











42 Length Measuring Machine Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for length measuring machines as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 42 length measuring machine manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked length measuring machine companies as of July, 2024: 1.Quality Control Solutions, Inc., 2.Greenlee, 3.Sulzer Ltd.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Length Measuring Machines
What Is a Length Measuring Machine?
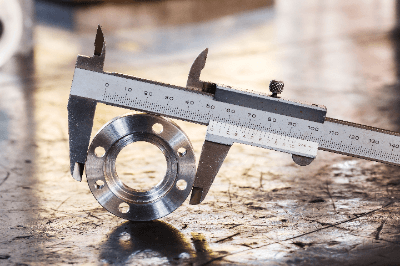
A length-measuring machine is, as the name implies, a device for measuring length.
Currently, length is defined by the distance light travels in unit time, based on the speed of light. There are two methods of measuring length: direct and indirect.
- Direct Method
This is a method of measuring length by comparing it to a standard length or scale using a commonly used ruler, tape measure, caliper, micrometer, etc. - Indirect Method
This is a method of measuring length by using other physical quantities related to length or by using electrical or optical methods.
In most cases, length can be measured by the direct method, but in the case of long structures or objects on the order of microns, the indirect method is used because it is difficult to prepare a standard length (scale). The indirect method is also used when the object is complicated in shape, inaccessible, or not allowed to be touched.
Uses of Length Measuring Machines
Length-measuring machines are used in a variety of fields, and the best one should be selected for each application. The types are as follows:
- A few millimeters to several tens of millimeters and small enough to fit in the palm of your hand or on a tabletop: e.g., rulers and calipers
- Several hundred millimeters to several meters long and rather large: e.g., tape measures, etc.
- Micrometers for microscopic observation of the finished product with an accuracy on the order of microns
- Out in the field, several meters to several tens of meters: e.g., optical methods (triangulation, laser length meter) measuring fine irregularities in precision industrial products such as lenses or semiconductor wafers (laser interferometry)
- In technologies such as X-ray CT: applied for measurements inside objects that are inaccessible by light or stylus
- In the nanotechnology industry: which requires measurements at the nanometer level, scanning electron microscopy is applied in this way
As a handy application, length measurement methods based on image analysis are also being developed, such as the recent development of an application for measuring length from a smartphone camera.
Principle of Length Measuring Machines
The meter is defined as the length that light travels in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second. The metric prototype based on this is the standard for length. In principle, the direct method is a comparison to this metric standard.
A measurement principle based on the definition of length is to measure the time of flight (ToF) of light. Since light is very fast, sophisticated electronic technology is required. Many laser-type instruments now commonly use a measurement method based on the phase difference between the intensity-modulated incident light and the reflected light.
By definition, this is the behavior of light in a vacuum, so in practice, it must be corrected for the refractive index of air. Laser interferometry uses the phenomenon of interference between laser beams.
By analyzing the interference fringes produced when the reflected light from the reference surface interferes with the reflected light from the measurement surface for the same laser irradiation, the distance of the measurement surface from the reference surface can be measured on the nm order. We have exemplified several length measuring instruments, but there are numerous other methods.
Other Information on Length Measuring Machines
1. How to Use Length Measuring Machines
The horizontal model employed by many length measuring machines consists of a bed, a reciprocating table with a built-in standard scale that moves on the bed, a measuring microscope that observes the standard scale, a measuring surface on which the specimen is placed under a constant measuring force, and a measuring table that supports the specimen to be measured. There are two types of horizontal length measuring instruments: one satisfies Abbe's principle and the other satisfies Eppenstein's principle.
In horizontal length measuring machines with a structure that satisfies Abbe's principle, measurement is performed by placing the measurement axis of the specimen and the scale face of the standard scale on the same straight line so that measurement error due to angular deviation from the measurement axis line of the reciprocating table based on non-straightness of the bed is negligible.
On the other hand, in horizontal length measuring machines having a structure that satisfies the Eppenstein principle, to eliminate measurement errors due to the non-straightness of the bed, measurement is performed by configuring the machine so that the focal length of the objective lens for the standard scale is equal to the distance between the measurement axis of the specimen and the standard scale when they are separated, and by optically placing the focal plane of the lens on the standard scale. Measurement is performed by optically placing the focal plane of the lens on the standard scale.
2. Laser Length Measuring Machines
Laser-length measuring machines irradiate a laser beam onto an object and use the reflected light to measure the distance of the object. Laser length measuring machines are called "displacement sensors" or "distance sensors" depending on the distance to be measured.
- Displacement Sensors
Displacement sensors are length-measuring machines that measure short distances (tens to hundreds of millimeters) in microns. - Distance Sensors
These are length-measuring machines that measure long distances (several millimeters to several meters) in millimeters.
The two known measurement methods for length-measuring machines are the triangulation method and the time of flight (ToF) method.
Triangulation Method
This is a measurement method that uses the principle of triangulation based on reflected light and consists of a light emitter and a light receiver. A semiconductor laser is used as the light emitter. In the measurement method, a laser beam focused from the semiconductor laser through a projection lens is irradiated onto the specimen. A portion of the diffuse reflection of the laser light irradiated on the specimen forms a spot image on the photosensor through the light-receiving lens. By detecting and calculating the position of the imaged spot, the amount of displacement from the specimen can be measured.
A system that uses a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) light-receiving element is called a CMOS system, while a system that uses a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) light-receiving element is called a CCD system.
Time of Flight (ToF)
This method measures the distance by measuring the time it takes for the irradiated light to reflect off the specimen and be received by the light-receiving part. There are two methods: the phase difference distance method, which uses the phase difference between the wavelength of the emitted light and the wavelength of the received light, and the pulse propagation method, which emits a laser beam with a fixed pulse width.
List of 42 Length Measuring Machine Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- Canada
- France
- Germany
- Japan
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom
-
-

