All Categories
History








This section provides an overview for survey meters as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 8 survey meter manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked survey meter companies as of March, 2026: 1.Industrial Nuclear Co, INC., 2.Berkeley Nucleonics Corporation, 3.FLUKE Corporation.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Survey Meters
1975~1995: Worked at Hitachi, Ltd.
Engaged in research on the irradiation effects of nuclear reactor materials at the Energy Research Institute.
Received the Japan-American Atomic Energy Society Award for his research achievements.
1996~2015,
Engaged in soft error research caused by environmental neutron beams in semiconductor devices at the Institute of Industrial Science.
Research achievements: Awarded the IEEE Fellow and the Teiichi Yamazaki Award.
Currently active as a writer.
Survey Meter is a portable and simple radiation measuring instrument used to measure the dose rate in the air or the amount of radioactivity (surface contamination) on workers' clothing in facilities where radiation or radioisotopes are handled.
Radiation includes, in order of penetrating power, neutrons, gamma rays, X-rays, beta (beta) rays, alpha (alpha) rays, and charged particle rays. The order of penetrating power depends not only on the type of radiation but also on its energy. The choice of the measuring instrument depends on the purpose, such as measuring the type and amount of radioactive materials or measuring the radiation dose.
Monitoring posts are installed in the vicinity of nuclear facilities and at designated points in each prefecture. Monitoring posts measure the amount of radioactive dust by measuring β-rays from radioactive dust adhering to air dose rate meters and dust monitors in order to monitor the leakage of radioactive materials (dust, etc.).
Scintillation survey meters with high sensitivity to γ-rays are most suitable for measurement in areas with low dose rates, such as urban areas. Measurement of radiation dose is legally required for radiation workers, and personal dosimeters such as film badges and TLD dosimeters (thermoluminescence dosimeters) are mainly used.
