



4 ELISA Kit Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for elisa kits as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 4 elisa kit manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked elisa kit companies as of April, 2024: 1.Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., 2.Boster Biological Technology Co Ltd, 3.Biomatik Corporation.
Table of Contents
What Is an ELISA Kit?
An ELISA Kit is one of the immunoassay method using antibodies for quantification by ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay).
ELISA is a method for quantifying trace amounts of biological substances using an antigen-antibody reaction.
Uses of ELISA Kits
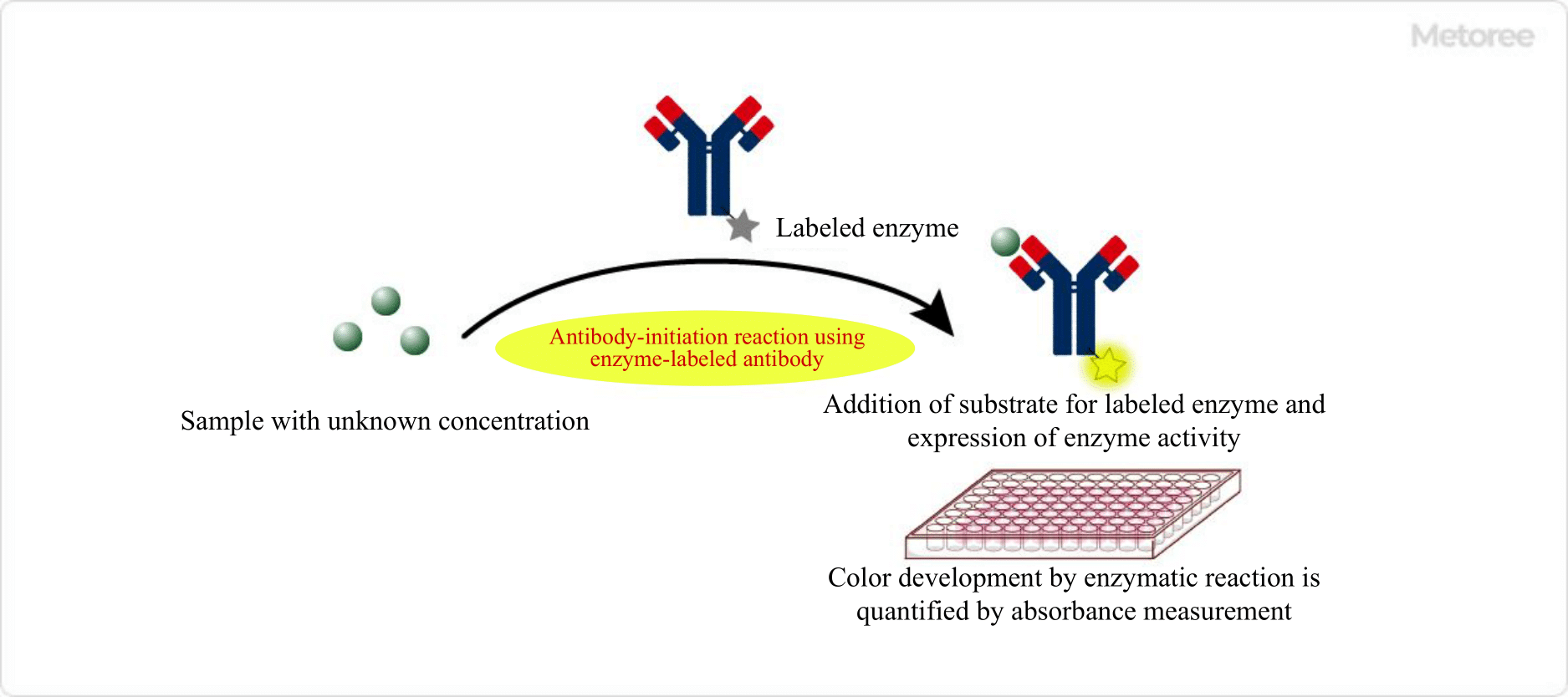
Figure 1. Overview of ELIS
ELISA kits are often used in the field of biology from the viewpoint that trace amounts of biological substances can be detected with high accuracy by antigen-antibody reaction. For example, they are used to measure blood proteins such as cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, or in immuno-oncology to measure soluble immune checkpoint molecules to elucidate the status of cancer immunity.
