











18 Mass Spectrometer Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for mass spectrometers as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 18 mass spectrometer manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked mass spectrometer companies as of April, 2024: 1.Teledyne ISCO, 2.PHOTONIS, 3.SCIEX.
Table of Contents
What Is a Mass Spectrometer?
Figure 1. Image of a mass spectrometer
A mass spectrometer (MS) is an instrument that ionizes molecules within a sample and detects and identifies the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of the resulting ions.
The abbreviation "MS" is used internationally. When molecules are ionized by an ionization method, they are propelled by electrostatic forces.
A mass spectrometer is an analytical instrument that separates and detects ions in motion based on their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) through electrical, magnetic, or other actions in a vacuum. The instrument primarily comprises a sample introduction section, an ion source, a mass separation section, and a detector.
There are several types depending on the ionization and mass separation methods, and they are used according to the measurement sample and application. Mass spectrometers are mainly used for sample identification, component analysis of unknown samples, and distinguishing and detecting isotopes.
Uses of Mass Spectrometers
Mass spectrometers are utilized for qualitative and quantitative analysis of a wide range of molecules, from low-molecular-weight compounds to high-molecular-weight compounds such as proteins and synthetic polymers.
Due to its effectiveness in identifying known substances and determining the structure of unknown substances, mass spectrometry is widely used in organic chemistry, biochemistry, and other chemical and biological fields. Specifically, it finds applications in research and development, quality control, analysis, and testing of various agricultural chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and naturally occurring compounds.
Recent advancements have enabled the ionization of proteins with large molecular weights, extending the use of mass spectrometers to the fields of life sciences and medicine.
Principle of Mass Spectrometers
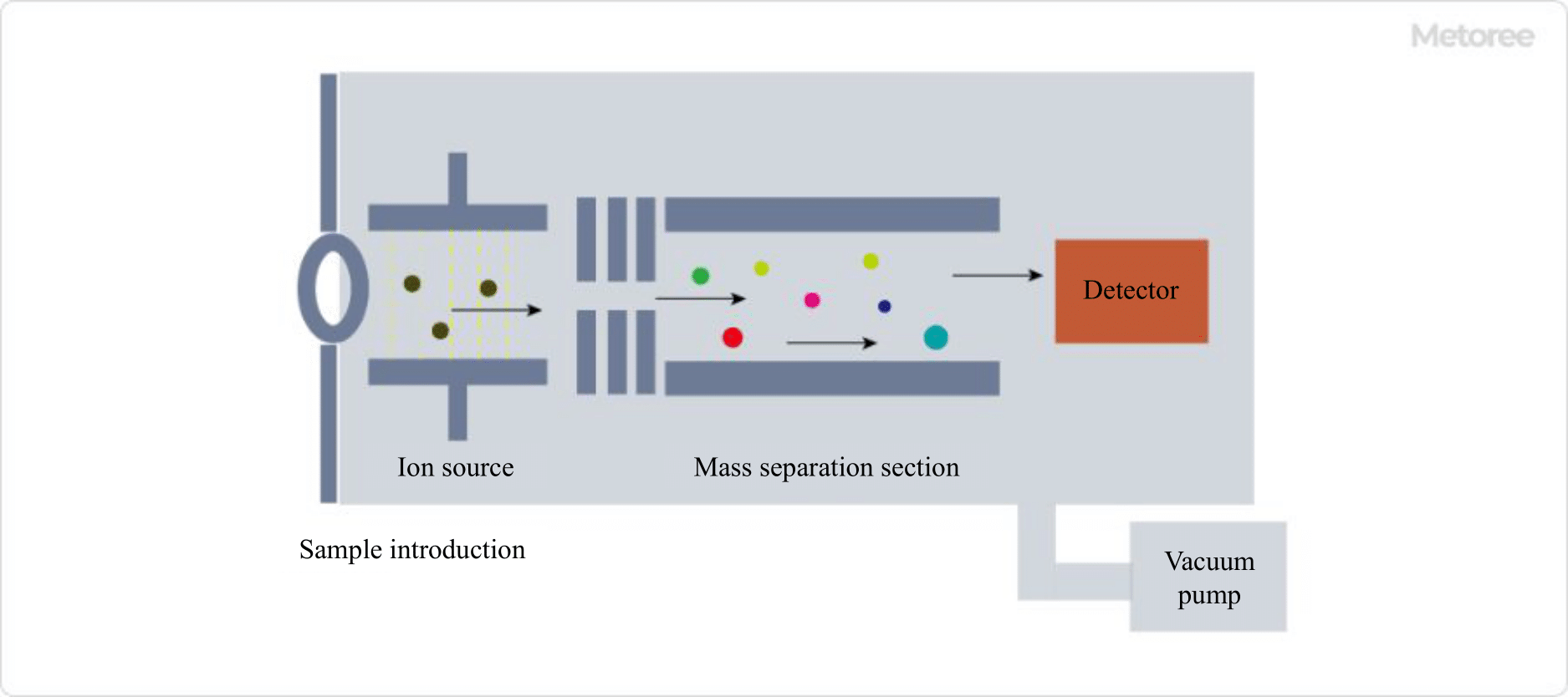
Figure 2. Principle of a mass spectrometer
The fundamental principle of a mass spectrometer involves the following series of steps, with the mass spectrum displayed using m/z as the abscissa and detection intensity as the ordinate:
- The sample is introduced into the instrument through the sample introduction section.
- The sample is ionized by the ion source.
- In the mass separation section, the sample is separated based on the different effects of magnetic and electric fields on ions according to their m/z, and detected by the detector.
Mass spectrometers can detect single-charged ions, which have only one charge, as well as multiply charged ions, fragment ions resulting from dissociation, or aggregate ions formed by the association of samples with each other. Peaks typically exhibit a unique distribution derived from the isotopic ratio of the original molecule.