Surface contamination is often measured using GM counter tube survey meters, which measure β-rays, scintillator survey meters, which measure α-rays, and proportional counter tube survey meters, which measure both α- and β-rays.
The standard values for radioactive contamination in food are extremely small, and a combination of a high-sensitivity germanium semiconductor detector or scintillation detector and an analyzer is used.
The basic atoms of a survey meter differ depending on the model (GM coefficient tube, ionization chamber, or scintillation type) and the type of radiation (especially neutron radiation).
As shown in Figure 1, a cylindrical detector is filled with an inert gas such as helium or argon, and a high DC voltage is applied between the central anode and the surrounding cathode. γ (X) rays can be ionized via electrons generated inside the detector by reaction with the cathode material, while α and β rays can ionize gas directly. The number of pulses from the discharge triggered by ionization can be used to measure the air dose rate, and the effective dose rate of about 0.1 μSv/h to 10 Sv/h can be obtained from the number of pulses counted in one minute.
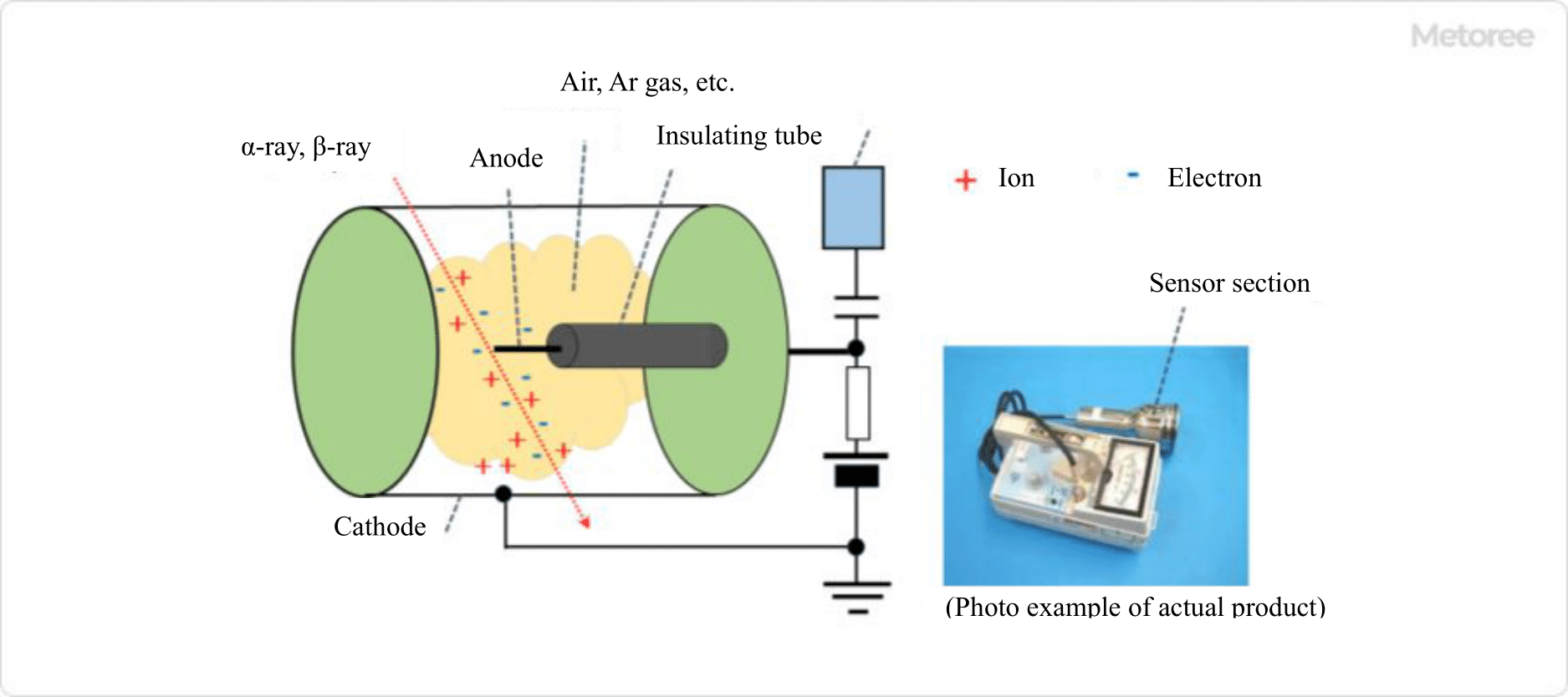
Figure 1. Basic structure and measurement principle of a GM-tube survey meter
An ionization chamber detector has the same structure as a GM-tube survey meter, with the detector filled with air or argon. When radiation strikes the detector, the air is ionized into cations and electrons, and the ionization chamber survey meter displays the minute current that flows between the electrodes. Ionization chamber survey meters are suitable for measuring β- and γ-rays and low-energy X-rays, and can measure effective dose rates in the range of 1 μSv/h to 5 Sv/h, depending on the model.
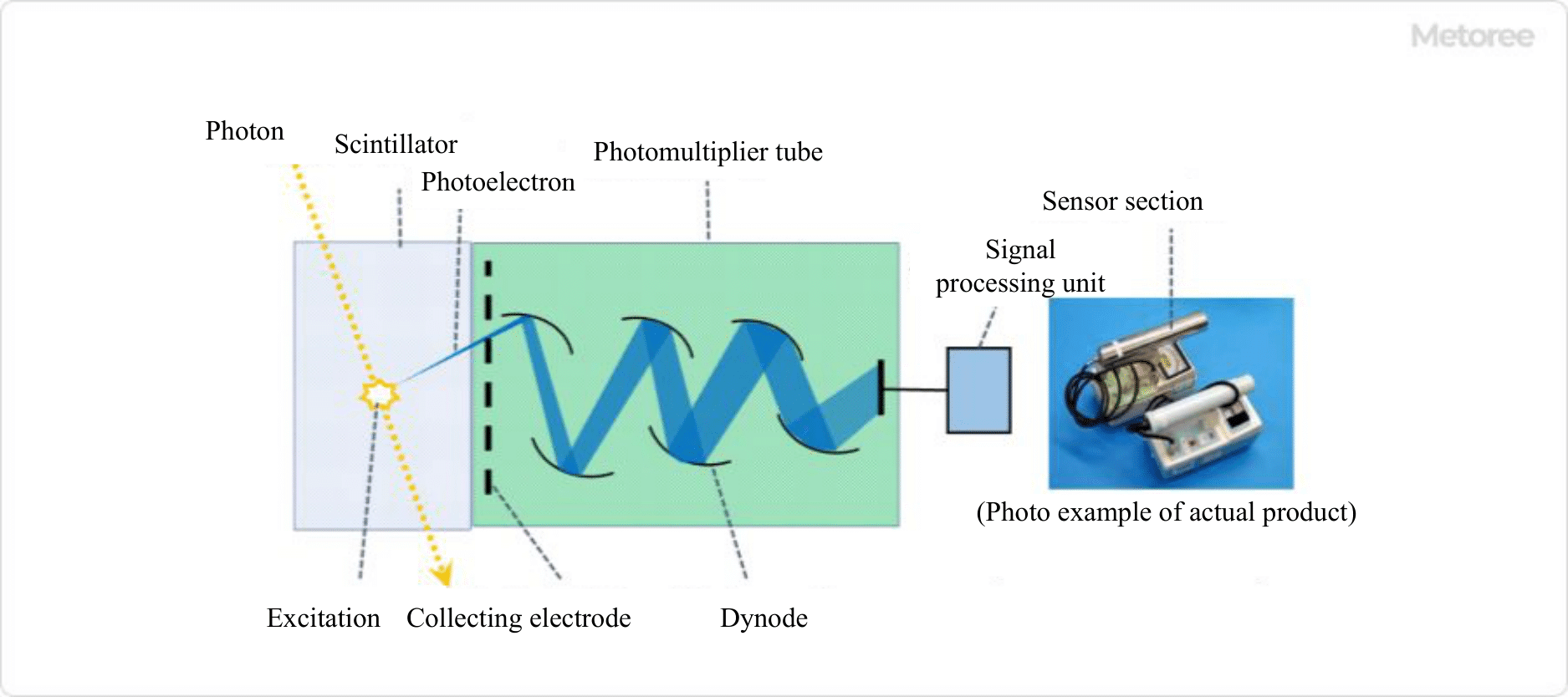
Figure 2. Basic structure and measurement principle of a scintillation survey meter
