All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for laser microscopes as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 12 laser microscope manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked laser microscope companies as of March, 2026: 1.Heidelberg Engineering Inc., 2.Holmarc Opto-Mechatronics Ltd., 3.Lasertec Corporation.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Laser Microscopes
 A laser microscope is a type of optical microscope in which a sample can be observed by scanning a laser beam to a light source.
A laser microscope is a type of optical microscope in which a sample can be observed by scanning a laser beam to a light source.
It generally employs confocal optics and is also called a confocal laser scanning microscope or CLSM. A laser microscope has high spatial resolution not only in the horizontal (XY) direction but also in the vertical (Z) direction because the confocal optics can exclude light from out-of-focus surfaces.
Therefore, by measuring microscope images while shifting them in the height direction, it is possible to obtain a three-dimensional image or an all-in-focus image.
Since laser microscopes use light for measurement, there is no need to touch the sample. For this reason, laser microscopes are used in the industrial field to observe the three-dimensional shapes and surface profiles of precision instruments, such as semiconductors and electronic components. They are also used in the life science field to observe cells and biological tissues labeled with fluorescent substances.
Some manufacturers offer customized measurement stages for laser microscopes, making it possible to measure large samples such as large flat panel displays.
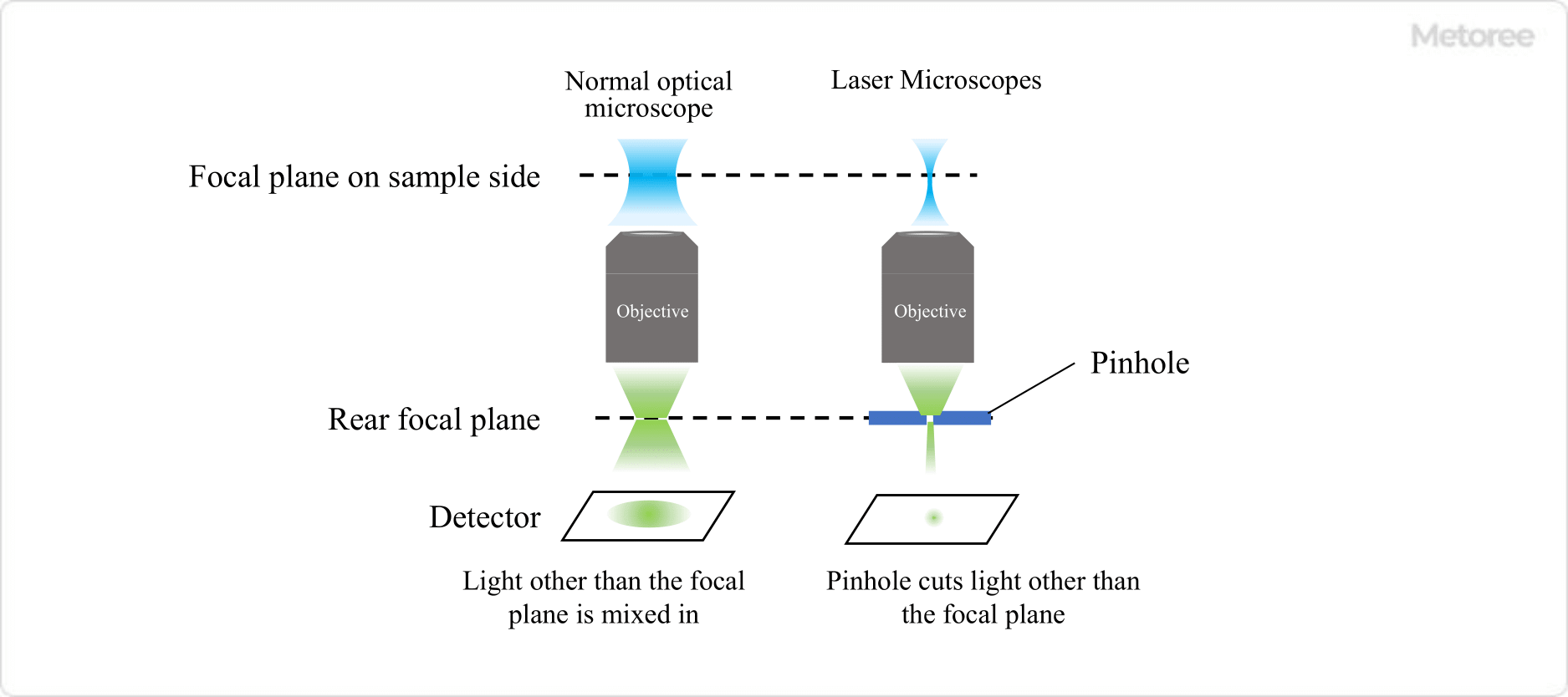
Figure 1. Comparison of optical and laser microscopes
