All Categories
History





This section provides an overview for photomultiplier tubes as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 5 photomultiplier tube manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked photomultiplier tube companies as of February, 2026: 1.KETEK GmbH, 2.ET Enterprises Limited, 3.PHOTONIS.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Photomultiplier Tubes
1975~1995: Worked at Hitachi, Ltd.
Engaged in research on the irradiation effects of nuclear reactor materials at the Energy Research Institute.
Received the Japan-American Atomic Energy Society Award for his research achievements.
1996~2015,
Engaged in soft error research caused by environmental neutron beams in semiconductor devices at the Institute of Industrial Science.
Research achievements: Awarded the IEEE Fellow and the Teiichi Yamazaki Award.
Currently active as a writer.
A Photomultiplier Tube (PMT) is one of the most sensitive optical sensors capable of converting light (photons) into electricity.
It consists of a glass tube in a vacuum with an incident window, a photocathode, a dynode, and other components. The principle is based on the external photoelectric effect, a phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal when light is irradiated on it in a vacuum.
Since even a single photon can be converted into a large electrical signal at high speed (10-9 seconds), photomultiplier tubes are used in electron microscopes, environmental analysis equipment, medical equipment, spectrophotometers, and spectral analysis equipment as photodetectors.
Photomultiplier Tubes are used as secondary electron detectors in electron microscopes and in photoanalytical instruments such as UV-visible spectrophotometers and emission spectrometers. They are also used in dust counters to measure particles in the air, in laser radar (LiDAR) to detect light scattered by suspended particles in the air, and in medical devices such as positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT) used for cancer screening.
LiDAR provides a means of detecting the position and movement of objects around a vehicle and is also expected to be a key technology for fully automated driving. The Super-Kamiokande, the world's most advanced facility for neutrino research, uses 13,000 20-inch diameter Photomultiplier Tubes to capture the Cherenkov light (light produced when electrons exceed the speed of light in water) generated in a 50,000 ton water tank.
Photomultiplier Tubes are extremely sensitive and are capable of converting faint light into a sufficient amount of electrical signals. On the other hand, they also have disadvantages, such as requiring high voltage for use and being prone to picking up noise caused by thermal electrons. Therefore, the power supply for Photomultiplier Tubes must have extremely low noise and high stability.
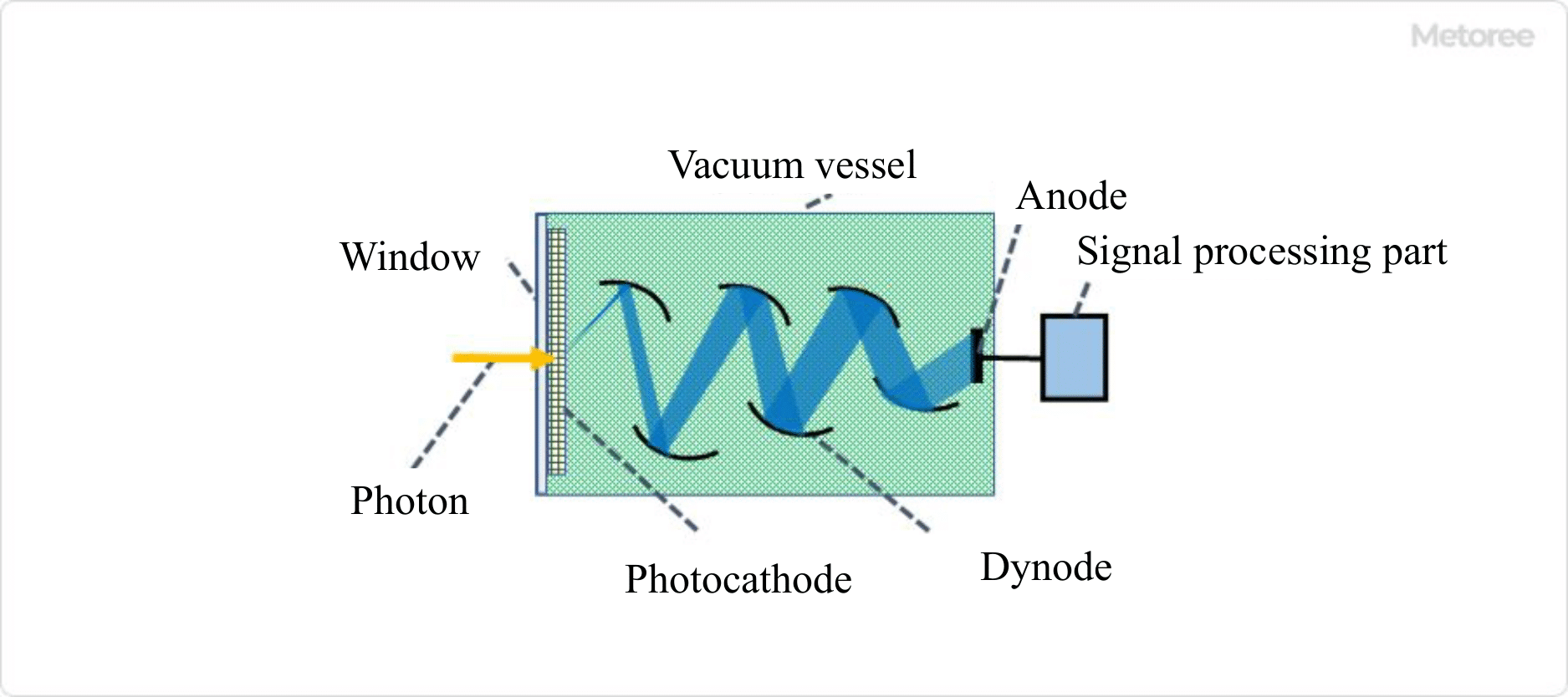
Figure 1. Basic structure of photomultiplier tubes
Photomultiplier Tubes are optical sensors that can detect light from a single photon and convert it into an electrical signal. Figure 1 shows the overall structure of a Photomultiplier Tube.
The glass tube in a vacuum state contains a window through which light enters, a photocathode that converts photons into electrons through the external photoelectric effect (the effect of electrons being emitted into a vacuum), a focusing electrode that collects the photoelectrons, a dynode with about 10 stages that multiplies secondary electrons, and an anode that generates an electronic signal. A DC voltage of about 1,000 V is applied to the entire area from the photocathode to the anode.
