











40 DC Servomotor Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for dc servomotors as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 40 dc servomotor manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked dc servomotor companies as of July, 2024: 1.ISL Products International., 2.esitron-electronic GmbH, 3.MOTOR POWER COMPANY.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to DC Servomotors
What Is a DC Servo Motor?
A DC Servomotor is a servomotor that operates on DC.
DC Servomotors are used in precision equipment, etc. Since DC Servomotors are controlled by detecting the motor's speed and position, they are generally integrated with a motor and a sensor that detects speed and position, such as an encoder or resolver. The motor is controlled by a sensor that detects the speed and position of the motor.
To rotate a DC motor, current supplied to the motor must be passed to the rotating shaft by a component called a brush, which wears out due to wear and tear on the brush, requiring periodic maintenance.
Uses of DC Servo Motors
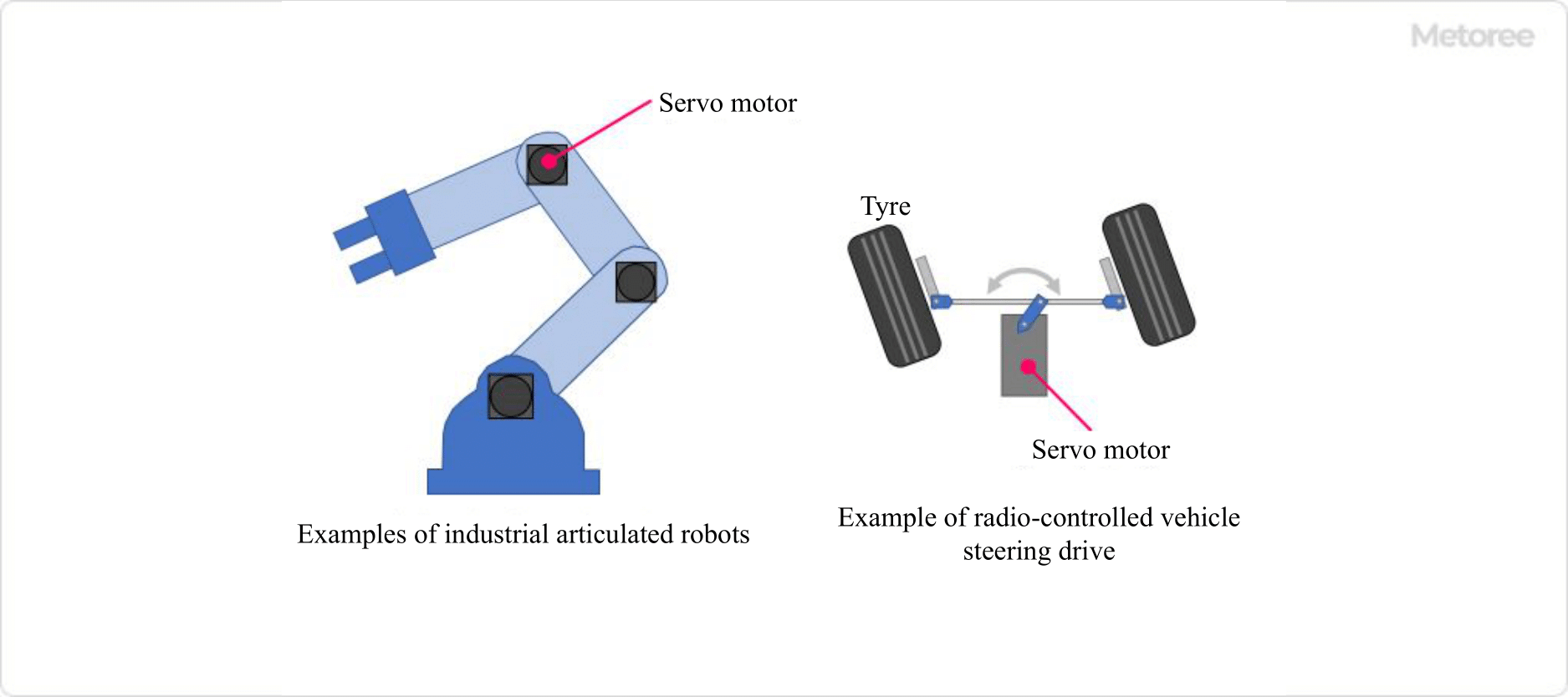
Figure 1. Uses of DC servo motors
DC servo motors are widely used in industrial robots that require precise control. Compared to general-purpose motors, DC servo motors respond more quickly to signals from robot controllers of industrial robots to output rotation speed and torque, and function as actuators for precise movement of robot arms and other parts.
DC servo motors are also used for the steering angle drive of radio-controlled vehicles, XYZ axis drive of machine tools, positioning drive of precision equipment, etc. It is important to select a DC servo motor appropriately according to the level of output and torque capacity, accuracy, and response speed required by the equipment to be used.
Principle of DC Servo Motor
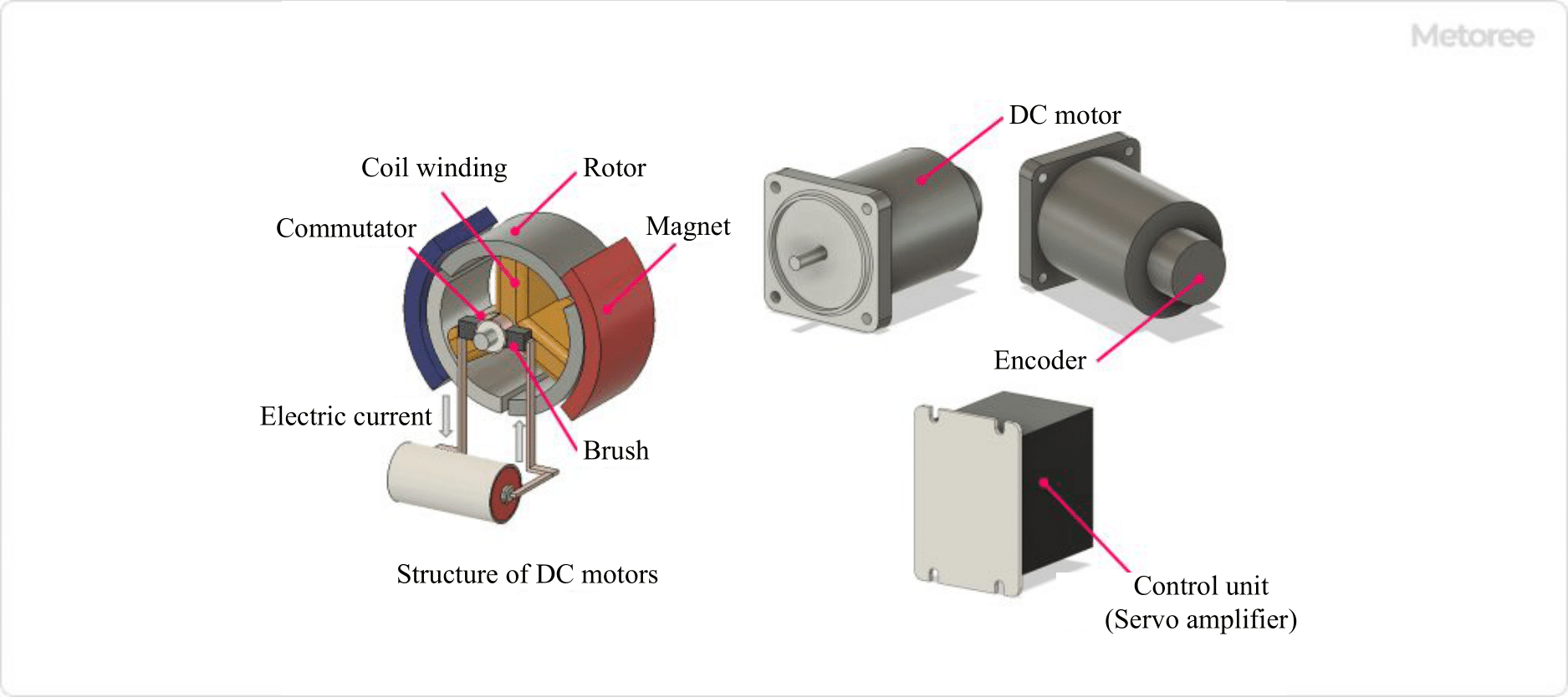
Figure 2. Principle of DC servo motors
A DC servo motor consists of a "motor," an "encoder," and a "controller." It is composed of a permanent magnet, an iron core (rotor) divided into two or more parts, coils wound around each iron core, electrodes, and brushes that pass current through the coils.