-
Sensata Technologies, Inc.
Incremental Draw Wires
Manufacturer Overview
Sensata Technologies was originally founded in 1916 as General Plate Company and is now headquartered in Attleboro, Massachusetts. The company is a developer, manufacturer, and seller of sensors and sensor-rich solutions, electrical protection components, and other products used in automotive, industrial, energy, telecom, and construction industries. The company has 20 product categories including force sensors, tire management solutions, inverters & charges, and pressure sensors.The company’s next generation of products are designed to improve the efficiency of industrial pumps, fuel efficiency in ICE cars and energy efficiency in TVs, and facilitate usage of IoT devices.
-
-
-
-

-
Greenlee
Power Return Tape Measure
Manufacturer Overview
Greenlee Textron, Inc., founded in 1862, operates as a significant manufacturer in the industrial and electrical tool industry. The company provides a range of products and solutions related to warehousing, transportation, and general storage. As a key contributor in the machinery manufacturing sector, Greenlee Textron, Inc. offers power-driven hand tools and other general purpose machinery, addressing various industrial needs. The company's business in multiple locations, including Rockford, IL, and Southaven, MS, underscores its run to serving diverse sectors and fulfilling the requirements of professionals worldwide.
-
-
-
-

-
Gilson Company, Inc.
Digital Calipers
Manufacturer Overview
Gilson Company, Inc. is an American manufacturer and supplier of construction material testing equipment based in Lewis Center, Ohio. The company was established in 1939 with a primary focus on manufacturing the testing screen, a laboratory-scale screening machine, to cater to the mining and highway construction industries' requirements. Over time, Gilson has expanded its product portfolio and now offers a wide range of equipment, including ovens and furnaces, scales and balances, general laboratory testing equipment, as well as material testing equipment for aggregates, asphalt, concrete, and soils.
-
-
-
-

-
Buckaroos, Inc.
Tape Measure
Manufacturer Overview
Buckaroos, Inc., founded in 1990 in Fishers, Indiana, USA, is a manufacturer of premium products for insulators. The products include insulator cleaning equipment, pipe support products, Clevishield, conductor handling tools, and safety equipment. These products improve the maintenance, safety, and performance of electrical transmission and distribution systems. The insulator cleaning equipment, for instance, helps prevent flashovers and power interruptions by keeping insulators clean and free from contaminants. The conductor handling tools enhance efficiency and safety during installation and maintenance tasks. These products find essential application in the electric utility industry, supporting optimum transmission of electricity to homes and businesses.
-
-
-
-