In neurobiology, they is used to quantify Aβ, tau, and α-synuclein proteins that are known to cause neuropathy.
Other ELISA kits, such as phosphorylation-specific kits and immunoglobulin kits, are available, allowing you to select the ELISA kit that best suits your research and objectives.
Competitive ELISA analysis is also appropriate when measuring histamine, pesticides, dioxin, etc.
Principle of ELISA Kits
ELISA uses an antibody or an antigen that binds specifically to the substance to be measured (antigen-antibody reaction). Finally, an enzyme-labeled antibody (or antigen) is used to detect and evaluate enzyme activity by absorbance measurement.
By measuring the enzyme activity, the concentration of the enzyme in solution, the substances in the reagents involved in the antigen-antibody reaction, and the target substance can be quantified.
There are four main methods: direct method, indirect method, sandwich method, and competitive method.
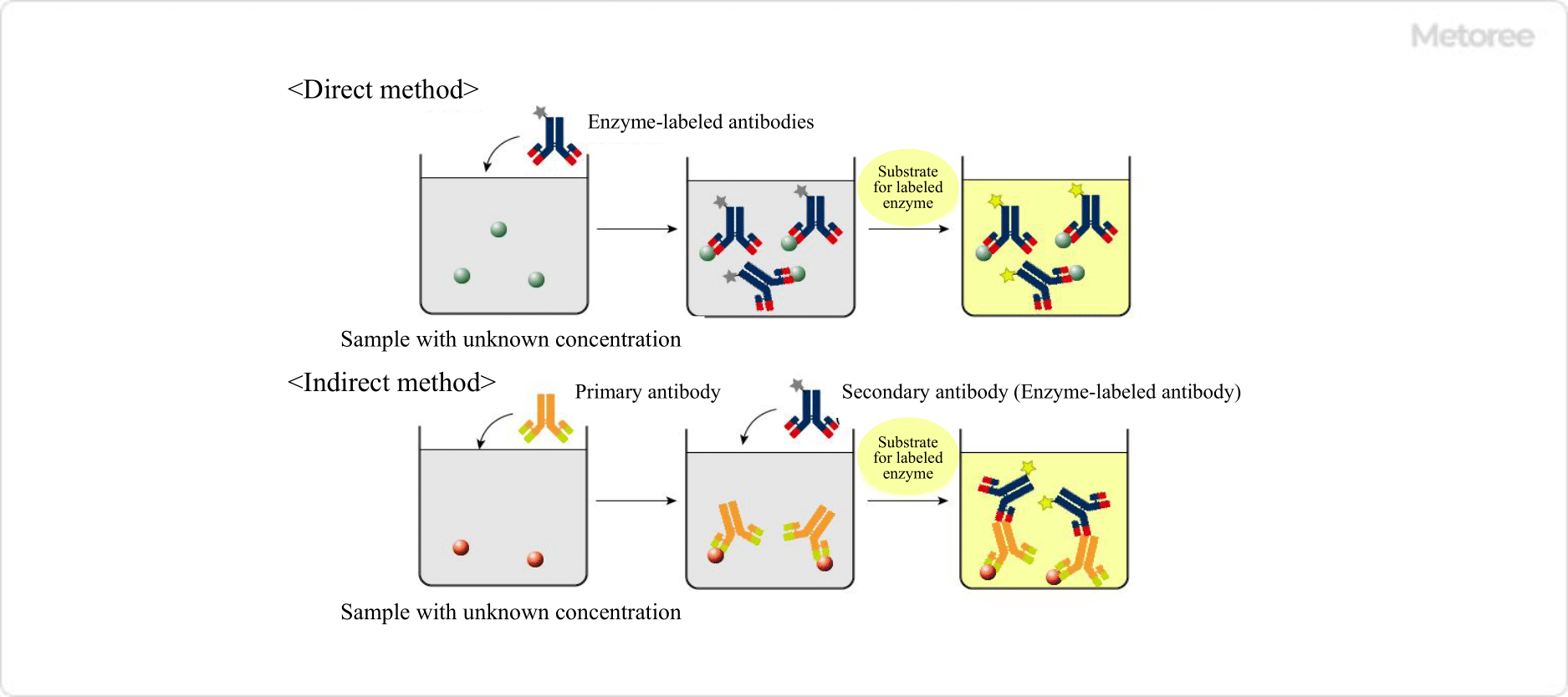
Figure 2. Direct and indirect methods
1. Direct Method
In this method, the target antigen or antibody is solid-phased on a microplate, and the labeled antigen or antibody directly interacts with it. After the antigen or antibody is applied, the plate is washed and the enzyme activity on the microplate is detected. Since no secondary antibody is required, this method can be performed in a single step and in a short time.
