All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for metering pumps as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 26 metering pump manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked metering pump companies as of July, 2025: 1.Unicontrols Co., Ltd, 2.Grundfos Pumps Corporation, 3.Jaeco Fluid Systems, Inc..
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Metering Pumps
Engaged in research on nitride semiconductor growth using the MBE method at Waseda University Graduate School. After graduating from graduate school in 2016, he joined a non-ferrous metal manufacturer.
Engaged in equipment maintenance and engineering work at metal smelting plants. Moved to a chemical manufacturer in 2022. Engaging in similar tasks.
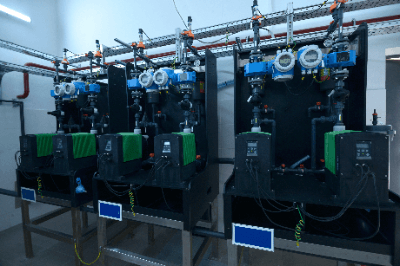
A metering pump is a device that repeatedly pumps a fixed amount of liquid.
It is suitable for accurate dosing of chemicals and other liquids. Metering pumps are constructed of corrosion-resistant materials because they are required to resist corrosion. Generally, electricity or compressed air is used as The driving force.
Metering pumps are used to pump out a certain amount of liquid.
The following are examples of applications for metering pumps:
Mainly used in industry as part of the manufacturing process, they are also widely used in infrastructure facilities such as water purification plants and wastewater treatment plants.
Metering pumps in the medical field require highly accurate liquid volume control, as errors can directly affect human lives.
Metering pumps are broadly classified into reciprocating and rotating mechanisms.
The reciprocating mechanism in a metering pump will pump liquid by reciprocating a piston. Liquid can be pumped as much as the volume of the piston. It has the advantage of pumping liquid at high pressure.
The rotary mechanism in a metering pump will pump liquid by rotating an impeller or the like. It is capable of pumping out liquid as much as the volume of the impeller and casing. The structure is simple and it can handle a wide range of liquids.
Various types of metering pumps are used.
A plunger pump is a type of reciprocating pump in which the plunger, a rod-like piston, moves back and forth. It is capable of continuously pumping a fixed volume of liquid at high pressure.
A piston pump is a type of reciprocating pump that pumps liquid through the reciprocating motion of a piston. It is characterized by the use of seals and valves on the piston side for pumping liquid. It can be used under high pressure and it has the advantage of high efficiency.
This is a type of reciprocating pump that pumps liquid using a reciprocating motion of an elastic membrane, such as resin. It is characterized by its seal-less feature and it is widely used for transferring chemical solutions.
It has the disadvantage of pulsation, and flow is generated only when the diaphragm operates. For instantaneous high flow rates, the piping diameter must be enlarged to match the peak flow rate. Pulsation flow can be counteracted by introducing an air chamber or accumulator downstream of the pump or by shifting the phase and installing multiple units in parallel.
The flow rate is adjusted by changing the stroke width and frequency. Drive sources vary, but mainly motor-driven and electromagnetic (solenoid) types are used. The former uses an inverter, and the latter uses electronic control to change the stroke rate.
Ultra-compact diaphragm pumps using piezoelectric elements (piezoelectric elements) are called micropumps. They can handle minute flow rates, such as several µL/min.
This is a type of rotary pump that pumps liquid by rotating a threaded rotor inside the pump. It is characterized by extremely low pulsation.
This is a pump in which two gears mesh with each other and pump liquid only as much as the volume of the gears and casing. When the flow rate is high to some extent, pulsation is minimal. Pulsation appears when the flow rate is reduced and the rotation speed decreases. The flow rate is adjusted by controlling the rotation speed with an inverter.
This is a type of rotary pump that pumps liquid only as much as the volume of the impeller-like vane and casing. The vanes can be installed slightly off-center from the center of the pump.
A tube pump is a pump that continuously pushes liquid in a tube by means of multiple rollers attached to a rotating rotor. It has a simple mechanism with high quantitative performance and it is used for pumping liquid for analytical instruments and adding chemicals.
It is capable of pumping a small amount of chemical solution at a few µL/min. The flow rate is adjusted by controlling the number of roller rotations with an inverter.
This pump pushes a syringe at a constant speed and can supply minute flow rates with absolutely no pulsation. However, it is a batch process and cannot supply continuously. It is used for medical applications.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area