A scintillation survey meter consists of a scintillator and a photomultiplier tube as shown in Figure 2. When radiation strikes the scintillator, the crystalline material of the scintillator is excited by the photoelectric effect and other effects.
The photomultiplier tube converts the faint light generated when the scintillator returns to the ground state into an electric current, amplifies it, and counts the resulting pulsed current. Scintillators for γ (X) rays are highly sensitive and suitable for low-level radiation measurements in general environments.
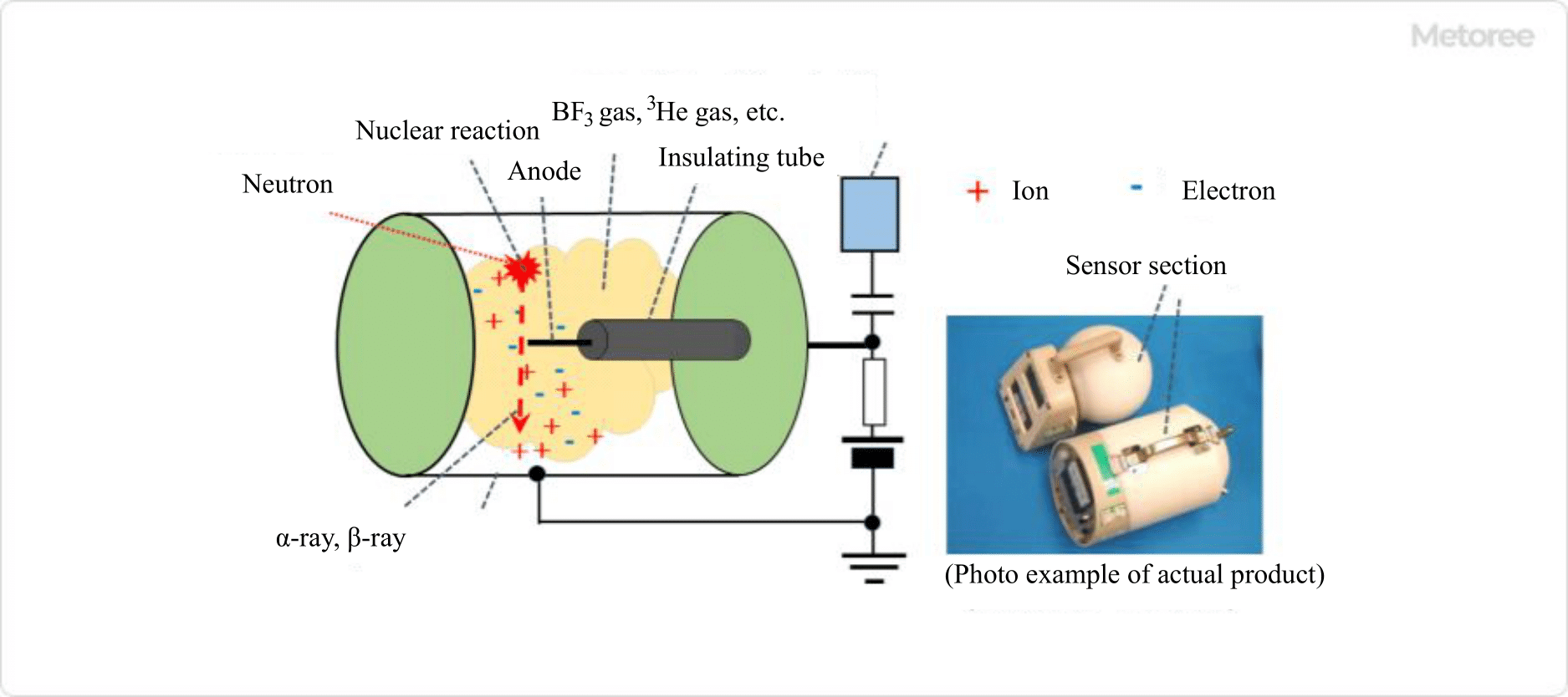
Figure 3. Basic structure and principle of a survey meter for neutrons
As a neutron survey meter, BF3 or 3He gas is filled into a detector consisting of a cathode and anode as shown in Figure 3, and α-rays and protons (p) produced by the nuclear reaction of 10B(n,α)9Li and 3He(n,p)3H are measured using the same principle as in an ionization chamber. Neutron energy ranges from thermal neutrons (0.025eV) to fast neutrons (10MeV). The effective dose rate is considered to be in the range of 0.01 μSv/h to 0.01 mSv/h.
Some detectors are spherical, usually called Bonner balls. By using multiple spheres of different sizes, the neutron energy spectrum (intensity distribution) can be obtained.
Integral dosimeters, such as film badges and TLD dosimeters, are used as personal radiation dosimeters. Film badges are based on the photosensitivity of photographic film to radiation and consist of a plastic case containing various filters and a small piece of film.
TLD dosimeters utilize the fluorescent properties of certain crystalline materials, such as CaSO4, which emit fluorescence in response to the amount of radiation received.
Radiation workers are required to ensure that their radiation dose does not exceed 100 mSv for five years and 50 mSv for one year. For women and pregnant women, lower limits are set by law. For the general public, the standard is 1 mSv or less per year of effective dose.