Laser microscopes are similar to a typical optical microscope configuration of lenses and mirrors, but use a laser as the light source and are designed as a confocal optical system. Laser light is characterized by the uniform wavelength and phase of the emitted light, and by its excellent monochromaticity, directivity, and linearity.
Since ordinary light has different phases and wavelengths, the optical paths are not aligned, and the reflected light generated by irradiating a sample is overlapped by scattered light, making it difficult to obtain a clear image. On the other hand, with laser microscopes, a pinhole is placed at the position where the reflected light is focused through transmission through the lens and reflection from the sample. Therefore, excess light, such as scattered light, can be eliminated. As a result, clean images with clear contours can be obtained.
In addition, there are two methods of obtaining two-dimensional images with laser microscopes: one is to move the stage, and the other is to move the laser mechanism. The features of each method are as follows.
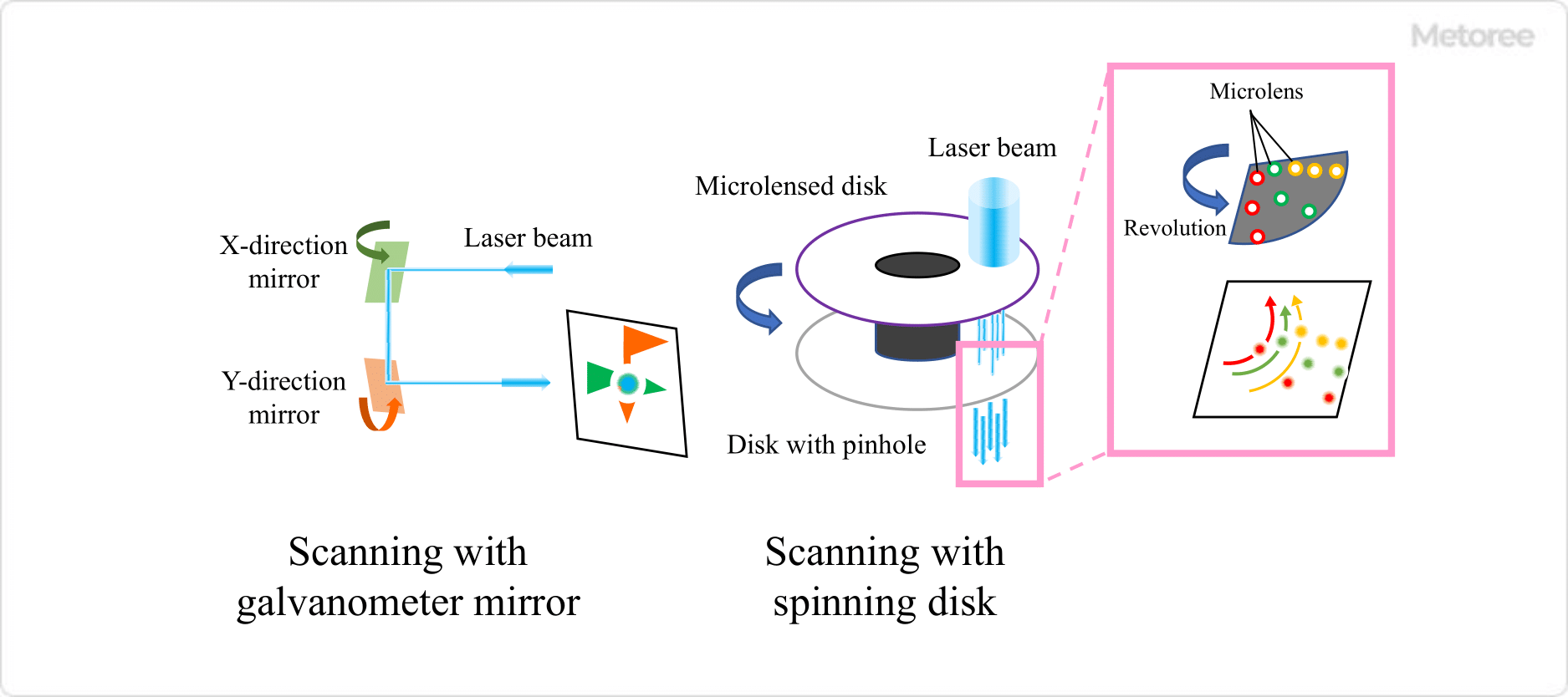
Figure 2. Laser microscope scanning method
There are various ways to scan with laser microscopes. For example, scanning with a galvano mirror involves mechanically moving the mirror, but a MEMS scanner or resonant scanner method can be used to increase the speed.
The spinning disk method is used for high-speed measurement, in which a laser beam is directed onto a disk lined with many micro-lenses and pinhole arrays to pick up many beams of light simultaneously reflected from the sample. This method can obtain a large amount of information at a time but requires a high-power laser that has sufficient intensity even when spread to some extent.