The principle of operation of a DC servo motor is explained separately for the motor and other functions.
1. Motor
The motor is made to rotate by the Lorentz force generated from two sources: the current flowing in the coil and the magnetic field from the permanent magnet, which causes the iron core to rotate. When applying current to the coils, direct current from the outside is passed through brushes to the iron core and then transmitted to the coils. Since the current is passed directly to the coil, the Lorentz force can be quickly controlled and the response speed is fast.
2. Other Functions
DC servo motors use command signals transmitted from an external controller to rotate the motor to achieve a commanded target value. The encoder attached to the motor sends speed and position information to the controller, which performs feedback control based on the position and speed information from the encoder in response to commands sent from the controller so that the motor's rotation speed and rotation position approach the target values.
Control of DC Servo Motor
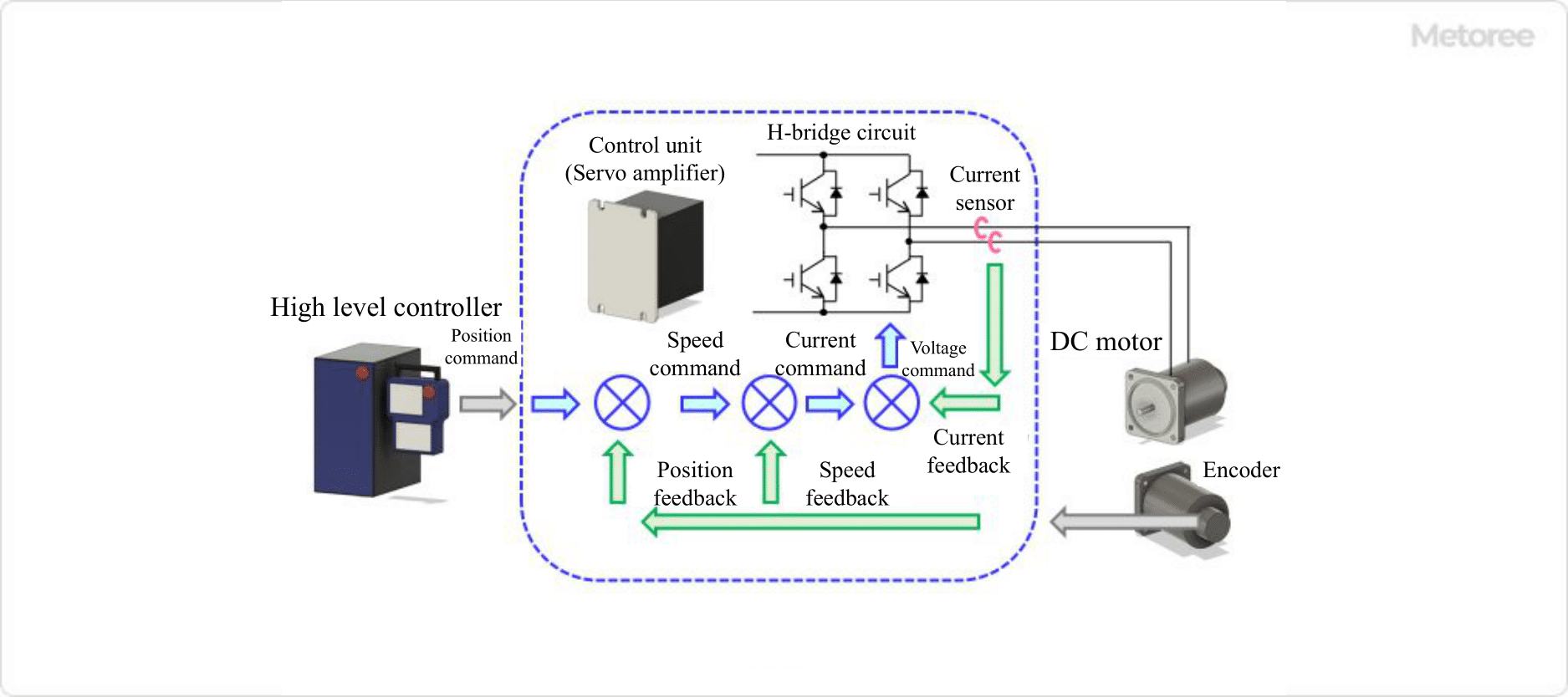
Figure 3. Control of DC servo motors
DC servo motors can be controlled in the following three ways
1. Position Control
DC servo motors are equipped with an encoder, a sensor that detects rotation angle and position and feeds back the detected rotation speed and position to the controller. If a position deviation from the command position is detected, a position correction command is issued by applying a gain to the amount of deviation to enable highly accurate control that moves the motor to the desired position and then stops the motor.
2. Speed Control
The simplest way to control the speed of a DC motor is to vary the voltage applied to the motor. In the case of a DC servo motor, a variable resistor is used to control the speed of the motor.