-
Titan Tool Supply, Inc.
Video Multi-Scale Stage Micrometer
Manufacturer Overview
Titan Tool Supply was founded in 1952 and operates out of Buffalo, New York. Titan Tool Supply is a supplier of optical instrumentation for research & development, quality control, and other professional industries. Titan Tool Supply’s product lines include borescopes, microscopes, illumination devices, and micro finishing. Titan Tool Supply also offers video systems and magnetics solutions. Titan Tool Supply offers customers a 10-day approval program that allows customers to trial products in their workplace to verify satisfaction before purchase.
-
-
-
-

-
Celera Motion
Absolute Linear Transducer
Manufacturer Overview
Celera Motion, founded in 1994 in the USA, is a motion control business of Novanta Inc. and a manufacturer of motion control devices and composite solutions for OEMs. The company's products, which include inductive encoders, direct-drive motors, servo drives, transducers, and air-bearing spindles, among others, are also used in the medical, Satcom, UAV, medical, and scientific markets. Celera Motion also offers ISO 9001 and ISO 13485-compliant encoders, motors, sensors, transducers, and servo drives in custom sizes.
-
-
-
-

-
NBK America LLC
Scale Plates
Manufacturer Overview
NBK America LLC, founded in 2015 and based in King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, is an American manufacturer and a subsidiary of Japan's Nabeya Bi-tech Kaisha, specializing in mechanical components. Their product range includes couplings, like miniature shaft couplings for precision machine tools and semiconductor manufacturing equipment, special screws, such as vacuum application screws and other machine components. NBK offers finite automaton (FA) solutions, including wireless positioning units for production lines and setup operations. NBK provides machine component servicing, such as vibration resistance treatment and laser engraving. Services for couplings and special screws include coupling stainless steel screw alteration and screw length adjustment.
-
-
-
-

-
Quality Control Solutions, Inc.
5357301 Linear 100 Length Measuring Machine
Manufacturer Overview
Quality Control Solutions, Inc. is headquartered in Temecula, CA, and it is a designer and manufacturer of video, touch probe, and laser multisensor measuring systems, providing solutions for different measurement and inspection requirements. The portfolio of the company includes 2D Video Measuring Systems, 3D Multisensor Video Measuring Systems, Digital Readouts, and many more. The company also uses lab calibration accessories, equipment, and precision measuring tools made by global producers. The company is an ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited company and is in constant lookout for developing its knowledge and technical expertise in the field of calibration.
-
-
-
-

-
Hymark Ltd.
Dimensional Measuring Gauge
Company Overview
Hymark Ltd, a company based in Owensboro, Kentucky, is a distributor of measuring and motion control products and manufacturer of Kentucky Gauge equipment. The company excels in long-lasting automated length stop gauges, pushers/feeder systems, manual length stop gauges, and digital length measuring equipment. It also specializes in length measuring gauges and turnkey automation solutions for drilling, sawing, punching, and shearing applications. The company provides customers tailored solutions for worldwide steel, sheet metal, aluminum, and wood industries. Its products are backed by a 2-year warranty against manufacturing defects, enhancing yield and productivity across any industry, material type, machine type, and location.
-
-
-
-

-
Assembly Tool Specialists, Inc.
100mm Scale
Company Overview
Assembly Tool Specialists, Inc., founded in 1938 and located in Twinsburg, Ohio, is a designer and manufacturer of standard and custom assembly tools. The company offers a diverse range of products, including fittings, spirals, sleeves, gages, and scales. These products are used for document binding and cable management, wire connection and insulation, quality control in manufacturing sectors, and serving the measurement and calibration needs of diverse industries. The company’s products cater to industries such as aerospace, automotive, machine shops, industrial maintenance, and construction.
-
-
-
-