The electron microscope is another type of microscope with high magnification, but the principles of these instruments are not identical. Laser microscopes use light, while electron microscopes use electron beams, and the magnification, equipment, and measurement techniques are very different.
Because electrons are very short in wavelength compared to visible light, the resolution of electron microscopy is very high; scanning electron microscopes (SEM) can observe structures down to a few nanometers. Laser microscopes, on the other hand, cannot observe structures at wavelengths shorter than their wavelengths and have a resolution of only a few hundred nanometers.
The equipment used for laser microscopy and electron microscopy differs greatly. Electron microscopy uses an electron beam and requires measurement under a vacuum. In addition, when highly insulating materials are measured with electron microscopes, the electron beam may cause charge to accumulate on the surface, distorting the image, and other limitations exist, so care must be taken to determine what the sample's unique physical properties are.
Also, as a measurement technique, electron microscopy requires skillful techniques for cutting out the surface and optimizing the observation conditions. On the other hand, laser microscopes can be used more universally than electron microscopes because there is no accumulation of electric charge and the surface cutout does not require precision.
Confocal laser microscopes can measure the roughness of a sample surface in a non-contact manner. Although atomic force microscopy is the most common method for measuring the roughness of a sample surface, confocal laser microscopy has the advantage of non-contact measurement. Conversely, the resolution differs from that of the atomic force microscope, so the appropriate instrument should be selected depending on the roughness of the sample surface.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

