











15 CT Scanner Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for ct scanners as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 15 ct scanner manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked ct scanner companies as of July, 2024: 1.NeuroLogica Corp., 2.Ryoei USA, 3.PRIZMED IMAGING SOLUTIONS CORP..
Table of Contents
1987~1991: Engaged in research on wire covering materials at Polymer Materials Laboratory.
1991~1997: Worked as a patent Engineer at Koike International Patent Office.
1997~2005 Worked as an intellectual property member at GE Yokogawa Medical System, currently working as a writer.
Linkedinhttps://www.linkedin.com/in/%E8%A3%95%E5%AD%90-%E9%88%B4%E6%9C%A8-92b21a234/
researchmap
https://researchmap.jp/0315rs2017
What Is a CT Scanner?
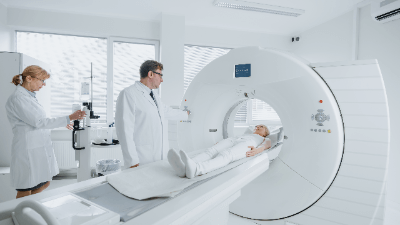 A CT (Computed Tomography) Scanner is a scanner used for inspection.
A CT (Computed Tomography) Scanner is a scanner used for inspection.
There are two main types of CT Scanners: Medical CT Scanners used for imaging the human body and animals, and Industrial CT Scanners used for non-destructive testing and shipping inspection of products.
Uses of CT Scanners
CT scanners are used in the medical field to diagnose abnormalities in the brain and lungs.
In the industrial field, they are commonly used to detect the internal structure of products to measure the internal dimensions of wiring, to elucidate the internal state of forged products, to measure errors, and to detect the alignment of fibers.
When used in the medical field, X-ray output must be suppressed to avoid excessive exposure to radiation, but when used for industrial applications, X-ray output can be increased without any problem, thus enabling information to be obtained with higher precision than in medical applications.
Principle of CT Scanners
The principle of a CT scanner is similar to that of an X-ray. They consist of an X-ray irradiator, a detector, and an image processor that converts the detected data into an image.
Since each material absorbs X-rays differently (X-ray absorption coefficient), when X-rays are irradiated to an object to be examined, they penetrate at different rates of transmission depending on the material. Using this principle, we irradiate an object to be inspected with X-rays and detect the different transmission doses for each part of the object to be inspected. The general principle is to create an image by image processing based on this detection data.
The major difference between X-rays and CT scanners is that X-rays are irradiated from one direction on the specimen, while CT scanners irradiate X-rays from various directions on the specimen. For this reason, X-rays produce only flat images based on two-dimensional data, while a CT scanner uses three-dimensional data to produce a series of images of the specimen sliced in a circle at multiple locations, as well as images and movies that are composed in three dimensions.
Two physical phenomena are used in CT scanner produced scans: Compton scattering and the Photoelectric effect.
1. Compton Scattering
This occurs when X-rays collide with electrons, imparting some of the energy of the X-rays to the electrons, causing them to be blown out of their atomic orbits and reducing the energy of the X-rays.
2. Photoelectric Effect
This occurs when X-rays collide with electrons and all the energy of the X-rays is absorbed by the electrons, causing the electrons to be blown away from their atomic orbits and the X-rays to disappear.
Differences Between CT Scanners
There are two main types of CT Scanner applications: medical and industrial. The differences between them are explained from the following perspectives:
1. X-Ray Output
Medical CT scanners need to suppress X-ray output to avoid excessive exposure. On the other hand, industrial CT scanners can use relatively high X-ray output because the object to be inspected is an object, and thus can obtain highly accurate information.
2. Configuration
Medical CT Scanner
A medical CT scanner consists of a doughnut-shaped gantry in which an X-ray irradiator and a detector are placed relative to each other. The gantry has a bed-like part on which the object to be examined is placed within the ring of the gantry. The gantry rotates around the bed, and the X-ray irradiator and detector rotate around the object to be inspected.
Industrial CT Scanner
In the industrial CT scanner, the X-ray irradiator and detector are fixed relative to each other, and the part to be inspected is placed between them. By rotating the part on which the object to be inspected is placed, the object itself is rotated for inspection.
Therefore, depending on the size of the object to be inspected, industrial CT scanners can be made smaller.
Industrial CT scanners are equipped with an X-ray leakage cabinet to confine X-rays inside the device, which also makes it possible to reduce the size of the scanner.
In both medical and industrial CT scanners, there are two types: one with a single row of detectors along the X-ray transmission plane in the width direction of the object to be inspected, and the other with multiple rows of detectors along the length direction of the object to be inspected.
The one with multiple rows of detectors can acquire data for each row at a time, which makes it possible to acquire data faster than the one with only one row.
In the case of industrial CT scanners, multiple-row CT Scanners are more suitable because efficiency is more important. Medical CT scanners are also often used because the faster the examination can be completed, the less burden is placed on the patient.
Other Information on CT Scanners
1. The Relationship Between CT Scanners and Cancer
CT scans are widely used for everything from examination to diagnosis and even medical treatment, although the image of CT scans is that they are used to find cancer. Although, there is a risk of cancer from CT scans, and it is necessary to fully understand the risks when CT scans are performed.
A CT scanner is an important device in medicine, but it is not without risks of causing cancer because of the x-ray irradiation.
The risk of developing cancer from a single CT scan is considered low, and the risk of not undergoing a CT scan is much higher than the risk of undergoing a CT scan.
2. Difference Between CT and MRI
The main difference between CT and MRI is the principle of measurement.
CT scanners form images based on differences in the transmission of X-rays through different materials, as described above, whereas MRI creates images based on the magnetic resonance of materials. CT scanners have the advantage of short acquisition times and the ease of obtaining tomographic images, and are more indicated for emergency head lesions (such as suspected hemorrhage). and the ability to image bone.
On the other hand, MRI is inferior to CT in terms of radiation exposure and differences in density between lesions and normal tissue.
Another advantage is that any tomographic image can be obtained, and images of blood vessels can be obtained without the use of contrast media. The disadvantage, on the other hand, is that those with implanted devices in the body cannot be examined.
List of 15 CT Scanner Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- China
- Czech Republic
- Deutschland
- Germany
- Japan
-
-