-
Flexbar Machine Corporation
Universal Style Caliper
Company Overview
Flexbar Machine Corporation, founded in 1965 and located in Islandia, New York, is a Manufacturer and distributor of metrology-grade replicas, casting materials, and precision measuring instruments. Its diverse range of products includes video and optical inspection devices, gages, borescopes, gage stands, and machine tool accessories. The company's products are used in quality control, metrology, and precision measurement applications across various industries. Flexbar's products cater to industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and other sectors where precise measurement and inspection are essential for maintaining product performance. The company also holds ISO 9001 certification.
-
-
-
-

-
Hitachi High-Tech America, Inc.
Metrology Solution
Company Overview
Hitachi High Tech was established in April 1947 and operates in 26 countries with products and services ranging from semiconductor manufacturing equipment and Medical and Biosystems to Analytical Systems and Manufacturing related equipment and solutions. A unique state-of-the-art technology company with two functions as a manufacturer and a trading company with the motto of "Tackling social issues," the Hitachi High-Tech Group aspires to be a company that pursues not only economic value, such as revenue and profit, but also provides social and environmental value by contributing to resolving social issues through its business activities, including products and services. They also provide one-stop services, such as evaluations and analysis at a global level.
-
-
-
-

-
Eisen Machinery Inc.
Long Length Measuring Instruments
Company Overview
Eisen Machinery Inc. is an importer and distributor of precision industrial machinery and machine components headquartered in Ontario, California. Established in 2002, their distribution includes machine tools such as grinders, milling machines, and engine lathes, as well as machine parts like forward reverse switches and power feeds. The company primarily serves machinery and equipment manufacturers as well as wholesalers in the energy, automation, and security industries. With partners in over three continents, Eisen Machinery Inc. can supply machinery and parts from Germany, Taiwan, and Japan, as well as accommodate custom orders for items not currently available.
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
DEWALT
Fiberglass Long Tape
Company Overview
Dewalt Inc. is a power tool manufacturing firm started in 1924 by Raymond DeWalt. It began as a small enterprise in Maryland but quickly expanded. They were reformed and reincorporated as DeWalt Inc. in 1947 and were purchased by American Machine & Foundry Co.Inc in 1949. Dewalt Inc. provides a diverse range of products such as power tools, hand tools, accessories, outdoor equipment, and workplace equipment. As of 2001, they produced and sold over 200 hand power equipment and 800 accessories. DeWalt is now a well-known tool brand among commercial contractors.
-
-
-
-

-
JOHANN FISCHER ASCHAFFENBURG Präzisionswerk GmbH & Co. KG
Length measuring machine
Manufacturer Overview
Johann Fischer Aschaffenburg Präzisionswerk GmbH & Co. KG, founded in 1929 and based in Aschaffenburg, Germany, is a manufacturer of high-precision measuring instruments. The company is also a metrology service provider in the precision engineering industry and sells items such as concentricity test devices, measuring cylinders, and rotary positioning tables. The company also offers contract manufacturing and will help with milling, polishing, and assembling. The company’s laboratory is an accredited calibration laboratory for the dimensions’ straightness, flatness, and angles 90° by DAkkS since 1988, and the company offers calibration services regardless of where the product is manufactured.
-
-
-
-

-
Jakob Thaler GmbH
Length Measuring Device
Manufacturer Overview
Thaler Company was founded in 1964 and is headquartered in Bad Bramstedt, Germany is a manufacturer of underground cable laying products. The company offers an array of products including cable drum transport and laying trailer, pipe cleaning and pipe renewal winches, and cutting tools for cable and pipe. Based on the standard products, special machines were developed like pipe cleaning and pipe rehabilitation winches were developed from the tested cable capstan winches. These products find applications in domestic power supply, internet supply, and cable aerial transportation.
-
-
-
-

-
DR. JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GmbH
Absolute length gauges
Manufacturer Overview
HEIDENHAIN, founded in 1889 and headquartered in Traunreut, Germany, is a manufacturer of precision measurement and control equipment. Specializing in industries requiring precise solutions, the company offers rotary and linear encoders, digital readouts, touch probes, and motion controllers. These products serve sectors like manufacturing, electronics, and aerospace, ensuring enhanced precision and efficiency. The company holds ISO 9001 certification and is an EMAS-certified company, thereby meeting the demanding, globally recognized environmental certification standards of the European Union.
-
-
-
-