SOL Instruments, founded in 1989, is a manufacturer of advanced instruments based in Germany. The company primarily manufactures optical and photometric measurements and related products. One sample product is its Confocal Raman Microscope. This cutting-edge product is an invaluable tool for materials science, chemistry, and biology researchers. These instruments enable high-resolution, non-destructive analysis of sample composition. Additionally, the company provides customized solutions for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to develop specialized instruments based on specific customer requirements. The company caters to the scientific community and various industrial sectors such as chemical, pharmaceutical, environmental monitoring, and manufacturing.

Ushio Inc., established in 1964 in Tokyo, Japan, is a manufacturer and supplier of specialized light sources, with a particular interest in ultraviolet (UV) and visible light. The company boasts an extensive product portfolio that includes various lighting solutions, including laser diodes, UV lamps, visible lights, lamps designed for projectors, and halogen lamps. These diverse products cater to a wide array of industries and applications, including architecture and landscape illumination, disinfection and deodorizing, litho-patterning, optical systems, as well as curing and bonding processes.

Becker & Hickl GmbH, headquartered in Berlin, Germany, has been a manufacturer of time-correlated single-photon counting (TCSPC) electronics and systems since 1993. The company offers various products, including TCSPC electronics, pulsed lasers, detectors, laser scanning FLIM microscopes, and related components. These products cater to professionals and researchers working in time-resolved fluorescence and associated fields, where precision and accuracy are paramount. Its flagship product is the TCSPC photon counting modules and systems, designed for precision time-resolved measurements in various scientific and industrial applications.

ZEISS Microscopy, established in Jena, Germany, in 1846 is a manufacturer of optics and optoelectronics used in Precision Mechanics, Binoculars, Microscopy, and Eyeglass Lenses. Their product portfolio includes precision optics, such as lenses, mirrors, and prisms, laser mirrors used in laser cutting, and medical devices, optoelectronic devices and Coatings and Thin Films. The company also provides solutions including industrial quality, microscopy research, project simulation, sample testing and product development. The company also offers customer services that include support, custom research projects and customized services.

Lasertec Corporation, founded in 1960 and headquartered in Yokohama, Japan, is a manufacturer and supplier of semiconductor-related systems, FPD-related systems, and laser microscopes. The company's product portfolio includes mask inspection systems, mask edge inspection systems, FPD photomask inspection systems, laser microscopes, and lithium-ion batteries. These products find applications in various sectors, including materials science, the flat panel display industry, semiconductor manufacturing, biomedical and life sciences, as well as research and development. The company is ISO 45001 and ISO 9001 certified, with offices in the USA, China, Singapore, Taiwan, and South Korea for global outreach.

HÜBNER Photonics is a manufacturer of high performance laser and photonics products, including single-frequency lasers, diode laser modules, tunable lasers, and fiber-coupled laser diodes. These products are used in a variety of applications, including spectroscopy, metrology, sensing, and microscopy.


BestScope, established in 1998 and based in Beijing, China, is a manufacturer and supplier of microscopes and cameras for the industrial sector. The company primarily produces its Catchbest brand industrial cameras for industrial imaging and process inspection applications. It also offers biological microscopes for medical as well as biological R&D, and LCD digital microscopes equipped with digital displays for use in educational institutions. The company chiefly serves clients in the industrial, educational, and laboratory research sectors.

Nano Instruments Ltd. is a supplier and distributor of scientific instruments based in Israel. The company specializes in importing, marketing, and servicing scientific instruments, research and development tools, failure analysis equipment, and production systems. It represents global manufacturers and offers comprehensive technological solutions to various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, chemistry, physics, and polymers. Its technological offerings include Raman and infra-red microscopes, atomic force microscopes, optical profilers, two-photon laser scanning microscopes, and dynamic light scattering instruments.


Evident Corporation is a scientific research and development company in Shinjuku, Tokyo that was established in 2008. Formerly known as Olympus Scientific Solutions, the company specializes in developing cutting-edge technology and products for various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, energy, and medical research. Evident Corporation has proliferated and expanded its product offerings and services to meet the needs of its customers. Their product offerings include non-destructive testing (NDT) solutions such as thickness gauges and automated inspection systems, XRF analyzers like handheld XRF analyzers, industrial microscopes, and video scopes and borescopes.