2. Indirect Method
First, an antibody specific for the target antigen is applied to the solid-phase microplate. Then, the enzyme activity of the enzyme on the labeled secondary antibody is detected. This method is characterized by increased sensitivity, but requires more time than the direct method.
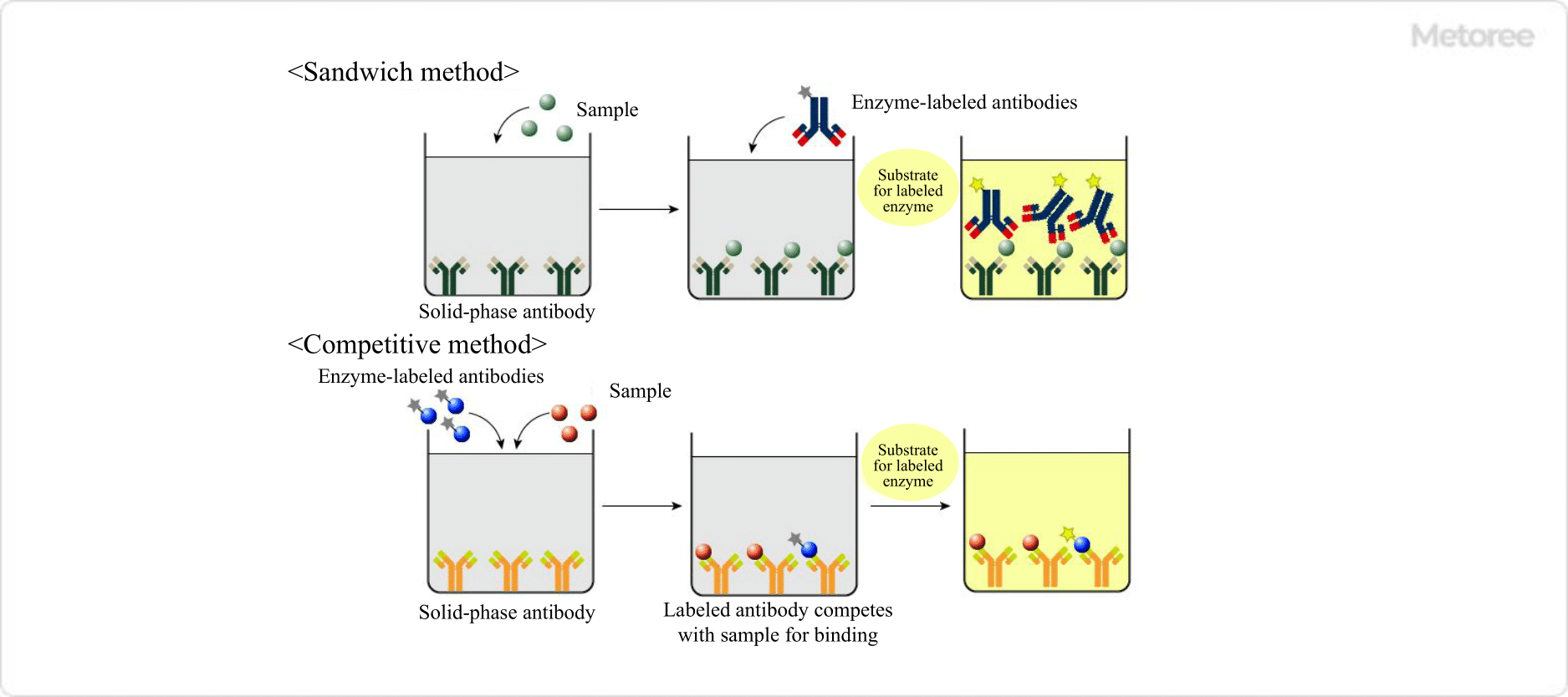
Figure 3. Sandwich and competitive methods
3. Sandwich Method
A microplate coated with an antibody that binds to the target substance in the sample is used to react with the sample as an antigen. Subsequently, the sample is reacted with another antibody labeled with an enzyme, and the excess antibody is washed off before the enzyme activity on the microplate is measured.