Borosilicate glass, quartz glass, UV-transmitting glass, MgF2 crystal, etc. are used as window materials, depending on the wavelength region of the light, mainly on the short wavelength side.
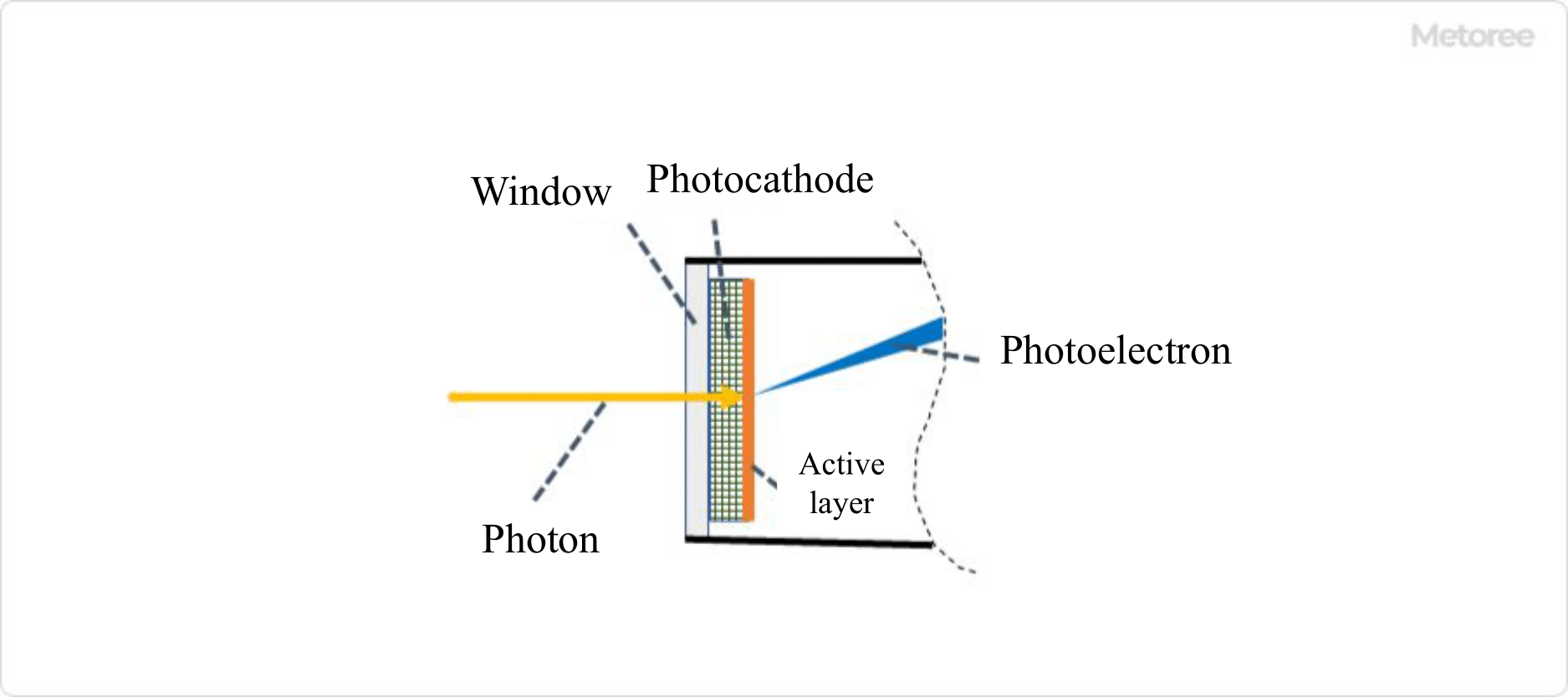
Figure 2. Photocathode and external photoelectric effect (Image)
The photocathode forms a quantum efficient (photoelectron generation efficiency) active layer on the surface in contact with the high vacuum. In the visible region, bialkali metal photocathodes, multi-alkali metal photocathodes of three or more types with sensitivity up to the infrared region, alkali halide photocathodes for UV detection, and photocathodes using III-V compound semiconductors with high sensitivity in the UV to near infrared region have been developed.
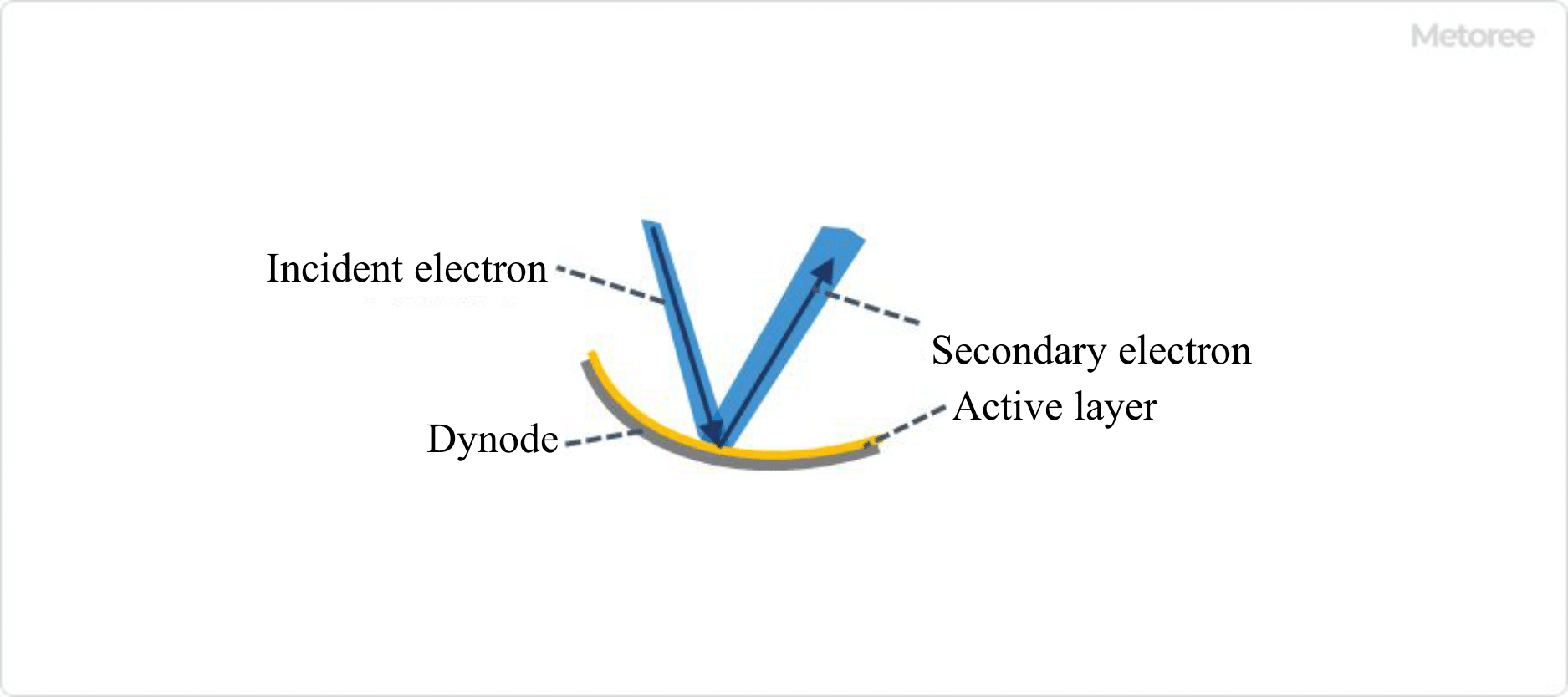
Figure 3. Structure and function of dynode (image)
Photoelectrons are accelerated by a focusing electrode and collected in a dynode. The dynode forms an active layer that increases the secondary electron emission ratio on a substrate metal such as nickel or stainless steel. Alkali metal-antimony (e.g., SbCs), beryllium oxide, and magnesium oxide are typically deposited on the layers.
When electrons strike the dynode, a large number of secondary electrons are emitted. The emitted secondary electrons collide with the next dynode, where more secondary electrons are emitted. This process is repeated until the number of electrons increases more than one million times, and is detected as a sufficient amount of electrical signal.