-
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Length Measuring Machine
Manufacturer Overview
DAI-ICHI Sokuhan Works Co, founded in 1944 is based in Ojiya, Japan, and is a manufacturer and supplier of machinery tool accessories. Their product portfolio includes measuring instruments, air micrometers, electronic micrometers, gauges, precision machine parts, spindle units, and kneading dispersibility measurement. The products are manufactured under superior technology and precision with quality control. The products are used in multiple industries which include aircraft, trains, automobiles, and other modes of transportation.
-
-
-
-

-
TOKYO SEIMITSU CO., LTD.
High Precisions Digital Measurement Instrument
Manufacturer Overview
Tokyo Seimitsu Co. Ltd., established in 1949 and headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is a manufacturer of semiconductor production equipment and precision measuring instruments. Its product portfolio includes optical measuring instruments, probing machines, polish grinders, X-ray CT systems, and coordinate measuring machines. In 1952, the company developed Japan’s first high-pressure flow-type air micrometer, and in 1958, it created the world’s first germanium pellet automatic thickness sorting machine. It also developed Japan’s first coordinate measuring machine in 1969, followed by Japan’s first wafer-dicing machine in 1970. The company is the industry’s only semiconductor equipment manufacturer with measurement technology.
-
-
-
-

-
Weir Group PLC
Certified Length Measurement Systems
Manufacturer Overview
Weir was established in 1871 as a manufacturer and supplier of mining solutions headquartered in Glasgow, Scotland. The company provides Processing equipment for Comminution, Classification, Pumping, and Slurry Transportation and Dewatering along with wear parts, and equipment attachments for similar purposes. There is Feeding, Crushing, and Screening equipment for the processes and wear parts for Face Shovels, Dozers, Motor graders, and more and these products are not just serving the mining industry but also the construction aggregates industry, Food Processing, Recycling, Chemical Processing, and Storage sectors.
-
-
-
-

-
Sulzer Ltd
UNIVERSAL LENGTH MEASURING MACHINE
Manufacturer Overview
Sulzer Ltd. is a fluid engineering and chemical processing solutions manufacturer originally founded in 1775. The company has been headquartered in Winterthur, Switzerland since 1834, maintaining a network of 180 manufacturing facilities and service centers around the world. The company has an expansive product portfolio including distillation and absorption columns, agitators, reactors, crystallizers, and polymerization systems. These supply clients in the metals, plastics, chemicals, power, and pharmaceutical industries. Sulzer Ltd. also offers a range of services, such as testing and diagnostics, prototyping, retrofitting, and upgrades, including technical training with long-term support for their customers.
-
-
-
-

Manufacturer Overview
FOBA Laser Marking + Engraving, established in 1969 in Selmsdorf, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of laser marking and engraving systems. The company's product portfolio includes laser marking systems and engraving machines that offer precise, permanent, and quality marking solutions for various materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. FOBA's technology is broadly used in industries like automotive, medical devices, electronics, and packaging. Their solutions enable traceability, branding, and identification, enhancing product safety and authenticity. The company also aims to provide cutting-edge solutions that empower industries with efficient marking and engraving capabilities.
-
-
-
-

Manufacturer Overview
Laserax, founded in Quebec City, Quebec, in 2010 is a manufacturer of laser machines to implement automated laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions. The company's product portfolio includes oem laser markers, oem laser cleaners, laser marking machines, laser cleaning machines and laser welding machines. The company serves industries such as Oil and Gas, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Construction, and Power Generation. The company provides services such as Product Selection Guidance, Engineering Support, and Custom Manufacturing.
-
-
-
-