Unicontrols Co., Ltd, established in 1976, and headquartered in Japan, is a manufacturer, specializing in crafting small to medium-sized pressurized stainless tanks and various fluid control units. Its product portfolio encompasses Fluid Dispensing Systems, Fluid Dispensing Valves, Plunger Pumps, Hibar Pumps, and Pressure Tanks. These offerings serve a multitude of purposes, from dispensing low to high viscosity liquids to precise filling and controlling fluid flow. The company is highly regarded in the industry for its adherence to manufacturing excellence and its fluid management solutions.

Plast-O-Matic was formed in 1967 in New Jersey, now situated in Cedar Grove, New Jersey. Plast-O-Matic serves aquarium, chemical dosing, chemical processing, metal finishing, semiconductor, wastewater treatment, water purification, and government application industries. Product offerings include product data sheets, CAD downloads, installation & maintenance instructions, ball valves, check valves, gauge guards, pressure regulators, process cooling sticks, anti-siphon valves, shut-off and diverter valves, sight glass & level indicators, solenoid valves, venting valves, other process controls & pumps, and custom valves.

Blackmer, founded in Grand Rapids, MI, in 1903 is a manufacturer of sliding vane, gear, regenerative turbines and centrifugal pumps. The company's product portfolio includes compressor technologies for the transfer of liquids and gases, Positive Displacement Pumps, and PD Pumps. The company serves industries such as Oil and Gas, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Construction, and Power Generation. They also provide services including product selection, installation, preventative maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.

Walchem, Iwaki America, Inc., expanded and incorporated in 2013 with headquarters in the USA, is a manufacturer of online analytical instruments and electronic metering pumps used for wastewater systems in swimming pools and spas. The company's tangible product line includes treatment controllers to monitor and regulate various aspects of water treatment processes and water treatment sensors and accessories used to detect chemicals and impurities in water bodies. It also provides cloud-based software tools and instrumentation that integrate with its products. The company offers its know-how to assist clients with customized and full-scope chemical control systems.

Jaeco Fluid Systems Inc., founded in 1948 with headquarters in the USA, is a manufacturer of metering pumps and check valves. The company's product line includes diaphragm metering pumps, plunger metering pumps, hi-flo pumps, pump maintenance parts, and a range of stainless steel check valves. These products are built-to-order and are used in various applications such as irrigation, chemical processing, and car wash. The company serves various markets including automotive, agriculture, food processing, petrochemical processing, among others.

Wanner Engineering, founded in 1972 and based in Minnesota, United States, is a manufacturer of high-pressure seal-less pumps with three product lines, Hydra-Cell, Vector, and Stan-Cor. It produces positive displacement pumps, pulse-less pumps, T-series, and solenoid pumps. Additionally, it manufactures C-series regulating valves, system components, peristaltic pumps, and non-metallic centrifugal pumps. Hydra-Cell pumps are used in commercial, institutional, industrial, and municipal facilities throughout the world. The Hydra-Cell T100 Series pumps were honored with a "Spotlight on New Technology" accolade during the 2010 Offshore Technology Conference.

Grundfos Pumps Corporation, established in 1945, and located in Brookshire Texas, is a manufacturer and installer of pumps and pumping systems. The company offers a range of pumps, including CMBE circulator pumps for water circulation in various systems, SCALA2 booster pumps to enhance water pressure, MQ dosing pumps for controlled fluid dispensing, CR pumps for industrial use like water treatment and mining, and SP submersible pumps for well and borehole water pumping. The company holds both ISO 14001, and ISO 9001:2008 in adherance to quality management standards.