For DC servo motors, instead of a variable resistor, the voltage applied to the motor is controlled via an H-bridge composed of power semiconductors such as IGBTs and FETs that are incorporated in the servo amplifier.
On the other hand, the speed control of AC motors requires changing not only the voltage applied to the motor but also the drive frequency, whereas DC motors are widely used in small motors for speed control because they only change the voltage.
3. Torque Control
Torque control of the DC Servomotor is based on the proportional relationship between current and torque. Therefore, the current is controlled to maintain the torque at a constant value by detecting the current from the voltage value of the current sensor or current shunt resistor and feeding back the current command.
Other Information on DC Servomotor
Types of Servo Motors
Servomotors are constructed to be more durable than ordinary motors to operate repeatedly even in harsh environments and can be broadly classified into two types: DC Servomotors and AC Servomotors.
1. DC Servo Motor
DC Servomotor is a servomotor driven by a DC power supply. DC Servomotor is used in a wide variety of applications because it is easier to control rotation and more efficient than AC Servomotor, and its simple mechanical structure makes it inexpensive. However, the disadvantage of DC servomotors is that they have mechanical wear parts called "brushes" that require periodic replacement and maintenance.
2. AC Servo Motor
AC Servomotors are servo motors driven by an AC power source. Compared to DC motors, AC Servomotors are more complicated to control, but they are used in equipment in almost all industrial fields due to their high practicality, such as the progress in control technology and the trend toward smaller and lighter robots.
There are two types of AC motors: synchronous (SM) motors that use permanent magnets and induction (IM) motors that do not use permanent magnets, but currently synchronous motors are mainly used.
List of 40 DC Servomotor Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- China
- Denmark
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- Spain
- Taiwan