-
Legrand
MEASUREMENT EQUIPMENT
Manufacturer Overview
Legrand Group, established in 1860 and headquartered in Limoges, France, is a manufacturer specializing in electrical and digital building infrastructures. The company’s product offerings encompass a range of electrical components, including air circuit breakers (ACBs), miniature circuit breakers (MCBs), molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs), and residual current devices (RCDs). It also offers Deutsche Institut fur Normung (DIN) rails, as well as head equipment and electrical busbar systems. Additionally, the company provides enclosures and equipment for cabling components and charging stations, along with wiring accessories. It also offers lighting management devices, emergency lighting units, access control and safety equipment for building infrastructures.
-
-
-
-

-
Mitutoyo Corporation
CRYSTA-Apex V500/700/900, Measuring Machines
Manufacturer Overview
Mitutoyo was founded in 1934 and headquartered in Kawasaki City, Japan. The company is a manufacturer and seller of precision measuring instruments including software, optics, machinery, and electronics. The company is ISO/IEC 17025 accredited for calibration services for measuring instruments. The company’s product lines include Micrometers, Calipers, Calibration Equipment, Vision Measuring Systems, and many others. The company’s coordinate measuring machines and roundness/cylindricity measuring machines are sol in over 60 countries worldwide.
-
-
-
-

Manufacturer Overview
Mahr GmbH, Providence, RI, in 1888 is a manufacturer of dimensional metrology equipment from simple handheld gages to technically advanced measurement systems for form, contour, surface finish and length. The company's product portfolio includes electronic precision pointers, Touch control buttons used for sensitive measuring tasks, Length measurement technology & components used for electrical linear encoders and Calibration & setting machines. Their products are used in industries such as Food and Beverage, Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology, Medical and laboratories. The company provides services such as Product Selection Guidance, Engineering Support, New Product Design and Development and Custom Manufacturing.
-
-
-
-

-
Renishaw plc
Equator™ 500 gauging system
Manufacturer Overview
Renishaw is a British manufacturer and supplier of engineering technology products and solutions established in 1973 and based in Gloucestershire, United Kingdom. The company primarily produces equipment for metrology, spectroscopy, and healthcare, including coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), dental scanners, and Raman spectrometers. They also offer long-term support services, such as calibration, refurbishment, repair, and upgrades. Renishaw has more than 5,000 employees across its network of subsidiaries and sales offices in over 36 countries.
-
-
-
-

Manufacturer Overview
Jenoptik was established in 1991 and is based in Jena, Germany, as a manufacturer of optical technologies with majority of their products and services being provided to the photonics market. The company's products portfolio includes imaging solutions and cameras, laser and laser technology, optics and optical systems, and LiDAR technologies, which are mainly used in industries such as, semiconductor and equipment manufacturing, automotive, medical technology, security and defense technology, and aviation.
-
-
-
-

-
Hi-Tech Seals
O-Ring Cone
Manufacturer Overview
Hi-Tech Seals Inc. is a manufacturer of sealing and gasket components established in 1990 and headquartered in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. The company’s products include a wide selection of o-rings, seal kits, and gaskets. It offers products fabricated from BoKure urethane, KasPex PEEK, and RyFlor compounds. The company primarily serves clients in the oil and gas, water treatment, and aerospace sectors. It also offers custom molding services, in-house rapid prototyping, and optical measurement inspections.
-
-
-
-

-
The Eraser Company, Inc.
Measuring Meter
Manufacturer Overview
The Eraser Company, Inc. is an ISO 9001:2015-certified manufacturer of cable, wire, and tube processing products that was established in Syracuse, New York, USA, in 1911 before it was incorporated in 1935. The company offers wire and cable strippers for electrical applications, wire twisters for efficient installation or maintenance processes, and wire, cable, and tube cutters. It also offers heat shrink machines, infrared heating tools, and various measuring products such as roll tape. The company’s products are commonly used by clients in the telecom, construction, and engineering industries.
-
-
-
-