IWAKI AMERICA INC. is an Iwaki Pumps manufacturer established in Holliston, Massaschussets since 1974. Being part of a global network of manufacturers, the company produces magnetic drive pumps used to pump acids, caustics, and low- or high-temperature fluids. It also makes chemical metering pumps, for chemical dosing applicatications, and other technologies. Its products are used in industries like the power generation, mining, marine and the biofuels markets. In addition, the venture follows ISO9001 quality control standards.

IWAKI Europe GmbH is a manufacturer and supplier of precision chemical process pumps and fluid handling equipment based in Germany. Established in 1985, the company offers a wide range of products, including magnetic drive pumps, air-operated double diaphragm pumps, metering pumps, and other fluid control equipment. Their pumps are suitable for various applications in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and semiconductor manufacturing. One sample product is their MX-F Series Magnetic Drive Pumps. These pumps are designed for handling various chemicals and liquids, offering leak-free performance due to their magnetic drive technology.

Tohkemy Corporation, established in 1963, and headquartered in Osaka, Japan, is a manufacturer that specializes in water processing machinery and equipment. The company's products include anthracite filter media, chemical pumps, and polymer dissolving units. It also provides water measuring equipment and Mixers. Its products are designed to purify all types of water, from drinking water to industrial-use applications. It serves the water treatment and environmental conservation industries and is classified under the industrial machinery manufacturing industry.



Orbray was originally founded in 1939 in Japan. Orbray serves the automotive, medical, fashion, information communication, audio, and robotics industries. Orbray develops a variety of products including small motors, fiber optics components, and precision jewelry tools. Applications for Orbray’s products include small robots, diaphragm pumps, inner wall metrology systems, and semiconductors.

Iwaki Co., LTD was founded in 1956 in Japan. Iwaki is a producer of pumping products and water quality control systems and is the world’s leading pump manufacturer maintaining a global sales and distribution network. Serviced industries include semiconductors, water treatment, surface treatment, food processing, paper production, chemicals and pharmaceuticals.

LEWA is a manufacturer of diaphragm metering pumps, process pumps, complete metering systems, and plants in Leonberg, Germany, founded in 1952. It has 14 subsidiaries and over 100 sales partners on every continent. The company owns three brands: LEWA Pumps, LEWA Systems, and NIKKISO Pumps. LEWA Pumps specializes in diaphragm metering pumps, packed plunger metering pumps, and process pumps. LEWA Systems builds customer-specific units, systems, skids, and packages, including the associated planning, testing, and calculation of secondary systems and pressure conditions. NIKKISO Pumps are centred in the field of cryogenic submersible pumps for the energy, oil, and gas sectors.

Prominent, established in 1960 in Heidelberg, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision chemical dosing and fluid control solutions. The company's diverse product portfolio includes metering pumps, controllers, sensors, and complete systems used for accurate and effective chemical dosing in various industries such as water treatment, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. Prominent's solutions play a vital role in ensuring precise chemical dosing, which is essential for maintaining process efficiency and product quality. Their ideal technologies ensures sustainability and resource optimization. Besides, the company aims to deliver advanced solutions that meet the unique requirements of each application.

Fimars, established in 2013 and headquartered in Lugano, Switzerland, is a manufacturer of metering pumps, polymer and emulsion preparation systems, and related accessories. The company manufactures pumps for chemical dosing, oil and gas, and food and beverage industries, including diaphragm, plunger, and solenoid pumps. It provides tailored solutions for pumping needs, spare parts, and professional setup assistance for plant operations. Its pumps are used for water, pulp, paper, and air treatment. The company also provides pumps on consignment, immediate replacements for major failures, and long-term dosing pump rental services.

Diener Precision Pumps, established in 1994 and based in Lodi, California, USA, is an ISO 9001 and ISO 13485-certified manufacturer of micro gear and metering pumps. The company offers precision metering pumps for micro-dosing or metering applications, as well as its Silencer series gear pumps for medical applications, such as in dialysis machines. It also offers OEM services for high volume orders of precision gear pumps. The company’s products are commonly used in the food processing, industrial, and medical sectors.