It is necessary to select an antibody that has a different antigen recognition site from the antibody used for solid phase and the enzyme-labeled antibody.
The advantage of the sandwich method is that the specificity of the reaction is higher than that of the direct method, resulting in higher detection accuracy.
4. Competitive Method
The competitive method can be used to measure small molecules that are difficult to detect with the sandwich method, or when there is only one binding site for the antibody.
An antibody that binds to the target substance is coated on a solid phase, and the sample is simultaneously reacted with a labeled antigen of known concentration. If the sample contains a large amount of the target substance, the absorbance decreases because there is little enzyme-labeled antigen that can bind to the antibody.
Conversely, if the sample contains less of the target substance, more of the enzyme-labeled antigen is available to bind to the antibody, resulting in an increase in absorbance.
How to Select an ELISA Kit
As mentioned above, since detection is performed using specific antigen-antibody reactions, the first prerequisite is to use a product that uses the correct combination of reagents for the sample. In addition, whether using direct, indirect, sandwich, or competitive methods, each method has their own advantages and disadvantages, so it is necessary to select the most preferable one according to the purpose of the measurement.
Solid-phase attachment to a microplate is generally by hydrophobic interaction or covalent bonding, and it is important to select the correct microplate according to the binding mode. In addition to hydrophobic and hydrophilic types, many types are available, including those processed with amino and carboxyl groups for covalent binding applications.
List of 4 ELISA Kit Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- Canada
-
-

-
Boster Biological Technology Co Ltd
ELISA Kits
Manufacturer Overview
Boster Biological Technology Co., Ltd., founded in 1993 and based in Pleasanton, California, USA, is a manufacturer of life sciences equipment and products. Specializing in the development and production of advanced research reagents, the company offers a broad range of products, including ELISA Kits and antibodies, to support scientific research and diagnostics. It holds ISO 13485 certification, for the consistency of its products and the products find applications in various industries, such as academic research, pharmaceutical development, and clinical diagnostics.
-
-
-
-

-
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
ELISA Kits
Company Overview
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., founded in 1956 and headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts, is a manufacturer and supplier of life science solutions, analytical instruments, specialty diagnostics, laboratory products, and biopharma services. Through its brand names, including Invitrogen, Fisher Scientific, Patheon, Applied Biosystems, and Gibco, among others, the company provides a wide range of products, which include chromatography systems, thermal cyclers, automated cell counters, fermenters, and DNA polymerases. The company’s annual revenue is over 40 billion USD, and it serves several fields, including customers working in clinical diagnostic labs, research institutions, hospitals, government agencies, and pharmaceutical/biotech companies.
-
-
-
-

-
Biomatik Corporation
ELISA Kits
Manufacturer Overview
Biomatik Corporation, founded in 2002 and headquartered in Cambridge, Ontario, Canada, is a manufacturer of biotechnology products and integrated life sciences. The company specializes in the production of BioReagents, ELISA kits, & Peptide Synthesis, and Protein & Antibody Services, serving the comprehensive needs of the global research community. It holds ISO 9001 certification, and scientists utilize its extensive product range, facilitating advancements in genomics, proteomics, and immunology research. The adaptable applications of its offerings span academic research, pharmaceutical development, and clinical diagnostics.