-
Magnescale
Laserscale
Manufacturer Overview
Magnescale Co., Ltd., established in 1969 as Sony Magnescale Co., Ltd. and headquartered in Tokyo, is a manufacturer specializing in encoder scales used extensively in the Computer Numeric Control (CNC) machine tool industries. The company offers a range of products, including the Magnescale lineup of magnetic scales for rotational and linear position measurement. Additionally, they develop the Laserscale lineup, utilizing hologram technology and semiconductor lasers as light sources to achieve measurement resolutions at the picometer scale. These scales exhibit position and angle control, as well as environmental resistance to severe conditions such as temperature changes and air pressure fluctuations.
-
-
-
-

-
CATU
Insulated rule
Manufacturer Overview
CATU, formed in 1919 and based in Bagneux, France, is a manufacturer of safety solutions and equipment against electrical risks for transportation and distribution networks of electrical energy. The company crafts protection kits for electrical intervention, insulating blankets, locking padlocks, and regulatory posters and flags. It also produces maneuvering and rescue sticks, installation controllers and measuring devices, as well as jumper clamps and accessories. Its insulating blankets have acid resistance, oil resistance, and ozone resistance properties. It has passed the ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certifications.
-
-
-
-

-
Chotest Technology Inc.
Universal Length Measuring Machine SJ5100
Manufacturer Overview
Chotest Technology Inc., founded in 2005, is a manufacturer of precision measuring instruments headquartered in Shenzhen, China. The company offers a range of high-precision measuring equipment, including White Light Interferometer SuperView W1, Laser Tracker GT series, universal length measuring machines, laser interferometer SJ6000, and profilometers SJ5700 series. Its products are manufactured in accordance with ISO9001 and 6S standards, ensuring quality products for its customers. The company's precision measuring equipment is used in various industries, including government metrology and quality inspection agencies, automotive, aerospace, and machinery. Its instruments are employed for accurate measurements in quality control and industrial applications.
-
-
-
-

-
EDDY Pump
Universal Length Measuring Machine
Manufacturer Overview
EDDY Pump, operating from the United States, established in 1984, is a manufacturer of state-of-the-art dredge, pump, and excavation equipment. The company designs and produces solutions for industries like mining, oil and gas, and environmental cleanup. EDDY Pump's core aim is to provide reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly pumping solutions. EDDY Pump offers a comprehensive range of patented products, including slurry pumps, dredge equipment, and excavator attachments. These solutions cater to the diverse needs of their clients, enabling them to tackle challenging pumping and dredging applications with ease.
-
-
-
-

Manufacturer Overview
Omtech was established in 2002 in the United States, and is a manufacturer and supplier of packaging materials and machinery for diverse industrial applications. The company offers a comprehensive range of products including packaging films, machinery, fiber laser maker, fiber laser cutting machine, production materials as well as automation systems that enhance operational efficiency while reducing environmental impact. It also offers accessories such as laser tube, air purifier, inline fan, and more. The company caters to a wide range of clients, including small enterprises and large corporations, while streamlining packaging processes and ensuring product integrity.
-
-
-

-
Trumeter
Length Measurement Tools
Manufacturer Overview
Trumeter, established in 1937 and based in Coconut Creek, Florida, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision measurement instruments. They provide test and measurement equipment such as digital panel meters used to measure electrical and physical quantities. The company is catering to similar industries for accurate testing and measurement, offering industrial controls to automate processes like conveyors, valves, and pumps which are utilized across various industries, including manufacturing, power, telecommunications, and healthcare.
-
-
-
-

-
ADITYA ENGINEERING
Universal Length Measuring Machine
Manufacturer Overview
ADITYA ENGINEERING was established in 1984, headquartered in Hadapsar, Pune, India, and is a manufacturer of Measuring Instruments and Gauges. The portfolio of the company includes Measuring Machines, Calibration Masters, Gear Measurement, and much more. The company works to provide solutions for sustainable progress. The Universal Length Measuring Machine, Model: Lab Microcal 600 has a measuring spindle cross-section of 60x40mm size for straightness and accuracy. To ensure parallelism of anvil measuring faces, these machines are made in an adjustable anvil design.
-
-
-
-