To obtain correct measurement results in environmental monitoring, periodic calibration (correction of deviations in indicated values), daily inspections, and bag-ground measurements should be performed to provide a guide in case of abnormalities or malfunctions. Cases of accidents involving radiation workers leading to serious fatalities have been reported in many countries around the world. Accidents at nuclear facilities and other facilities are caused by structural defects and deviations from worker procedures, and there is a need for safety management of facilities and adherence to worker procedures.
High-energy ion accelerators used for particle physics research can also be used as a high-energy neutron source by injecting protons into targets such as W (tungsten) or Li (lithium). LINAC (linear electron accelerator), etc., are used for tire hardening and treatment.
Alpha-ray sources such as 241Am (americium) are used to evaluate alpha-ray soft errors (reversal of 1, 0 data) in semiconductor devices. γ-ray irradiation equipment using 60Co (cobalt), which is used for sterilization, prevention of potato germination, and various irradiation effect studies, requires radiation exposure control for workers and researchers.
The above research and testing facilities are usually classified as "controlled areas" under the "Law Concerning Regulation of Radioactive Isotopes, etc.", and radiation exposure and surface contamination of objects, workers, and researchers, as well as the carrying in and out of radioisotopes, are strictly controlled.
Low-energy neutrons are used in experimental reactors such as those at Kyoto University, MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), and the Halden reactor in Norway to treat brain tumors. In this process, living organisms and surrounding equipment may be activated.
On the other hand, commercial nuclear reactors in normal operation are required to have a periodic inspection of the reactor building and equipment approximately once a year. During the inspection, the reactor is shut down and there are no neutron rays. On the other hand, in an operating reactor core, radioactive isotopes such as 60Co are produced by the activation of structural materials and other materials.