- DC motors and gear motors that offer control and feedback and are fully configurable to meet a broad range of requirements.
- Brushed or Brushless motor options.
-
-

-
ISL Products International.
DC Servo Motors
Manufacturer Overview
ISL Products is a designer, manufacturer and supplier of engineered electromechanical component solutions, founded in 1975 and headquartered in New York. With a focus on meeting specific application requirements, they provide unique solutions at the component level. They specialize in a wide range of components such as dc motors, dc gear motors, electronic ballasts for uvc lamps and audio components. Their comprehensive component solutions are tailored to match the unique needs of diverse industries, including healthcare, medical, commercial, and industrial applications. Alongside their product offerings, they also provide integration assistance, industry leading customer service, and global logistical support.
-
-
-
-

-
Aerotech, Inc.
MOTORS
Manufacturer Overview
AEROTECH creates solutions for motion and positioning of devices. Customers are from industries as diverse as data storage, medical devices, and aerospace. AEROTECH develops controllers, drives, motors, and other parts for motion and positioning devices and offers custom-engineered motion systems. AEROTECH’s serves both manufacturers of individual parts as well as equipment operators offering full range of support rom design to manufacturing to deployment.
-
-
-
-

Manufacturer Overview
Moog Inc. was incorporated in 1951 and is headquartered in East Aurora, New York. The company designs manufactures and integrates precision motion and fluid controls and control systems for customers including OEMS in industries such as aerospace, defense, industrial machinery, motorsports, and construction. The company’s product offerings include both systems and components. Examples of systems include actuation systems, naval systems, turreted weapon systems, and space vehicles. Examples of components include manifolds, slip rings, actuators, and servo actuators.
-
-
-
-

-
ElectroCraft, Inc.
PMDC Brush Motors
Manufacturer Overview
ElectroCraft Inc., established in 1960 and headquartered in Stratham, United States of America, is a supplier of application-engineered fractional-horsepower motor and motion products. The company provides DC motors, motor drives, linear actuators, and brush motors. It also delivers AC motors, gear motors, mobile drivetrains, and cables. It provides advanced precision solutions for the lowest cost of ownership for the largest brands and the newest cutting-edge companies. The products are used for medical equipment, laboratory automation, mobile robotics, industrial automation, agricultural automation, and military & defense industries. It serves North America, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia markets.
-
-
-
-

-
Canon U.S.A., Inc
Brushless Servomotors
Distributor Overview
Canon U.S.A., Inc., established as the New York branch in 1955 and then was formally incorporated in 1965, is a supplier of consumer, business-to-business, and industrial digital imaging solutions based in the United States. The company opened their new headquarters in 2013 and continues to realize growth, oversees operations in North, Central and South America. Located off the Long Island Expressway and near the technology corridor of Route 110, the headquarters features modern amenities and a 52-acre campus.
-
-
-
-

-
NIDEC SANKYO
Motor-related products
Manufacturer Overview
Nidec Corporation was founded in Kyoto, Japan in 1973 and is a conglomerate with over 200 subsidiaries. Primary products are hard-disk drive motors and automotive parts, and specializes motors ranging from miniature to gigantic. Nidec’s products are used in robotics, automotive, home appliances, agriculturel equipments well as molding, cutting, and machining equipment and sensors.
-
-
-
-

-
3X Motion Technologies Co., Ltd.
PRODUCT
Manufacturer Overview
3X Motion Technologies Co. Ltd, established in 2002 and headquartered in LuCheng Changzhou, China, is a manufacturer and designer specializing in control motor solutions. The company offers a range of products, such as hybrid stepper motors, brushed DC geared motors, and brushed DC motors. These products are widely used in various applications, including industrial automation, security systems, and automatic doors. Additionally, the company offers unique customization options and complete engineered systems, tailored to meet specific customer needs.
-
-
-
-

