All Categories
History









This section provides an overview for thermal relays as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 9 thermal relay manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked thermal relay companies as of February, 2026: 1.Eisen Machinery Inc., 2.Legrand, 3.FUJI ELECTRIC INDUSTRY CO., LTD..
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Thermal Relays
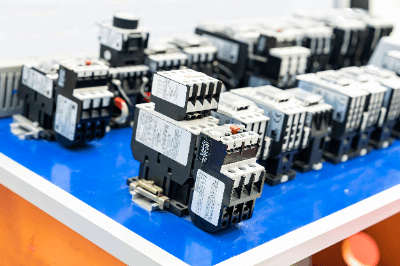
A Thermal Relay is a component that outputs a contact when a current exceeding a set value flows into an electrical circuit. They are mainly used to prevent overloading of motors and wiring. By incorporating thermal relays into circuits, problems such as circuit burnout can be prevented.
Thermal relays are mostly used for motor protection. When a motor is subjected to a torque over its rating, a current more than the rating will flow. This phenomenon is called overcurrent.
When a motor is in an overcurrent state for an extended period, the internal windings heat up. This causes the internal varnish to melt or the windings to burn out. This is called motor burnout. When a current exceeding the rated value flows, the thermal relays shut off the power supply using a contact output to protect the motor.
In most cases, bimetals are used as circuit conductors inside thermal relays. Bimetal is a material that combines two types of metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion. When heat is generated by an electric current, it is biased and deformed due to the difference in thermal expansion coefficients.
The bimetal inside the thermal relays use this bias to drive the contact point and output the contact. Thermal relays are available with different current settings depending on the thickness of the bimetal and other factors.
When a motor starts, the current is more than twice the rated value. Since the bimetal heats up and deforms, there is a delay time until it warms up. Due to this delay time, they do not react to the high starting current of the motor.
The output contact of thermal relays are fixed by a spring, and once activated, in most cases the output continues to be output until the reset button is pressed. This prevents overloaded equipment from restarting.
Thermal relays are selected according to the current rating of the motor to be protected. There are two types of motor protection elements: instantaneous and time-limited.
The momentary element is a protective element that shuts off the motor power supply instantaneously to protect the upper circuit in the event of a motor malfunction. Power fuses and motor relays are used for high-voltage motors, while shock relays and breakers are mainly used for low-voltage motors.
A time-limiting element is a protective element that detects motor overload and shuts off the power supply to protect the motor. Overcurrent relays are used for high-voltage motors, and thermal relays are used for low-voltage motors.
For low-voltage motors, a breaker, drive unit, and thermal relays should be selected in conjunction with the above. The breaker should be at least twice the motor's rated current to avoid tripping due to the starting current. The drive and thermal relays should be selected according to the motor's rated current, referring to the manufacturer's catalog.
Thermal relays are classified into two types: bimetal type and electronic type.
The thermal relays have two types of contacts: a normally open contact (a-contact) for monitoring and a normally closed contact (b-contact) for breaking the circuit.
When an overload condition persists and the thermal relays operate, the output contact of the thermal relays must be deactivated after the cause is removed. This procedure is called "recovery" or "resetting."
There are two types of reset procedures: manual reset and automatic reset. The manual return type is simple, press the reset button after removing the cause of the overload. By pressing the reset button, the output contact is released.
The automatic reset type does not require pressing the reset button, but the thermal relay automatically resets itself. It is used in special applications where it is difficult for people to approach the thermal relays.
Although it varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, the recommended replacement period for thermal relays is approximately 10 years. However, since periodic replacement of thermal relays are costly, in most cases only periodic replacement of thermal relays for critical loads is required.
Since thermal relays are composed of bimetals and resins, which do not deteriorate easily, they rarely deteriorate naturally. The following four factors are known to cause forced deterioration.
Thermal relays are often used as part of electromagnetic switches. In such cases, the primary side of the main circuit is usually connected with a copper bar for power supply in commercial products. The secondary side wiring should be designed to have an allowable current greater than the rated current of the thermal relays.
The allowable current for wiring varies depending on the type of wiring, but each type is defined by the internal wiring regulations. Wiring sold in Japan complies with the extension regulations.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Eisen Machinery Inc. is an importer and distributor of precision industrial machinery and machine components headquartered in Ontario, California. Established in 2002, their distribution includes machine tools such as grinders, milling machines, and engine lathes, as well as machine parts like forward reverse switches and power feeds. The company primarily serves machinery and equipment manufacturers as well as wholesalers in the energy, automation, and security industries. With partners in over three continents, Eisen Machinery Inc. can supply machinery and parts from Germany, Taiwan, and Japan, as well as accommodate custom orders for items not currently available.

Fuji Electric Industry Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer of electrical products such as control switches, connecting devices, pilot lamps and indicators, and electronic devices founded in February 1953, in the town of Nijo, Nakagyo-ku, Kyoto, Japan. In 70 years, the company has three sales offices with Kyoto as its headquarters. Other sales office are in Tokyo and Shiga. It currently has three factory offices located in Shiga, Japan. The company released its first product in 1959-a multi-window indicator. Since 1953, the company released 26 more products. Aside from manufacturing electrical products, the company offers scholarships for students which they started in 1976.

Wieland, established in 1910 and based in Bamberg, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of electrical connection technology. Their product range includes pluggable connections for seamless plug-and-play electrical device connections, insulated connectors that provide electrical insulation in device connections, cable glands for safeguarding cables and ensuring a watertight seal, terminal blocks used for connecting electrical wires, and contact systems facilitating connections between electrical components. Wieland's products find applications in diverse industries, such as building construction, electrical engineering, and automation.