-
Princess Auto Ltd.
Laser Measure
Company Overview
Princess Auto Ltd., founded in 1933 and based in Winnipeg, Canada, is a supplier of an assortment of tools and equipment with over 50 stores across Canada. In 1977, it opened its first store in Edmonton, Alberta, and became a retailer. The company serves several workers, including inventors, farmers, and tradespeople and stocks products such as outdoor power equipment, hand tools, and hydraulics. It sells items from several brands, such as Dealer’s Choice, Braber Equipment, and King Canada, and it also has a foundation that provides financial assistance to trades students enrolled at Canadian colleges.
-
-
-
-

-
Renish
Calibration products
Company Overview
Renishaw plc., established in 1973 and based in Wotton-under-Edge, United Kingdom, is a manufacturer of analytical instruments, medical devices, and manufacturing technologies. Some of the products it stocks include additive manufacturing systems, open optical encoders, and neurological products, and it operates in the Americas, EMEA, and APAC regions, with 67 locations in 36 countries. Throughout its history, the company has spent 13% to 18% of its annual sales in R&D and engineering. In 1981, it set up its first international manufacturing facility in Ireland, and in 1984, it was listed in the London Stock Exchange unlisted securities market.
-
-
-
-

Company Overview
Trumpf Inc. Was founded in Farmington, Connecticut in 1923 were it remains to this day. The company is a developer of connect production technology, making customer’s upstream and downstream operations more efficient, precise, and future-proof. The company serves the automotive, photovoltaic, aerospace, dental, and construction industries. The company’s product segments include hardware, software, and services; machines & systems, power electronics, and power tools. Services include process optimization, technical assistance, training, aftermarket product enhancement, and financing.
-
-
-

-
Gesswein Co, Inc.
Fiberglass Dial Caliper
Distributor Overview
Gesswein Co, Inc., established in 1914 and headquartered in Bridgeport, Connecticut, is a distributor of jewelers' tools and supplies. The company offers a wide range of products, including additive manufacturing tools, abrasives, bench tools, burs & drills, casting tools, cleaning tools, dust collection tools, engraving tools, power tools, and more. These products are utilized by professionals in the jewelry and metalworking industries for precision work. Gesswein Co, Inc. also provides various services, such as operations review, product sampling, account maintenance, quality control, and price matching.
-
-
Length Measuring Machine Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of July 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quality Control Solutions, Inc. |
5.9%
|
| 2 | Sulzer Ltd |
5.0%
|
| 3 | Greenlee |
4.5%
|
| 4 | FOBA |
4.5%
|
| 5 | Eisen Machinery Inc. |
4.5%
|
| 6 | EDDY Pump |
4.0%
|
| 7 | Trumeter |
4.0%
|
| 8 | Hymark Ltd. |
3.5%
|
| 9 | omtech |
3.5%
|
| 10 | Laserax |
3.5%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the length measuring machine page as of July 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
- Hitachi High-Tech America, Inc.: 13,397
- Weir Group PLC: 11,500
- Mitutoyo Corporation: 5,374
Newly Established Company
- NBK America LLC: 2015 (9 years ago)
- Magnescale: 2010 (14 years ago)
- Laserax: 2010 (14 years ago)
Company with a History
- Sulzer Ltd: 1834 (190 years ago)
- Mahr GmbH: 1861 (163 years ago)
- Gesswein Co, Inc.: 1868 (156 years ago)
Length Measuring Machine Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
- Sensata Technologies, Inc.
- Greenlee
- Gilson Company, Inc.
- Buckaroos, Inc.
- Titan Tool Supply, Inc.
- Celera Motion
- NBK America LLC
- Quality Control Solutions, Inc.
- Hymark Ltd.
- Assembly Tool Specialists, Inc.
- Flexbar Machine Corporation
- Hitachi High-Tech America, Inc.
- Eisen Machinery Inc.
- Reid Supply
- DEWALT
Global Distribution of Length Measuring Machine Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
15 | 51.7% |
 Germany
Germany
|
6 | 20.7% |
 Japan
Japan
|
3 | 10.3% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
2 | 6.9% |
 Switzerland
Switzerland
|
1 | 3.4% |
 Canada
Canada
|
1 | 3.4% |
 France
France
|
1 | 3.4% |