-
GEORGII KOBOLD GmbH & Co. KG
Synchronous Servo Motors KSY
Manufacturer Overview
GEORGII KOBOLD GmbH & Co. KG was founded in 1924 and is a manufacturer of premium electromechanical drive system based in Horb am Neckar, Germany. The company manufactures various products such as torque motors, hygienic motors, synchronous servo motors, digital AC servo drive systems, and KOBOLD magnetically-geared motors. The products have been used in various industries such as food, medical, pharma, and general automation. The company has passed the certification of ISO 14001 and ISO 9001 standards.
-
-
-
-

-
Changzhou Fulling Motor Co., Ltd
SERVO MOTOR
Manufacturer Overview
Changzhou Fulling Motor Co., Ltd was established in 2001 and is a manufacturer of motor products based in Changzhou, China. The company offers various products such as hybrid stepping motor, outer rotor BLDC motor, and closed-loop brushless servo motor. The products have been applied in various industries such as office automation, bank equipment, and green energy. The company has passed the certification of ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and ISO 14001. The products are manufactured under RoHS and CE standards, and some products are also UL approved.
-
-
-
-

-
JAT - Jenaer Antriebstechnik GmbH
Compact Servo Drives
Manufacturer Overview
JAT - Jenaer Antriebstechnik GmbH, founded in 1990 and headquartered in Messe Nuremberg, Germany, is a manufacturer of high dynamic positioning and motion systems in the sub-micrometer range for demanding industrial applications. The company offers a diverse product catalog, including multi-axis systems, rotary systems, servo amplifiers, compact servo drives, and linear-axis systems. It also provides services that include full-service support, from requirement analysis and project planning to manufacturing, free individual CAD design, spare part planning and procurement, and customer-specific documentation upon request.
-
-
-
-

-
AXOR IND. S.a.s
Brushless servo-motor
Manufacturer Overview
AXOR Industries, established in 1988 and headquartered in Vicenza, Italy, is a manufacturer of servo drives and AC brushless motors. The company offers a diverse product catalog, including universal servo drives, integrated servo motors and drives, AC-DC servo drives, brushless servo motors with integrated drive MackTron2, and multi-axis brushless systems with a single power unit. These products have applications in automation in production, paper-converting machines, automated guided vehicles, low-voltage equipment, and the mechanical engineering industry.
-
-
-
-

-
Servotecnica SpA
Servomotors
Manufacturer Overview
Servotecnica SpA., established in 1980 and headquartered in Monza e Brianza, Italy, is a manufacturer that specializes in industrial automation and mechatronics. The company offers a range of products, including slip rings, coreless micro motors, tubular actuators, servo drives, and encoders. It also offers customized mechatronic solutions to meet the specific needs of its clients. Its capsule slip rings are the transmission of low-current and high-frequency signals, such as Fieldbus and RF. It serves a range of industries such as packaging machinery, medical, pharmaceutical, and machine tools.
-
-
-
-

-
HDT Srl
Servomotor
Manufacturer Overview
HDT Srl, established in 1969 and based in Monte di Malo, India, is a manufacturer of drives and brushless motors for industrial automation. The company has a DC wound field motor line with square section stator, brushless line with rare earth brushless motors with the respective digital drives, permanent magnet line consisting of compact DC motors and the respective drives for simple and economic automation, and planetary gear line of motors that can be customized to customer requirements. The company also offers a software tool designed to calibrate servo drive and motor via Microsoft Windows operating systems.
-
-
-
-

-
Haiyang Changchuan Motor Co., Ltd.
DC Servo Motor
Manufacturer Overview
Haiyang Changchuan Motor Co., Ltd., founded in 1968 and located in Shandong, China, is a manufacturer specializing in motors and spindles for the automotive industries. The company offers a diverse product catalog, including end trimming motors, SYX series DC servo motors, and SYT series DC servo motors, among others. These products find applications in woodworking and metalworking machinery, precision motion control applications like robotics, and providing rotational force for drilling holes in various materials.
-
-
-
-

-
Canon Finetech Nisca Inc.
DC Motors
Manufacturer Overview
Canon Finetech Nisca Inc. is a Japanese manufacturer of printers and related products that was established in Saitama in 1953. The company’s product portfolio includes CANON brand printers for office or home use, thermal printers utilizing thermal transfer or dye sublimation, and inkjet printers for printing on various media including cards, labels, or tags. It also offers embeddable print modules for integration into kiosks or terminals. The company’s products are commonly marketed by retailers of office supplies, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics.
-
-
-
-

-
NSK Ltd.
Megatorque Motor
Manufacturer Overview
NSK Ltd., based in Japan, is a manufacturer of precision bearings and motion control solutions which started its journey in 1916. The company has established itself as a major supplier for multiple industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace. Their extensive product portfolio encompasses ball bearings, roller bearings, and linear motion components. Their Motion & Control products and technologies support the motion that brings comfort and convenience in cars, planes, wind turbines, satellites, and almost anything with moving parts.
-
-
-
-