Various structures have been devised for the secondary electron multiplier, such as circular cage type, line focus type, box-and-grid type, fine mesh type, and metal channel type, depending on the arrangement and shape of the dynodes and other components.
For each structure, the optimum electrode design is made by electron orbital analysis. Electrons travel in a high vacuum, enabling fast time characteristic acquisition. The high sensitivity and fast response characteristics that count light as a grain are the reasons why PMTs are used at the forefront of the industry.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Newport is a division of MKS Instruments, Inc. that was incorporated in 1961 and headquartered in Andover, Massachusetts. The company is a manufacturing company that serves the specialty industrial, advanced electronics, and semiconductor industries. The company markets its products through Spectra-Physics, MKS Instruments, Richardson Grating, and other brands. Their product categories include motion, optomechanics, optics, and vacuum instruments. Product categories include lasers, MKS vacuum & gas solutions, laser diode controls, and tables & isolation systems.

ET Enterprises Limited, founded in 1930 with headquarters based in Uxbridge, United Kingdom, is a manufacturer of photomultiplier tubes and related products that are designed to meet customer requirements worldwide. Apart from photodetector modules, the company also provides technical and application support. The company's products include HV bases, voltage dividers, sockets, electronic modules, and HV power supplies. ET Enterprises distributes the ADIT range of photomultipliers outside the US as a subsidiary of Ludlum Measurements Inc. The company holds ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 certifications.