-
North Star Imaging Inc.
X-ray CT Systems
Manufacturer Overview
North Star Imaging Inc., founded in 1986 and based in Rogers, USA, is a manufacturer of industrial X-ray systems non-destructive testing (NDT) equipment. The company designs and manufactures 2D digital radiography & 3D computed tomography systems. These products are frequently used for failure analysis, Quality Control and internal measurements. This technology is used by many different markets including medical devices, electronics and aerospace. The company is ISO certified for its quality and environmental standards, and has ASNT & NAS 410 certified employees.
-
-
-
-

-
NeuroLogica Corp.
MOBILE CT
Manufacturer Overview
NeuroLogica Corp., founded in 2004 and headquartered in Danvers, Massachusetts, USA, is a manufacturer of modern medical equipment. The company specializes in the development and manufacturing of modern point-of-care Computed Tomography (CT) scanners. Its product line includes various CT scanners designed for medical facilities and private practices, providing advanced imaging solutions for enhanced diagnostic capabilities. The features of its scanners include precise-resolution imaging, portability, and efficient point-of-care diagnostics. These devices find application in various medical industries, resulting in improved patient care and diagnostic precision.
-
-
-
-

-
Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc.
CT Technologies & Innovations
Manufacturer Overview
Siemens Healthineers USA (formerly known as Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc.), founded in 1847 and a subsidiary of Siemens Healthineers, is a manufacturer based in Malvern, Pennsylvania, specializing in healthcare solutions and services. The company’s portfolio includes a range of medical and diagnostic imaging equipment and machinery. It also provides products and services for laboratory diagnostics, including assays, automation, testing systems, and educational resources. Moreover, the company offers therapeutic concepts and minimally invasive procedures for clinical conditions. The company also offers value partnerships, aiding enterprises in enhancing performance and achieving healthcare targets, along with consulting services facilitated by ECG Management Consultants.
-
-
-
-

-
Ryoei USA
CT scanner
Manufacturer Overview
RYOEI USA, established in 1973, is a manufacturer of die-casting machinery and custom equipment located in Indiana, USA. The company primarily produces die casting spray systems designed to meet diverse requirements and specifications. Its die casting solutions include its EcoShot Spray System, designed to improve efficiency and reduce pollution emissions, a robotic ladle that automates molten aluminum and magnesium pouring, and a robotic part extractor. The company also provides custom inspection and material handling systems, both of which come with full-service installation and integration support and support for ongoing maintenance and repairs.
-
-
-
-