-
MOTOR POWER COMPANY
ESA DC servo motors
Manufacturer Overview
Motor Power Company S.r.l. (MPC) is an Italian ISO 9001, 14001, and 45001 certified motion control systems and products manufacturer since 1989. Headquartered in Reggio Emilia with a secondary location in Taicang, China, the company produces various servo motors, motor driven rollers, mechatronic systems, and drives with customization options. These are primarily used by clients in material handling and processing, medical device and pharmaceutical manufacturing, robotics, and textile production. MPC also offers custom engineering, testing, and certification services to customers with unique specifications.
-
-
-
-

-
Jetter AG
Servo motor
Manufacturer Overview
Jetter AG, established in 1979 and headquartered in Ludwigsburg, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial automation solutions. The company's product portfolio includes programmable logic controllers (PLCs), industrial PCs, human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and motion control systems, designed to streamline and optimize industrial processes. Jetter's cutting-edge automation technologies are used across various industries, including automotive, packaging, and manufacturing. Jetter AG aims to create a good and unique automation solutions that enable businesses to succeed with an interest in constant improvement and client satisfaction.
-
-
-
-

-
Heidrive GmbH
Servo motor
Manufacturer Overview
Heidrive GmbH, established in 1938 in Schwabach, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of quality electric drive systems. The company's main products include motors, gears, and integrated drive solutions used in various industries such as automation, robotics, and medical technology. Heidrive's motors and gears play a vital role in delivering precise and efficient motion control to a wide range of applications. With its resilience to efficiency and reliability, Heidrive aims to meet the unique needs of its customers and provide them with tailor-made solutions for their specific requirements.
-
-
-
-

-
esitron-electronic GmbH
DC servo motor
Manufacturer Overview
esitron-electronic GmbH was established in 1989, in Germany as a manufacturer of controls. The company deals in products that are used to control the positioning of devices in the industry of automation technology such as they have Motion Controllers, Cam Controllers, and Digital Panels that enable the display of numbers, symbols, graphics, and text for displaying variables and data such as weight, pressure, speed, and temperature. There are also Signal converters that have applications where level conditioning and conversion of encoder signals is required.
-
-
-
-

-
Shinano Kenshi Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Servo motor & driver
Manufacturer Overview
Shinano Kenshi is an ISO 13485:2016 certified manufacturer, producer and seller of hardware and software development products, established in 1918 and is located in Nagano, Japan. The company manufactures a range of products, including drive systems, precision motors, customized motor solutions, motor pumps, and spun silk yarn. Its flagship product is the PLEXTOR, also known as PLEXLOGGER, which includes high-speed cameras, data loggers, and monitors. Additionally, the company is also engaged in developing and manufacturing welfare and life assistance equipment.
-
-
-
-

-
Shanghai MOONS' Electric Co., Ltd.
Servo motor
Manufacturer Overview
MOON’s is headquartered in Shanghai, China. MOON’s is a manufacturer or motion control products. Among these products are stepper drives and motors, brushed and brushless DC motors, servo drives and motors, integrated motors, BLDC drives, lighting drivers and control products, and condition monitoring products. MOON’s has achieved ISO 14001 and ISO 9001 certification.
-
-
-
-

-
Moog Animatics
SmartMotor
Manufacturer Overview
Moog Animatics is an American motion control products manufacturer founded in 1987 and acquired by Moog Inc. in 2011. Headquartered in Mountain View, California, the company offers power supplies, integrated servo motors, communication protocol devices, and actuators as well as specialized software packages, drivers, peripherals and accessories for various applications in robotics, satellite deployment, prosthetics, and manufacturing. Moog Animatics also provides technical support, training, and custom solutions to clients with demanding requirements.
-
-
-
-

-
STOBER
Synchronous Servo Motors
Manufacturer Overview
STÖBER Antriebstechnik, founded in 1931 with headquarters in Pforzheim, Germany, is a manufacturer of gear units, motors, and drive controllers. The company's product line includes a range of gears, synchronous servo motors, helical servo gear motors, cables, and drive controllers (PC stacks) that are also available in modular and freely scalable models. It also offers an online configuration service so clients can self-design assemblies and full-drive systems that are tailor-made after approval. The company serves markets that include fabrication automation, electronics product processing automation, and automotive drive components.
-
-
-
-

-
B&R
servo-motors
Manufacturer Overview
B&R Industrial Automation GmbH, founded in 1979 with headquarters in Austria, is a manufacturer of automation technology, including a complete portfolio of robotics, automation, and software. The company's standard and tailored products are used in the automotive, maritime, medical device assembly, packaging, and plastics markets, among many others. The product line includes industrial PCs, I/O systems, robotics, and software for industrial components. B&R joined the ABB Group in 2017 to specialize in the integration of technology and sophisticated engineering to provide industries with solutions for machine and factory automation, motion control, and integrated safety technology.
-
-
-
-