Types of Mass Spectrometers
There are various types of mass spectrometers classified primarily by the combination of the type of ion source and the type of mass separator. Examples include "MALDI-TOF-MS" and "ESI-TOF-MS."
1. Sample Introduction Section
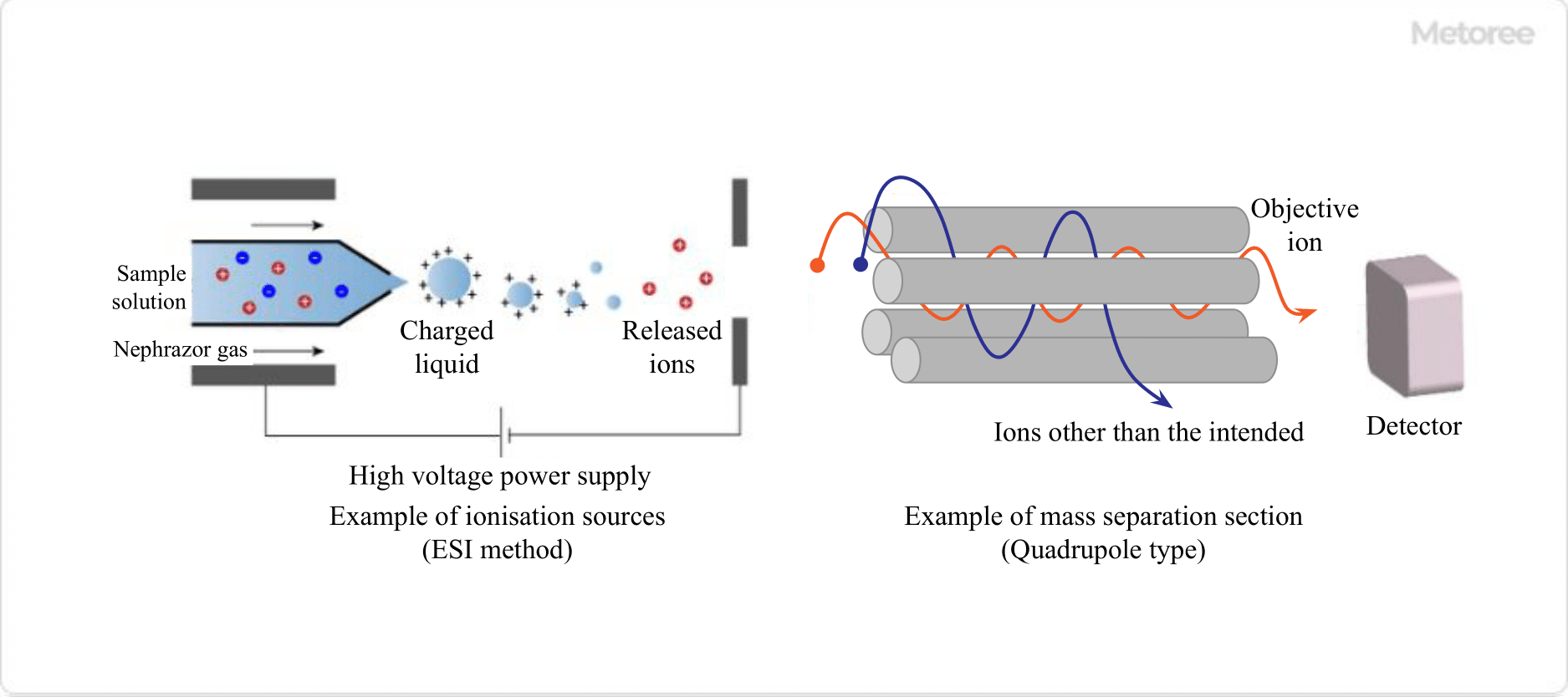
Figure 3. Example of ionization source and mass separation part
Some mass spectrometers are combined with other instruments before the sample introduction section and are used in research and development and quality control. Examples include LC-MS combined with liquid chromatography, GC-MS combined with gas chromatography, and ICP-MS combined with inductively coupled plasma.
2. Ion Source
Electron Ionization (EI) Method
Accelerated electrons collide with thermally vaporized molecules (M) in a high vacuum. The electrons are then ejected from the molecule, producing radical cations (M+) called molecular ions.
Electrospray Ionization (ESI) Method
- First, a sample solution is introduced into a capillary to which a high voltage is applied.
- Atomizing gas (nebulizer gas) flows from the outside of the capillary to spray it, forming charged droplets.
- As the charged droplets move, the solvent evaporates and the surface electric field increases, eventually causing the droplets to split when the repulsive force between the charges exceeds the surface tension of the liquid.
- This process releases sample ions into the gas phase.
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) Method
This method involves mixing a sample with a matrix, such as an aromatic organic compound, to form a crystal. The crystal is then ionized by irradiating it with a laser. It is suitable for ionizing high-molecular-weight compounds such as proteins.
Fast Atom Bombardment (FAB) Method
This method ionizes sample molecules by high-speed collisions with neutral atoms in the presence of a matrix and a sample solution dissolved in an organic solvent.
Other methods include CI, FD, APCI, and ICP methods.
3. Mass Separation Section
Quadrupole (Q)
This method uses four electrode rods to apply a high-frequency voltage to ions from an ion source. The electrodes are subjected to DC and AC voltages to create an electric field that allows ions with a specific m/z to reach the detector.
This method can measure ions in the desired m/z range up to approximately m/z 4000.
Double-Focusing Type
This is a magnetic sector-type mass separator. In magnetic sector-type separators, ions pass through a magnetic field, altering their flight paths due to the Lorentz force. The double-focusing type combines magnetic and electric field sectors to achieve both velocity and directional convergence of ions.
Time-Of-Flight (TOF)
This method accelerates ionized samples with known electric field strength and detects the time difference between the arrival of each ion at the detector. It can measure ions across a wide mass range.
Other methods include Ion Trap (IT), Fourier-Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance (FT-ICR), and Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS).
List of 18 Mass Spectrometer Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- United Kingdom
-
-