Tacmina USA, established in November 1956 and based in Osaka, Japan, is a manufacturer and distributor of precision pumps. The company's product range includes Smoothflow Pumps, Motor-Driven Metering Pumps, Solenoid-Driven Metering Pumps, Chemical Injection Systems, and Chemical Tanks. These products are essential for accurate and pulse-free fluid transfer in various applications. Serving industries such as batteries and electronics, chemical and biochemical, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, and water treatments, the company provides expert consultations, product customization, maintenance support, and swift customer assistance.

SPX Flow, established in 1912, is a manufacturer of industrial machinery to solve processing challenges based in Charlotte, North Carolina. The company manufactures various machinery such as mixers, pumps, valves, homogenizers, and heat exchangers. The machinery is used in nutrition, health, mining, construction, and chemical industries. The company provides services such as designing, engineering, and installing turnkey process units or full-scale plants. The SPX Flow brands include Anhydro, Bran+Luebbe, Gerstenberg Schrӧder, Pneumatic Products and Seital Separation.

Milton Roy, founded in 1936 in St. Petersburg, Florida, USA, is a manufacturer and supplier of metering pumps and fluid control equipment. The company offers a wide range of metering pumps, controllers, and accessories that are utilized in various industries, including water treatment, chemical processing, and oil and gas.Milton Roy's precision equipment ensures accurate and consistent dosing of fluids, critical for maintaining process efficiency and product quality. Additionally, the company provides cutting-edge solutions to meet the diverse needs of its global clientele. Their products ensures safe and efficient fluid handling in different applications, enhancing operational performance and sustainability.

TSUKASA ELECTRIC CO.,LTD was founded in 1969 in Japan. Tsukasa primarily develops two types of components. First are motors, which are used in vending machines, ATM machines, and amusement machines. These also include gear motors, gear pumps, linear motion units, and rotary actuators. Secondly, Tsukasa develops tube pumps which are generally mounted to the aforementioned motors.






Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unicontrols Co., Ltd |
23.9%
|
| 2 | Grundfos Pumps Corporation |
10.3%
|
| 3 | Jaeco Fluid Systems, Inc. |
7.5%
|
| 4 | Blackmer |
6.8%
|
| 5 | Plast-O-Matic Valves, Inc. |
6.0%
|
| 6 | Walchem |
5.2%
|
| 7 | IWAKI AMERICA INC. |
4.5%
|
| 8 | Wanner Engineering, Inc. |
3.7%
|
| 9 | LMI Pumps |
3.5%
|
| 10 | Milton Roy |
3.1%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the metering pump page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 Japan
Japan
|
7 | 41.2% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
7 | 41.2% |
 Germany
Germany
|
3 | 17.6% |
433 products found
433 products
Takumina Co., Ltd.
1160+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
For process lines that require strict control, such as optical films, IT, and expensive pharmaceuticals. Features ■Reproducibility accuracy less t...
10 models listed
Takumina Co., Ltd.
560+ people viewing
Last viewed: 23 hours ago
For quantitative transfer of chemical solutions and fluids that are difficult to transfer, such as UV curing resins, urethane resins, and slurry li...
5 models listed
Ohkita Koshoji Co., Ltd.
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
This machine is a device that discharges and supplies viscous substances (grease, adhesives, viscosity, etc.) from drums while measuring a certain ...
Sun Ten Consulting
390+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
The Extreme Series easily pumps difficult liquids, from colored ink to strawberry smoothies. With a flow rate of 1,500 to 5,000ml/min, it can accom...
SATACO Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Features ・Can control freely from small to large flow rates. ・Discharge of liquid, gas, and air can be controlled. - Easy control menu selection...
Kyowa Finetech Co., Ltd.
380+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
A gear pump that can handle various viscous fluids. This is a precision gear pump that can achieve stable discharge accuracy even when there are f...
Sun Ten Consulting
380+ people viewing
Last viewed: 20 hours ago
The Optima series is specially designed for small package sizes. Although it has the same structure as the Extreme series, the overall length is mu...
Nikkora Eiko
4450+ people viewing
Last viewed: 49 minutes ago
Advance & harmony ~ Endless progress of mankind and eternal harmony with nature- Adony Quantitative Pump AH Series is a direct -type quantitative p...
23 models listed
Sun Ten Consulting
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 53 minutes ago
Durable, reliable, chemically inert, quiet, leak-free, the silencer series has everything you need in a gear pump. Simplify plumbing with multiple ...
Takumina Co., Ltd.
570+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
For injection of sodium hypochlorite, flocculants, and pH adjusters in sewage treatment plants. Structure overview ■Direct-acting twin diaphragm m...
10 models listed
Sun Ten Consulting
380+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
The Precision Series is specialized for applications that require fast and accurate weighing and dispensing. The piston shape separates the outlet ...
Graco Inc.
600+ people viewing
Last viewed: 10 hours ago
Accurately measure and transfer raw materials. Ideal for transporting abrasive and corrosive materials, as well as raw materials that are sensitive...
5 models listed
Grundfos Pumps Corporation
3230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
It exceeded the renovation drive. Solve mottled injection and pulsation by variable speed drive It is a pump with excellent accuracy and durability...
5 models listed
Grundfos Pumps Corporation
520+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
In addition to simple operability, accurate injection is achieved with a wide range of flow range of 60 to 940 liters per hour. ・ The adoption of...
Meito Kakoki Co., Ltd.
870+ people viewing
Last viewed: 38 minutes ago
The vertical design of the pump saves space and is convenient for installation. Additionally, aluminum is used inside to reduce weight. ■Features ...
7 models listed
Takumina Co., Ltd.
1290+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
For high-pressure injection of boiler chemicals and injection of additives to resin molding lines. ■Flow rate does not decrease due to pressure fl...
10 models listed
Nikkora Eiko
650+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Advance & harmony ~ Endless progress of mankind and eternal harmony with nature- Adony Quantitative Pump AH Series is a direct -type quantitative p...
2 models listed
Meito Kakoki Co., Ltd.
900+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
Chemical liquid metering injection pumps are widely used for injection of chemical liquid for waste liquid treatment in various factories, steriliz...
7 models listed
Nikkora Eiko
1150+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
Advance & harmony ~ Endless progress of mankind and eternal harmony with nature- Adony Quantitative Pump AH Series is a direct -type quantitative p...
7 models listed
Meito Kakoki Co., Ltd.
750+ people viewing
Last viewed: 56 minutes ago
It can be used over a wide range from a minimum of 300mL/min to a maximum of 30L/min. Teflon specifications are also available. ■Features ・Variou...
5 models listed
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
・The calibration function makes it easy to calibrate the flow rate. ・Low noise, low vibration, self-contained type, can run dry, and can easily c...
Meito Kakoki Co., Ltd.
340+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
Designed exclusively for slurry liquids, it is possible to transfer a wide range of liquids. ■Features ・Special design for slurry liquid allows f...
2 models listed
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
- Suitable for dripping extremely small amounts, and the flow rate can be set digitally using the jog dial. - External control is possible for the ...
Meito Kakoki Co., Ltd.
590+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
■Features ・All models equipped with pulse control as standard equipment ・Equipped with an in-line automatic air bleed mechanism to improve air bl...
3 models listed
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
■Features - Excellent liquid delivery accuracy (reproducibility ±1%) due to pulsation-free and continuous flow. - Accurate and wide range of flow r...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 10 hours ago
■Features ・An ultra-compact pump that integrates the control part and pump part. - Equipped with a control circuit that reduces the burden on the ...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Can be used as a discharge pump or suction pump (self-priming type).
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 hours ago
Can be used as a suction pump, discharge pump, or liquid pump.
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
■Features ・Excellent wear resistance. ・It is completely self-priming and can be operated. ・Has a high discharge head. - Air-driven and inherentl...
Meito Kakoki Co., Ltd.
660+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
By adopting a dual head, you can install one instead of the usual two. It is possible to send two types of liquid separately, and it is also possib...
6 models listed