-
Festo Corporation.
Servo motor EMME-AS
Manufacturer Overview
Festo Corporation, established in 1925 and headquartered in Esslingen, Germany, is a supplier of automation technology and technical education and is ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and ISO14001 certified. It has around 33,000 catalog products, customized components, and ready-to-install solutions, including grippers, motors, and sensors used in industrial and process automation. The company won the German Future Award in 2010 and serves 300,000 customers worldwide, while its education division provides training solutions for 56,000 industrial companies and educational institutions. It registered €3.81 billion in the 2022 financial year and is available in around 60 countries, with 2,600 patents worldwide.
-
-
-
-

-
Shinano Kenshi
Servo motor
Manufacturer Overview
Shinano Kenshi Co. Ltd., founded in 1918 and headquartered in Nagano, Japan, is a manufacturer of drive systems and precision motors and also offers customized motion solutions. Its products include robotic grippers, drivers, actuators, blowers, and pumps, used in several industries, including automation, life environment, automotive, space, and assistive technology. The company stocks over 9000 drive system and motor models, and over 95% are customized. It is ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO13485 certified, and it also acquired IATF16949 accreditation.
-
-
-
-

-
SANYO DENKI CO., LTD.
DC Servo System
Manufacturer Overview
SANYO DENKI CO., LTD. was founded in 1927 and is a manufacturer and supplier of cooling systems, power systems, and servo systems based in Toshima, Tokyo, Japan. The company manufactures various electronic systems such as DC cooling fan, measuring device, power management products, static transfer switch, and AC servo systems. Various field of industry have been using the products, such as electronic manufacturing, financial, solar energy, medical, and robotic industries. The company has certified with ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, and ISO 45001:2018. The company has reached various accomplishments such as awarded winner in Good Design Award 2023.
-
-
-
-

-
Kollmorgen Corporation
Direct drive motor
Manufacturer Overview
Founded in New York in 1916, Kollmorgen designs and manufactures motion system, drives, motors, actuators, gear heads, automated guided vehicle (AVG) systems, and accessories across a number of implementations and industries. These include aerospace, AGV, food&beverage, machine tools, metal forming, medical automation and imaging, energy, packaging, pharmaceutical, postal sorting, printing, robotics, smart warehouses, and tire and rubber production. Kollmorgen assists customers both in custom designs and in allowing customers to design their own devices based on individual needs.
-
-
-
-

-
NAKANISHI INC.
Product Lines
Company Overview
NAKANISHI, founded in 1930, is a manufacturer and supplier of surgical, dental, and general industrial products applying high-speed rotation technology located in Tochigi, Japan. The products include micro grinders & controllers that are electrically or air-driven, sub-spindle machine tools, high-speed machining spindles, special-purpose machines & robots, and milling machines. The company offers solutions to drilling, milling by endmills, deburring by carbide cutters, grinding by grindstones, and finishing applications in the automotive, medical, mold, micromechanics, and electronics industries.
-
-
-
-

Company Overview
JVL A/S, established in 1974 and founded in Denmark, is a manufacturer and supplier of IntegraMotion Motors. The company's product range includes integrated servo motors and stepper motors, such as MAC motors, QuickStep motors, MIS motors, and StepMax. These products find utility in various industries, including automation, and motion control. Whether it's robotics, CNC machines, wind turbines, or medical equipment, JVL A/S's motors cater to a wide range of applications. As a certified ISO 9001:2015 company, it provides quality products and services.
-
-
-
-

-
WITTENSTEIN motion control GmbH
Subsea servo motors for the oil and gas industry
Company Overview
WITTENSTEIN motion control GmbH was founded in 1949 and is a manufacturer and supplier customized mechatronic products and systems based in Igersheim, Germany. The company produces various products such as servo actuators, servo systems, control loading systems for simulators, servo motors, and servo drives. The products have been applied in various fields such as aerospace, defense, simulation, and subsea. The company also offers supporting services such as consultation, sizing, engineering, and repair.
-
-
-
-

-
Mavilor Motors S.A.
DC servomotor
Company Overview
Mavilor Motors S.A., established in 1979 and headquartered in Barcelona, Spain, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in the production of servomotors. The company's product portfolio includes AC servo motors, DC servo motors, brakes, tachogenerators, and power generators. These products are utilized in various sectors, including electronics, renewable energy, medical devices, aerospace and defense, and entertainment and amusement. The company holds both ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 certificates and has global distributors in France, Germany, the United States, Mexico, and other countries.
-
-
-
-

-
NOVOTRON Industrie-Automation GmbH
DC servo motor
Company Overview
Novotron, founded in 1978 and headquartered in Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of quality radio remote controls and electronic controls. The company’s product range includes radio remote controls and electronic controls for various applications such as industrial cranes, material handling, and mobile machinery. Novotron aims to provide efficient and cutting-edge solutions to improve the safety and convenience of remote operations. Novotron’s advanced controls enhance user experience and ensure precise control over machinery. Courtesy of the company’s devotion to quality and performance, it continues to be an ideal partner in the field of remote control technology.
-
-
-
-