-
Linseis, Inc.
Evolved Gas Analysis
Manufacturer Overview
Linseis Messgeräte GmbH (Linseis Inc. USA), established in 1957 and headquartered in Selb, Bayern, Germany, is a manufacturer of thermoanalytical instruments. The company's products include thermal conductivity analyzers, thermoelectric analyzers, and differential scanning calorimeters. These products are used in various industries in the field of research and materials testing, such as bridge support expansion measuring, vehicle construction, and the aerospace industry for the development of higher-thermal materials. Its notable clients include Intel, NASA, JPL, and Mitsubishi.
-
-
-
-

-
Shimadzu Scientific Instruments
Triple Quadrupole LC-MS/MS
Manufacturer Overview
Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, established in 1875 in Japan, is a renowned manufacturer and supplier specializing in analytical instruments and testing equipment. The company offers a wide range of products, including chromatographs, spectrophotometers, and material testing machines. Shimadzu's history reflects a devotion to innovation and precision. Catering to industries such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental analysis, their products enable accurate research and quality control. Shimadzu's extraordinary products, such as liquid chromatographs used in pharmaceutical analysis and universal testing machines for evaluating material strength, empower scientific exploration and quality assurance across diverse sectors.
-
-
-
-

-
Bruker Corporation
GC-MS
Manufacturer Overview
Bruker, founded in 1960 and based in Billerica, Massachusetts, is a manufacturer and distributor of scientific instruments and analytical and diagnostic solutions. The company's product range includes analyzers, microscopes, and imaging solutions, which have applications in fields such as life science research, cell biology, and microbiology. In 1969, the company developed the world's first FT-NMR spectrometer system, enabling broadband proton decoupling. In 1997, it further expanded its capabilities by acquiring the analytical X-ray division of Siemens AG. The company holds ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 certifications, and its products are available for sale worldwide.
-
-
-
-