-
-
-
-

-
Merck
ELISAs and RIAs
Manufacturer Overview
Merck, started in 1668 and based in Darmstadt, Germany, is a supplier of solutions and services for research, development, and manufacture of pharmaceutical and biotechnological drug therapies. The company serves the life science industry and has a broad portfolio of 300,000 products, including biopharmaceutical manufacturing, industrial microbiology, reagent, life science research, and water purification products. It is available in 66 countries, brings together six brands, and has several ISO certifications, including ISO 13485, ISO 14001, ISO 13485, and ISO 50001.
-
-
ELISA Kit Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of April 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. |
35.3%
|
| 2 | Boster Biological Technology Co Ltd |
29.4%
|
| 3 | Biomatik Corporation |
23.5%
|
| 4 | Merck |
11.8%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the elisa kit page as of April 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
ELISA Kit Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
Global Distribution of ELISA Kit Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
2 | 66.7% |
 Canada
Canada
|
1 | 33.3% |
List of ELISA Kit Products
159 products are listed.
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit allergy
60+ people viewing
Last viewed: 22 hours ago
[For allergies] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 w...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA Kit Alzheimer's disease
[Alzheimer's disease] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ Fo...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit Others
[Others] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reactions Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 wel pla...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA Kit antibody medical care
[Antibody Medical] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 9...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 Well plate Format ELISA Kit Cell Adhesion
[For cell adhesion] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For ...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 Well plate Format ELISA Kit Citchin
[For cytokine] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 we...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA Kit for liver / kidney
20+ people viewing
[For liver / kidney] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reactions Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ Fo...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit metabolism
[Metabolism] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 wel ...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit inflammation
30+ people viewing
[For inflammation] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 9...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA Kit bone
[For bones] ELISA kit series using antigen -antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 wel ...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA Kit for Angiotensin
[For Angiotensin] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit for blood vessels
[For blood vessels] ELISA kit series using antigen -antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit tumor
[For tumor] ELISA kit series using antigen -antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 wel ...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit for blood
[Blood] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 wel plate...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 Well plate Format ELISA Kit Immunity
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
[Immunity] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 wel pl...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit for aging
[For aging] ELISA kit series using antigen -antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 wel ...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA Kit for diabetes
[For diabetes] ELISA kit series using antigen antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 we...
Ato
Antigen antibody reaction ELISA KIT (for research) 96 well plate Format ELISA kit stress
[For stress] ELISA kit series using antigen -antibody color reaction Purpose / use ・ ELISA kit for various antigen antibody reactions ・ For 96 wel...
Hakarel
Research reagent human EPCAM positive exosomine (CD9) ELISA kit
From blood sample and cell culture supernatant, EPCAM can be quantified to high sensitivity (sensitivity; 1 pg/ml) by 2Step elisa method. Human EP...
Hakarel
Research reagent human PD-L1 Positive exosomine (CD9) ELISA kit
PD-L1-positive exosomes can be directly quantified by the 2STEP ELISA method from blood samples and cell culture supernatant. The PD-L1 is also ex...
Hakarel
Human PD-L1 ELISA kit
PD-L1 can be quantified to high sensitivity (sensitivity; 1pg/ml) from the blood sample and cell culture supernatant. Cancer cells are expressed o...
Hakarel
Research reagent human origin Exosomium ELISA kit
As for the quantitative method of exosomes, there are substitutes in the amount of protein containing exosomes, and particle analysis by nanotracki...
Hakarel
Inunu HER2 ELISA kit
Dog's serum and urinary HER2 can be quantified by the 2STEP ELISA method. IHC tests (immuno -tissue chemical dyeing methods), which examine protei...
Hakarel
ELISA kit for research reagent dog derived derived amount of Exosomes
Exosomes can be directly quantified by the 2Step elisa method from blood samples and cell culture supernatant. As for the quantitative method of e...