Radioactive materials dissolve in the reactor coolant and are absorbed by the inner surface of the reactor cooling system piping, causing external radiation exposure to workers. When disassembling and repairing equipment, surface contamination must also be taken into consideration, so a survey meter is a must-have item during work.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Berkeley Nucleonics Corporation, San Rafael, CA, in 1963 is a manufacturer of Test, Measurement, Nuclear and Life Sciences instrumentation. The company's product portfolio includes Digital Delay Generators, RF & Microwave Signal Generators, and Nuclear Radiation Detectors and Isotope Identification. Their products are used in industries such as Food and Beverage Processing, Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology and Chemical and Petrochemical. The company also provides services including national distribution, product selection, installation, preventative maintenance, troubleshooting, repair and customer service.

Industrial Nuclear Co, INC. is a manufacturer of industrial gamma radiography equipment and radioactive sources headquartered in San Leandro, California, and was founded in 1972. The company offers varied models and product catalogs from its solution including Gamma Radiation Monitors Model-P, LED high-intensity film viewers, Radiation Beacon Model-L, Rad Survey Meters- Model 4, 2S, 2D, and Gamma Radiation Projection devices. The company also manufactures accessories including penetrometers and shims, barricade tapes and ropes, swivel clamps and source strands, and dosimeters. The industries served by the company are usually in the Oil and Gas market.


Arrow-Tech, Inc. is headquartered in Rolla, North Dakota, and has been a manufacturer of direct-reading dosimeters since its establishment in 1982. The dosimeters, which are manufactured to ANSI standards, provides solutions for immediate and accurate dose measurements of Gamma and X-ray radiation. The company also manufactures and distributes radiation related detection products such as emergency response kits, survey meters, and area monitors which find ideal applications in radiology departments in the medical settings.

Ludlum Measurements, Inc., founded in Sweetwater, TX in 1962 is a manufacturer of radiation detection instruments and technologies. The company's product portfolio includes Portable Survey Meters, Personal Radiation Meters, Benchtop Meters, Scalers / Counters and Pulsers. Their products are used are in applications such as routine personnel and material monitoring, border security, and emergency response situations. The company serves markets including Medical and Healthcare, Aerospace and Defense, Consumer Goods, Industrial Manufacturing and Construction and Building. The company also offers services including service repair and calibration, Training Courses, and a full list of product videos.

Headquartered in Everett, Washington, Fluke is an American-born company operating since 1948. Fluke offers a variety of testing equipment including digital multimeters, thermal cameras, solar PV testing equipment, thermometers, oscilloscopes, leak detection devices, as well as testing-equipment related accessories. Fluke offers direct online sales.

Mirion Technologies, Inc., established in 2005 and headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, USA, is a global service provider in radiation safety, science, and medicine. With a rich history dating back to its origins between 1950 and 2004, Mirion's journey has included expansion into healthcare and ongoing advancements in radiation safety technologies. The company’s products and services are aimed at protecting people and the planet from the harmful effects of ionizing radiation. With a diverse portfolio of products and services, Mirion serves across various end markets, from radiation detection and measurement to diagnostic imaging and radiation therapy and more.

Electronic & Engineering Co. (I) Pvt. Ltd. is a manufacturer of non-destructive testing products that is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, and was established in 1958. The company provides solutions for magnetic particle inspection, radiography testing, ultrasonic inspection, and eddy current inspection. Its product catalog includes ultrasonic flaw detectors, custom-made test systems, probes and accessories for standard and special ultrasonic equipment, and magnetic particle testing equipment. The industries served by the company are markets in steel, aerospace, automotive, railway, NDT service providers, and educational institutes.

Nuclear Shields B.V. | Radiation Shielding Manufacturers is a manufacturer of radiation shielding that is headquartered in Vortum-Mullem, Netherlands, and was founded in 1972. The company offers vial shields, syringe shields, cabinets, radiology, and storage. The company also provides equipment and service solutions through equipment ranging from Full CAD/CAM designs, CNC machines, 5-axis, milling, and turning. The company serves industries including medical, nuclear, industrial, and defense markets. The company also caters to lead weights, custom shielding, and imaging solutions.