-
PRIZMED IMAGING SOLUTIONS CORP.
CT SCANNERS
Distributor Overview
PrizMED Imaging Solutions, Inc., established in 1990, is a CT and MRI machine supplier headquartered in Highland, Ohio. The company serves the healthcare and medical imaging industries by providing computed tomography scanners and magnetic resonance imaging for hospitals, clinics, and private medical imaging centers. It stocks veterinary, whole-body, and cardiac CT scanners and MRI equipment, all of which are delivered and installed with one-on-one technical assistance and minimal prep work. The company also offers various service plans to provide ongoing maintenance support.
-
-
-
-

-
ZEISS Microscopy
Industrial CT- and X-Ray Solutions
Manufacturer Overview
ZEISS Microscopy, established in Jena, Germany, in 1846 is a manufacturer of optics and optoelectronics used in Precision Mechanics, Binoculars, Microscopy, and Eyeglass Lenses. Their product portfolio includes precision optics, such as lenses, mirrors, and prisms, laser mirrors used in laser cutting, and medical devices, optoelectronic devices and Coatings and Thin Films. The company also provides solutions including industrial quality, microscopy research, project simulation, sample testing and product development. The company also offers customer services that include support, custom research projects and customized services.
-
-
-
-

-
TESCAN
micro-CT
Manufacturer Overview
TESCAN, established in 1991 with headquarters in the Czech Republic, is a manufacturer of SEM (scanning electron microscopes). The company's products include gallium ion and xenon ion plasma FIB SEM, 4D-STEM (scanning transmission electron microscopy) systems, and micro-CT 3D and 4D scanners. The company's products are used to facilitate image acquisition, reconstruction, visualization, quantification, and analysis of microscopic samples in the materials science, life sciences, earth sciences, and semiconductor markets among others.
-
-
-
-

-
YXLON International
CT metrology
Manufacturer Overview
Building on decades of experience and an unfailing passion for technology, Comet Yxlon is a globally leading company for industrial X-ray and CT system solutions with integrated services for industrial environments – from R&D labs to production settings. Comet Yxlon supplies tailored service solutions for a wide range of production environments through offline applications, at-line scenarios, or in-line implementation, and their diverse field of quality assurance and quality control. With inspection systems that help manufacturers and developers control product quality, their specialized systems are used in the most diverse areas such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, science & research, and many more.
-
-
-
-

-
Toshiba IT & Control Systems Corporation
TXScanner
Manufacturer Overview
Toshiba IT and Control Systems Corporation, established in 1983, and based in Tokyo, Japan is a manufacturer and supplier of power electronics and inspection systems. The product portfolio includes power electronics, mechatronics, X-ray non-destructive inspection systems, control engineered systems, development design creation. The company also offers maintenance services and sales for industrial as well as public use. The products are used in many industries with various applications which include electronics, sensors, resins, chip-mounted boards, batteries, and other devices.
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
Baker Hughes Company
Radiographic Testing and Industrial CT Solutions
Manufacturer Overview
Baker Hughes Co. (BHC) is an American service provider and manufacturer of industrial oilfield equipment that was established in 1987 following the merger of Baker International and Hughes Tool Company. Based in Houston, Texas, the company produces several categories of oilfield products including drilling equipment, pipe and subsea production systems, generators, and storage systems. It also offers process control components and actuators such as pumps, valves and regulators. BHC provides various services for oilfield and liquefied natural gas (LNG) operations, including regasification, well construction, transportation, and storage.
-
-
-
-

-
Omron
PCB Inspection System
Manufacturer Overview
Omron Corporation, started in 1933 and headquartered in Kyoto, Japan, is a manufacturer of automation components, equipment, and systems, and it developed the first contactless proximity switch in 1960. It has four domains, including industrial automation, electronic components, healthcare, and social systems, and it provides products and services in around 120 countries and regions. Some of its products include microsensing devices, access control systems, industrial robots, surveillance cameras, and blood pressure monitors. In 1971, it developed the first online cash machine, and in 1972, it established Japan’s first welfare factory.
-
-
-
-

