscopic (Gyro) Sensor Products
2 products are listed.
SENSATEC Co., Ltd.
Shape AGS Gyro Sensor
30+ people viewing
Use ・ Procedure control of agricultural equipment, robots, etc., turning control ・ Procedure control of unmanned transport vehicles (AGV), turning ...