Ranking as of March 2026
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Industrial Nuclear Co, INC. |
19.6%
|
| 2 | Berkeley Nucleonics Corporation |
12.9%
|
| 3 | FLUKE Corporation |
12.9%
|
| 4 | Electronic & Engineering Co. (I) Pvt. Ltd. |
11.3%
|
| 5 | Nuclear Shields B.V. | Radiation Shielding Manufacturers |
11.3%
|
| 6 | Arrow-Tech, Inc. |
11.3%
|
| 7 | Mirion Technologies, Inc. |
10.8%
|
| 8 | Ludlum Measurements, Inc. |
9.8%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the survey meter page as of March 2026. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
6 | 75.0% |
 India
India
|
1 | 12.5% |
 Netherlands
Netherlands
|
1 | 12.5% |
56 products found
56 products
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
500+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
This is an electronic pocket dosimeter that measures the cumulative radiation dose received by an individual. This is a device that measures person...
3 models listed
Japan Shielding Giken Co., Ltd.
630+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
Rolf -The standard radiation meter-Simplify radiation measurement work.That's the Rolf series. ■Points -The program supports two measurement metho...
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
750+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
It can handle a variety of isotopes handled at RI facilities such as medical institutions, research laboratories, and nuclear power plants. ・Smal...
Jpi Japan Co., Ltd.
420+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
Quart's dosimeters for diagnostic equipment and dosimeters for CT pursue high user convenience. Thanks to the manufacturer's specialized technology...
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
850+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
It can handle a variety of isotopes handled at RI facilities such as medical institutions, research laboratories, and nuclear power plants. ・Smal...
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
530+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
■Ideal measurement tool for basic radiation education Alpha-chan is a measuring device for α-rays, Beta-chan is a measuring device for β-rays. This...
2 models listed
Jpi Japan Co., Ltd.
390+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
Quart's dosimeters for diagnostic equipment and dosimeters for CT pursue high user convenience. Thanks to the manufacturer's specialized technology...
Jpi Japan Co., Ltd.
550+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
Quart's dosimeters for diagnostic equipment and dosimeters for CT pursue high user convenience. Thanks to the manufacturer's specialized technology...
Jpi Japan Co., Ltd.
460+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
Quart's dosimeters for diagnostic equipment and dosimeters for CT pursue high user convenience. Thanks to the manufacturer's specialized technology...
Berthold Japan Co., Ltd.
540+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
LB6414 is a new highly sensitive portable neutron survey meter used for plutonium contamination and nuclear waste surveys. A He-3 proportional coun...
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
590+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
It can handle a variety of isotopes handled at RI facilities such as medical institutions, research laboratories, and nuclear power plants. ・Smal...
Aynac System Co., Ltd.
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■The radiation dose measurement system proposed by Aynac System is in operation. This work involves constructing a temporary treatment facility wit...
Berthold Japan Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
This is a space-saving hand and foot cloth monitor designed with the installation area in mind. Hand detectors can be used as clothing detectors, r...
4 models listed
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
780+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
Ionization chamber type survey meter with excellent energy characteristics. Two modes of measurement are possible: 1cm dose equivalent rate and int...
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
520+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
This is a neutron survey meter that uses a highly sensitive 3He proportional counter. It is possible to measure neutrons from thermal neutrons to a...
Berthold Japan Co., Ltd.
400+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
The LB124SCINT series can distinguish between α and βγ rays and measure them at the same time. It is compact and lightweight, making it easy to han...
4 models listed
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
610+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
It employs a NaI (Tl) scintillation detector with high gamma-ray sensitivity, making it suitable for measuring changes in air dose rate from backgr...
SANKO ELECTRONIC LABORATORY CO.,LTD
350+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■ Features ・ Measure invisible radiation ・ Anyone can easily measure the spatial radiation dose
2 models listed
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
720+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
TGS-1146 is a β-ray survey meter that uses an end window type organic GM tube with a diameter of 50 mm. ・Improved visibility with 3.5-inch touch ...
Chiyoda Technol Co., Ltd.
610+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■A small dosimeter that records data and records. You can feel safe because you can check with your own eyes the cumulative dose for the previous d...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
550+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■Features - Data being measured can be stored in real time on an SD card (sold separately). ・Temperature can also be measured using a thermocouple...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
800+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
■Features - When radiation (gamma rays) is detected, a buzzer and detection mark will notify you. - A buzzer will notify you when the dose is high...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
520+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■Features - UVA/UVB measurement is possible. ・Highly accurate measurement is possible due to the zero adjustment function. -Data hold function mak...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
570+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■Features ・Can measure UVA and UVB. -Separate type sensor allows measurement even in remote locations. ■Specifications ・Resolution: 1・10μW/cm2 ...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
740+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
■Features - Equipped with a high-performance scintillator type sensor, enabling higher-grade measurements. - Quick measurements are possible just b...