-
DirectMed Parts & Service, LLC
MRI&CT Service
Manufacturer Overview
DirectMed Parts & Service, LLC was established in 2011 and is based in San Diego, California as a manufacturer and supplier of medical devices and health equipment. The company specializes in the design, repair, and distribution of parts and medical devices for healthcare professions. Their portfolio includes GE, Siemens, and Philips parts to healthcare networks, imaging centers and independent service organizations around the world. With a customer centric approach the company offers comprehensive solutions to healthcare providers extending the lifespan of medical devices while minimizing the costs.
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
WENZEL Group
exaCT series
Company Overview
WENZEL Group, founded in 1968 and headquartered in Wiesthal, Bayern, Germany, is a manufacturer of industrial metrology and styling solutions. The company offers a range of products, including coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), gear measuring machines, optical high-speed scanning systems, 3D X-ray measuring technology via computer tomography, and multi-sensor systems. These tools cater to diverse industries such as automotive, aircraft, mechanical engineering, and medical technology for precise measurement and analysis. It holds ISO 9001 and VDA 6.4 certifications for its quality management system, alongside accreditation confirming competence in dimensional measurands as per DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2018 standards.
-
-
CT Scanner Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of July 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | NeuroLogica Corp. |
22.1%
|
| 2 | Ryoei USA |
13.8%
|
| 3 | PRIZMED IMAGING SOLUTIONS CORP. |
10.9%
|
| 4 | North Star Imaging Inc. |
7.9%
|
| 5 | Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc. |
7.2%
|
| 6 | Omron |
7.1%
|
| 7 | YXLON International |
5.5%
|
| 8 | DirectMed Parts & Service, LLC |
5.2%
|
| 9 | Shimadzu Seisakusho Co., Ltd. |
4.4%
|
| 10 | Toshiba IT & Control Systems Corporation |
4.2%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the ct scanner page as of July 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
- ZEISS Microscopy: 35,000
- Shimadzu Seisakusho Co., Ltd.: 13,499
- YXLON International: 400
Newly Established Company
- Sanying Precision Instruments Co.,Ltd: 2013 (11 years ago)
- NeuroLogica Corp.: 2004 (20 years ago)
- YXLON International: 1998 (26 years ago)
Company with a History
- ZEISS Microscopy: 1846 (178 years ago)
- Shimadzu Seisakusho Co., Ltd.: 1875 (149 years ago)
- WENZEL Group: 1968 (56 years ago)
CT Scanner Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
- North Star Imaging Inc.
- NeuroLogica Corp.
- Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc.
- Ryoei USA
- PRIZMED IMAGING SOLUTIONS CORP.
Global Distribution of CT Scanner Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
5 | 41.7% |
 Germany
Germany
|
2 | 16.7% |
 Japan
Japan
|
2 | 16.7% |
| Deutschland | 1 | 8.3% |
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
|
1 | 8.3% |
 China
China
|
1 | 8.3% |
List of CT Scanner Products
6 products are listed.
Japan Equipment Development
High -speed X -ray CT scanner CTH320/300μFPD
50+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
Large/high -speed dual X -ray CT scanner/CT innovation Feature ・ Compatible with three -dimensional electronic components ・ Large mechanical part...
Tanida
X-ray CT Scanning can also be used for internal analysis X-ray ct scanning y.ct compact
30+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
A mini -focus X -ray CT system that is ideal for large work inspections. It corresponds to the thickness of 65mm for iron and 250mm for aluminum. S...
Japan Equipment Development
High -speed X -ray CT scanner CTH200FPD
20+ people viewing
High-speed X-ray CT scanner (industrial high-speed X-ray inspection device) /HIGH-SPEED X-RAYS CT Scanner Feature ・ Supporting three -dimensional...
Japan Equipment Development
High -speed X -ray CT scanner CTH150μFPD
20+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
Micro Focus High Speed X-ray CT Scanner/High-Speed X-Rays CT Scanner Feature ・ Compatible with three -dimensional electronic components and me...
Japan Equipment Development
High -speed X -ray CT scanner CTV110μFPD
20+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
High-speed X-ray CT scanner (industrial high-speed X-ray inspection device) /HIGH-SPEED X-RAYS CT Scanner Feature ・ Board electronics parts compa...