-
Harmonic Drive SE
Servo actuator
Company Overview
Harmonic Drive AG, established in 1969 in Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision gears, servo actuators, and motion control solutions. The company’s product range covers a wide spectrum of precision gears, strain wave gears, and rotary actuators, serving diverse industries such as robotics, aerospace, and medical devices. Harmonic Drive AG delivers great-performance motion control solutions that offer accuracy, reliability, and durability. Their quality products play a crucial role in achieving precise and smooth motion in various applications. With a strong emphasis on engineering success, Harmonic Drive AG continues to provide cutting-edge motion control technology for global markets.
-
-
-
-

-
Haydon Kerk Pittman
Motors
Company Overview
AMETEK, Inc., headquartered in Waterbury, Connecticut, and founded in 1930, is a supplier and manufacturer of advanced linear and rotary solutions. The company offers a product portfolio, including multi-axis motion systems, linear rail systems, and lead screw and nuts assemblies. These solutions find applications in various fields, such as playing a key role in purge and trap analysis for gas chromatography sample preparation, ensuring the precise and accurate delivery of dyes and agents in contrast injector systems, and contributing to dialysis pump applications with linear stepper actuators.
-
-
-
-

Company Overview
KEBA, founded in 1968 and headquartered in Linz, Austria, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial machinery automation. The company's primary areas of focus include industrial automation, handover automation, and energy automation. These offerings aim to provide solutions in various industries, striving for sustainable competitive advantages for its clients. Besides, it serves industries that bridge the physical and digital world, emphasize renewable energy, and require tailored industrial solutions. Furthermore, the company offers specialized solutions in banking and service automation, e-mobility, and heating automation.
-
-
-

-
ESR Pollmeier GmbH
Servo Motors
Company Overview
ESR Pollmeier GmbH, established in 1969 and based in Ober-Ramstadt, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of servo drives and servo systems. The company's product range includes Servo drives, Multi-axis servo systems, Servo motors with gearboxes, Torque motors, and Linear drive systems. These products have applications in precise motor and drive operations for industries requiring high precision. They primarily serve sectors like manufacturing, automation, robotics, and industrial machinery. It offers services such as drive system configuration, customer-specific adaptations, commissioning services, and ongoing maintenance.
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
King Right Motor CO., LTD.
Servo motor
Company Overview
KING RIGHT MOTOR CO., LTD of Taoyuan City, Taiwan, specializes in the research and development and manufacture of DC brushed motors, servo motors, and DC gears. King Right Motor’s main products include DC motors, planetary gear motors, worm gear motors, spur gears, servo motors and pumps ranging in output power from 10W to 1,000W. These are used in equipment, industrial machinery, garage doors, elevators, elevator doors, mixers, medical equipment, health and welfare equipment, garden equipment tools, stage design and vehicle applications. King Right Motor has passed ISO 9001 certification.
-
-
DC Servomotor Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of July 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ISL Products International. |
17.0%
|
| 2 | esitron-electronic GmbH |
5.7%
|
| 3 | MOTOR POWER COMPANY |
4.9%
|
| 4 | Jetter AG |
4.9%
|
| 5 | ElectroCraft, Inc. |
4.4%
|
| 6 | Servotecnica SpA |
3.9%
|
| 7 | Heidrive GmbH |
3.4%
|
| 8 | AXOR IND. S.a.s |
2.9%
|
| 9 | HDT Srl |
2.9%
|
| 10 | Kollmorgen Corporation |
2.9%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the dc servomotor page as of July 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
- NIDEC SANKYO: 114,371
- NSK Ltd.: 30,577
- Shinano Kenshi Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.: 4,000
Newly Established Company
- 3X Motion Technologies Co., Ltd.: 2002 (22 years ago)
- Shanghai MOONS' Electric Co., Ltd.: 1994 (30 years ago)
- esitron-electronic GmbH: 1989 (35 years ago)
Company with a History
- NSK Ltd.: 1916 (108 years ago)
- Shinano Kenshi Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.: 1918 (106 years ago)
- GEORGII KOBOLD GmbH & Co. KG: 1924 (100 years ago)
DC Servomotor Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
Global Distribution of DC Servomotor Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 Germany
Germany
|
8 | 26.7% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
5 | 16.7% |
 Japan
Japan
|
5 | 16.7% |
 China
China
|
5 | 16.7% |
 Italy
Italy
|
4 | 13.3% |
 Denmark
Denmark
|
1 | 3.3% |
 Spain
Spain
|
1 | 3.3% |
 Taiwan
Taiwan
|
1 | 3.3% |