-
Skyray Instruments
Mass Spectrometers
Manufacturer Overview
Skyray Instruments, founded in 1992 with its headquarters in Texas, USA, is a manufacturer of analytical and measuring instruments. The company specializes in the design and manufacture of products for spectroscopy, chromatography, and mass spectroscopy. It has ISO 9001 certification and offers modern spectrometers, chromatographs, and mass spectrometers. These equipment have advantages such as high sensitivity, precision, and efficacy in analyzing a variety of compounds. It provides services to a diverse range of businesses, including pharmaceuticals, environmental surveillance, food & drinks, and research organizations.
-
-
-
-

-
LECO
Mass Spectrometry
Company Overview
LECO Corporation, headquartered in St. Joseph, Michigan, has been a manufacturer and distributor of metallographic equipment since 1936. The company specializes in producing metallographic equipment, serving laboratories worldwide. Its product range includes the 832 and 828 Series Combustion systems for organic material analysis, the 836 Series Elemental Analyzer for inorganic materials, and the Pegasus BT GC-TOFMS Mass Spectrometer. These instruments cater to elemental analysis, thermal analysis, metallography, and mass spectrometry that are essential for laboratories. It holds several certifications, including ISO/IEC 17025:2017 and the ANSI/NCSL Z540-1-1994 for calibration, as well as an ISO 9001:2015 certification for quality management.
-
-
-
-

-
MKS Instruments
Mass Spectrometers
Company Overview
MKS Instruments, founded in 1961 and based in Massachusetts, USA, is a manufacturer and distributor of instruments and process control solutions for advanced manufacturing processes. Its solutions are critical to addressing the challenges of miniaturization and complexity in advanced device manufacturing by enabling increased power, feature enhancement, and optimized connectivity. Its offerings include compact pressure transducers, mass flow meters, and microwave generators, used in advanced manufacturing and metrology applications. The company is certified to ISO 9001:2015, and has received an Innovators Award for its ESI CapStone system.
-
-
-
-

-
Advion, Inc.
mass spectroscopy & synthesis solutions
Company Overview
Advion is a manufacturer and supplier of mass spectrometry and ICP-MS solutions based in New York. The company provides chemist-centric, purpose-built mass spectrometers, nanoelectrospray ionization sources, and ICP-MS solutions for elemental analysis used in chemical biology and other applications and has collaborated with Interchim SAS, to establish Advion Interchim Scientific, an international frontrunner in pioneering instruments and solutions designed for applications in synthesis, life sciences, and analytical and purification processes utilizing chromatography. These solutions have various applications in clinical, pharmaceutical, environmental, and mass spectrometry analysis of compounds and elements and the food and ingredient sectors.
-
-
-
-

-
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Process Mass Spectrometers
Company Overview
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., founded in 1956 and headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts, is a manufacturer and supplier of life science solutions, analytical instruments, specialty diagnostics, laboratory products, and biopharma services. Through its brand names, including Invitrogen, Fisher Scientific, Patheon, Applied Biosystems, and Gibco, among others, the company provides a wide range of products, which include chromatography systems, thermal cyclers, automated cell counters, fermenters, and DNA polymerases. The company’s annual revenue is over 40 billion USD, and it serves several fields, including customers working in clinical diagnostic labs, research institutions, hospitals, government agencies, and pharmaceutical/biotech companies.
-
-
-
-

-
Hitachi High-Tech America, Inc.
Mass Spectrometer
Company Overview
Hitachi High Tech was established in April 1947 and operates in 26 countries with products and services ranging from semiconductor manufacturing equipment and Medical and Biosystems to Analytical Systems and Manufacturing related equipment and solutions. A unique state-of-the-art technology company with two functions as a manufacturer and a trading company with the motto of "Tackling social issues," the Hitachi High-Tech Group aspires to be a company that pursues not only economic value, such as revenue and profit, but also provides social and environmental value by contributing to resolving social issues through its business activities, including products and services. They also provide one-stop services, such as evaluations and analysis at a global level.
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
Hiden Analytical
SIMS
Manufacturer Overview
Hiden Analytical was established in 1981 and is based in Warrington, U.K., and is a manufacturer of quadrupole mass spectrometers for research applications and specialist process monitoring sectors. The company provides systems for precision gas analysis, plasma diagnostics, SIMS probes for UHV surface science applications, micro furnace reactors for catalyst research, and, dissolved gas & fermentation analysis, along with offering nanotechnology systems, quadrupoles for cluster analysis, and, fusion research systems for nuclear, food, aerospace & automotive, chemical & semiconductor, and, pharmaceutical industries.
-
-
-
-