TCK inc, founded in Japan in 2005, is a supplier of semiconductor related devices. The company's product portfolio includes precision machines, information industry machines, piezoelectric actuator mechanisms, piezoelectric actuator mechanisms, and particle beam imaging systems. It also provides services such as Equipment Calibration Services, Preventive Maintenance Programs, Repair and Equipment Upgrades, and Retrofits. it serves markets like Automotive and Transportation, Aerospace and Defense, Medical Devices and Healthcare, and Energy and Renewable Energy.
Ranking as of March 2026
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heidelberg Engineering Inc. |
16.7%
|
| 2 | HÜBNER Photonics |
9.3%
|
| 3 | SOL instruments |
9.3%
|
| 4 | Holmarc Opto-Mechatronics Ltd. |
9.3%
|
| 5 | Lasertec Corporation |
9.3%
|
| 6 | Becker & Hickl GmbH |
7.4%
|
| 7 | Toray Research Center, Inc. |
6.5%
|
| 8 | Ushio Inc. |
6.5%
|
| 9 | Nano Instruments Ltd. |
5.6%
|
| 10 | ZEISS Microscopy |
5.6%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the laser microscope page as of March 2026. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 Japan
Japan
|
4 | 44.4% |
 Germany
Germany
|
2 | 22.2% |
| Deutschland | 1 | 11.1% |
 China
China
|
1 | 11.1% |
 Israel
Israel
|
1 | 11.1% |
28 products found
28 products
Nakayama Electric Co., Ltd.
900+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
3D observation of opaque materials and parts, which was previously possible, is now possible. Realizes “3D observation” and “digitization” of inte...
Advanced Technology Research Institute Ltd.
680+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
■Summary The newly developed laser phase contrast microscope differs from the conventional Zernike phase contrast microscope in that it can not onl...
Omega Wave
610+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
The laser (tissue) blood flow meter OMEGAFLO is a device that can continuously measure tissue blood flow, tissue blood volume, and blood flow veloc...
Photoscience Co., Ltd.
1150+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Summary CARS (Coherent anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) CARS microscope system uses two pulsed lasers with different wavelengths to intersect within ...
Cosmo Trading Co., Ltd.
1300+ people viewing
Last viewed: 14 hours ago
Six functions to meet diverse needs. Based on two confocal optical systems, it is equipped with six functions: differential interference observatio...
Kitano Seiki Co., Ltd.
670+ people viewing
Last viewed: 22 hours ago
■Features This device is an observation and inspection device that uses a scanning laser microscope to observe changes in the behavior of samples i...
Oxford Instruments Ltd.
820+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Easily start Raman – upgrade to full system possible ・A system that can perform spot Raman spectrum measurement and Raman mapping. Although the p...
Vuor Imaging Co., Ltd.
690+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
This is a thermography microscope that achieves a long imaging distance with micron-level resolution. Infrared microscope systems that capture ther...
ULVAC Sales Co., Ltd.
910+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■Summary The world's best Raman imaging now comes with innovative usability. Raman spectroscopy has evolved to this point. Nanophoton's laser Rama...
Cosmo Trading Co., Ltd.
940+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
This is a Raman microscope equipped with a 300mm wafer stage. It is also possible to read coordinate data obtained by foreign object/defect inspect...
Cosmo Trading Co., Ltd.
1100+ people viewing
Last viewed: 17 hours ago
Nanophoton Raman microscopes have evolved to perfect resolution. Achieving the world's fastest and highest quality Raman imaging. The world's fast...
Oxford Instruments Ltd.
850+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Next generation alpha300apyron – Experience a new level of automation The alpha300apyron is the highest-end Raman imaging system in the WITec micr...
Cosmo Trading Co., Ltd.
840+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
A completely new type of Raman for observing wide fields of view. Raman imaging can be performed over a maximum area of 2.5cm square. Equipped w...
Ryokosha Co., Ltd.
770+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 hours ago
■Summary Equipped with a 405nm laser, this model is capable of high-resolution 3D shape observation, measurement, and roughness measurement in minu...