KETEK GmbH, founded in 1989, has headquarters in Munich, Germany, and is a manufacturer of silicon drift detectors that are used in various industrial material analysis applications. The company produces a product line that includes Vitus SDD modules, complete systems, accessories, and solutions for original equipment manufacturers. In 2021, KETEK GmbH sold its Silicon Photomultiplier (SiPM) assets to Broadcom Inc. The company's silicon drift detectors were also used as a component of the X-ray spectrometer on board the Mars rover Curiosity.

Hamamatsu Photonics K.K., established in 1953 and headquartered in Hamamatsu, Japan, is a manufacturer of sensors and emitters for both visible and invisible light. It stocks products like LEDs, lamps, and photodiodes used in several industries, including consumer electronics, dental imaging, and environmental monitoring. The sensor and light source components are also available as modules and units that can be incorporated into systems the company develops, like optical measurement systems or imaging systems. The ISO 9001-certified company stocks over 15,000 devices, units, and systems that ship to over 100 destinations worldwide, and it has ten research and production bases.

PHOTONIS, a well-reputed French company founded in 1937, specializes in manufacturing electro-optic components and detectors. They offer a wide range of products, including photomultiplier tubes, image intensifiers, and microchannel plates. PHOTONIS serves various industries, such as scientific research, defence, medical, and industrial applications. Their products are used in applications like night view, mass spectral analysis, and space exploration. PHOTONIS is present internationally with offices and distributors in different countries. Devoted to excellence and environmental responsibility with various certifications, ensuring reliability and safety for customers.
Ranking as of February 2026
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | KETEK GmbH |
30.4%
|
| 2 | ET Enterprises Limited |
23.3%
|
| 3 | PHOTONIS |
22.1%
|
| 4 | Newport Corporation |
15.0%
|
| 5 | Hamamatsu Photonics K.K. |
9.1%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the photomultiplier tube page as of February 2026. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
1 | 25.0% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 25.0% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 25.0% |
 Japan
Japan
|
1 | 25.0% |
39 products found
39 products
Tohoku Electronic Industry Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
Kemirmilm Nessence Analyzer is a weak light emission detection device in the world, which measures very weak light that is invisible to human eyes....
10 models listed
ANSeeN Co., Ltd.
390+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Applications For photomultiplier tube bias power supply ■Main specifications Output voltage range 200V to 1,100V (Polarity specified at time of o...
PRIMES Japan Co., Ltd.
410+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
■A wide variety of robust power meters The measurement principle of PMT is based on Newton's cradle. The palm-sized PMT uses the exact same impact ...
Tohoku Electronic Industry Co., Ltd.
420+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
Kemirmilm Nessence Analyzer is a weak light emission detection device in the world, which measures very weak light that is invisible to human eyes....
5 models listed
Optomechatro Co., Ltd.
510+ people viewing
Last viewed: 57 minutes ago
Low-level light measurement can be directly connected to a PC using a USB cable. Photomal control signals and measurement data can be transferred v...
Hoshin Electronics Co., Ltd.
300+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
A compact unit with one built-in charge amplifier hybrid IC (NO12-1). It is also very convenient when using N012-1 for the first time. A connector ...
Texol Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
A dark box that blocks out external light. Ideal for applications using photomultiplier tubes. When using a highly sensitive PhotoMul, it is necess...
3 models listed
Hoshin Electronics Co., Ltd.
380+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
Ideal for signal amplification of photomultipliers for photoelectric conversion of scintillation counters and Chilenkov counters ■Features ・High-...
Lambda Vision Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Microscope-mounted photomultiplier, C-mount compact PMT unit ・Compatible with OLYMPUS and NIKON rotating analyzers ・Using Hamamatsu Photonics ph...
Berthold Japan Co., Ltd.
910+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
A highly sensitive photon measurement device using a photomultiplier tube. In addition to brightness, spectrum measurement is also possible. This i...
Berthold Japan Co., Ltd.
640+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
A highly sensitive photon measurement device using a photomultiplier tube. Only brightness can be measured. Recommended if spectral measurements ar...
Cosmo Trading Co., Ltd.
520+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Summary The Thermo Scientific K-Alpha is a fully integrated monochrome small area X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) system. ■Designed to imp...