-
CAMECA Instruments, Inc
SIMS
Manufacturer Overview
CAMECA Instruments, Inc., founded in 1953 and headquartered in Wisconsin, United States, operates as a manufacturer specializing in scientific instruments. The company provides a wide range of products and services, including electron microprobes, ion microprobes, and secondary ion mass spectrometers (SIMS). It caters to industries such as materials science, geology, nuclear forensics, and semiconductor manufacturing. The company's cutting-edge scientific instruments find applications in elemental and isotopic analysis, enabling research and quality control in different fields.
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
Waters Corporation
Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry
Company Overview
Waters Corporation is an ISO 9001-certified manufacturer of laboratory consumables, equipment, and software established in 1958 in Milford, Massachusetts, USA. The company’s products include mass spectrometers for measuring mass-to-charge ratios of ions, liquid chromatography for separating or quantifying the components of different mixtures, and data analytics software for processing and managing data on a cloud-enabled platform. It also offers consumables and supplies for maintaining or enhancing the reliability of its portfolio products. The company’s products are used mainly by its clients in the biopharma, materials science, and biomedical research sectors.
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
SCIEX
Mass Spectrometers
-
-
-
-

-
SRA Instruments
MAXIMUS TGA-FTIR-GC/MS INTERFACE
Distributor Overview
SRA Instruments, founded in Italy in 1999, is a supplier of scientific instruments for laboratories. The company offers an extensive and diversified product portfolio, including mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, sensors and olfactometers, liquid chromatography, and more. These products find applications in various industries, including clinical and food analysis in hospitals, polymer characterization, analysis of odorous volatile organic compounds, examination of museum objects with SIFT-MS Mass spectrometry, and the identification and quantification of VOCs in breath analysis.
-
-
-
-

-
PHOTONIS
Resistive Glass Products
Distributor Overview
PHOTONIS, a well-reputed French company founded in 1937, specializes in manufacturing electro-optic components and detectors. They offer a wide range of products, including photomultiplier tubes, image intensifiers, and microchannel plates. PHOTONIS serves various industries, such as scientific research, defence, medical, and industrial applications. Their products are used in applications like night view, mass spectral analysis, and space exploration. PHOTONIS is present internationally with offices and distributors in different countries. Devoted to excellence and environmental responsibility with various certifications, ensuring reliability and safety for customers.
-
-
Mass Spectrometer Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of April 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Teledyne ISCO |
20.3%
|
| 2 | PHOTONIS |
8.6%
|
| 3 | SCIEX |
8.1%
|
| 4 | Skyray Instruments |
8.1%
|
| 5 | Advion, Inc. |
5.9%
|
| 6 | Linseis, Inc. |
5.9%
|
| 7 | Hiden Analytical |
5.4%
|
| 8 | Variolytics GmbH |
4.5%
|
| 9 | Shimadzu Scientific Instruments |
4.5%
|
| 10 | Bruker Corporation |
4.5%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the mass spectrometer page as of April 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
- Shimadzu Seisakusho Co., Ltd.: 13,499
- Hitachi High-Tech America, Inc.: 13,397
Newly Established Company
- Variolytics GmbH: 2020 (4 years ago)
- Hitachi High-Tech America, Inc.: 2002 (22 years ago)
- SRA Instruments: 1999 (25 years ago)
Company with a History
- Shimadzu Seisakusho Co., Ltd.: 1875 (149 years ago)
- CAMECA Instruments, Inc: 1929 (95 years ago)
- LECO: 1936 (88 years ago)
Mass Spectrometer Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
- Linseis, Inc.
- Shimadzu Scientific Instruments
- Bruker Corporation
- Skyray Instruments
- LECO
- MKS Instruments
- Advion, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Hitachi High-Tech America, Inc.
- Teledyne ISCO
Global Distribution of Mass Spectrometer Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
10 | 66.7% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 6.7% |
 France
France
|
1 | 6.7% |
 Japan
Japan
|
1 | 6.7% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 6.7% |
 Italy
Italy
|
1 | 6.7% |
List of Mass Spectrometer Products
3 products are listed.
Cons Technology Co., Ltd.
Highly reliable data acquisition residual gas analyzer
It is a quartzed mass analyzer that is the basis of SRS mass filter. Not only reliable data acquisition, but also high -priced and high maintenance...