Hitachi, Ltd was established in 2002 and headquartered in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo is a manufacturer of industrial electrical equipment and system solutions. The company offers an extensive and diversified product portfolio including industrial drive systems, power electronics, energy-related equipment, power distribution systems, and various other industrial solutions. These products serve as integral components that drive advancements in industrial capabilities across diverse sectors by playing a pivotal role in promoting energy conservation and storage, automating robot systems in large factories, enabling smarter manufacturing through digital solutions, and facilitating efficient transportation within industrial facilities.





Legrand Group, established in 1860 and headquartered in Limoges, France, is a manufacturer specializing in electrical and digital building infrastructures. The company’s product offerings encompass a range of electrical components, including air circuit breakers (ACBs), miniature circuit breakers (MCBs), molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs), and residual current devices (RCDs). It also offers Deutsche Institut fur Normung (DIN) rails, as well as head equipment and electrical busbar systems. Additionally, the company provides enclosures and equipment for cabling components and charging stations, along with wiring accessories. It also offers lighting management devices, emergency lighting units, access control and safety equipment for building infrastructures.

TE Connectivity Ltd., started in 2007 and headquartered in Schaffhausen, Switzerland, is a designer and manufacturer of sensor and connectivity solutions for harsh conditions. It operates three primary segments, namely transport, industrial, and communication solutions, and its product portfolio includes automotive connectors, fiber optic connectors, analog power meters, RTD sensors, and circuit breakers. It serves customers in approximately 140 countries and several industries, including aerospace, automotive, rail, IoT connectivity, and E-mobility. The company manufactures 192 billion products annually and has invested over 610 million USD in research development and engineering.

Omron Corporation, started in 1933 and headquartered in Kyoto, Japan, is a manufacturer of automation components, equipment, and systems, and it developed the first contactless proximity switch in 1960. It has four domains, including industrial automation, electronic components, healthcare, and social systems, and it provides products and services in around 120 countries and regions. Some of its products include microsensing devices, access control systems, industrial robots, surveillance cameras, and blood pressure monitors. In 1971, it developed the first online cash machine, and in 1972, it established Japan’s first welfare factory.
Ranking as of February 2026
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Legrand |
27.6%
|
| 2 | Eisen Machinery Inc. |
25.0%
|
| 3 | FUJI ELECTRIC INDUSTRY CO., LTD. |
11.8%
|
| 4 | Wieland ELECTRIC GMBH |
10.5%
|
| 5 | TE Connectivity |
10.5%
|
| 6 | Omron |
7.9%
|
| 7 | Hitachi, Ltd. |
6.6%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the thermal relay page as of February 2026. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 Japan
Japan
|
4 | 57.1% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
1 | 14.3% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 14.3% |
 France
France
|
1 | 14.3% |
66 products found
66 products
Daiichi Electronics Co., Ltd.
710+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Protection and monitoring of earth leakage current and overload are integrated into one unit. Realizes protection and monitoring of leakage current...
Sawafuji Electric Co., Ltd.
600+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
High reliability considering installation in commercial vehicles Compatible with large current applications
3 models listed
Daiichi Electronics Co., Ltd.
670+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■DMR-Pro product overview DMR-Pro is a protection relay for power receiving and substation equipment that integrates protection, control, and measu...
Mio Corporation Co., Ltd.
620+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Overview and features ・Indoor use ・Explosion-proof structure: d2G4 ・Economic type ■Caution ・Specification: Format ・When using outdoors, plea...
2 models listed
Sunk Japan Co., Ltd.
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
It is for control of robots and handling units in case of collisions or overloads. Advantages and benefits ■ Automatic reset Production can be res...
10 models listed
Leadec Co., Ltd.
340+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Quickly detects damage to cutting tools. It detects slight differences in the current of an AC motor and outputs a signal. Since the no-load curre...
2 models listed
Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd.
370+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 hours ago
■High capacity cutoff relay ・400V DC high voltage switching possible. Lineup with current capacity up to 300A ・Main applications: Solar power gen...
Leadec Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Thyristor brakes reduce the stopping time of three-phase induction motors. This is an epoch-making brake unit that can freely control speed and spe...
3 models listed
Shinko Technos Co., Ltd.
540+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
・ Contribute to the construction of a product system with cost reduction ・ Built -in barista with excellent outpatient surge absorption ・ Easy t...
3 models listed
Nakamura Electric Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Houses a hardwire circuit breaker and electromagnetic switch, allowing options to be installed inside and outside. *The thermal relay is an automa...
6 models listed
Leadec Co., Ltd.
340+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Thyristor brakes reduce the stopping time of three-phase induction motors. This is an epoch-making brake unit that can freely control speed and spe...
2 models listed
Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd.
390+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
■High capacity cutoff relay ・400V DC high voltage switching possible. Lineup with current capacity up to 300A ・Main applications: Solar power gen...
Sunk Japan Co., Ltd.
430+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
It is for control of robots and handling units in case of collisions or overloads. Advantages and benefits ■ Trigger power and torque can be adjus...
5 models listed
Nakamura Electric Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Contains an electromagnetic switch and can be used as a starter for electric motors *The thermal relay is an automatic return type. *Only one amme...
5 models listed
IDEC Co., Ltd.
970+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Relays that are environmentally friendly, including lead wire-free and cadmium-free. Features ■Safety - A model with a 5-window mechanical indicat...
IDEC Co., Ltd.
1160+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Features ・Eco & slim safety measures. 2-pole force-guided relay that reduces costs and saves space ・Forced guide type contact structure (EN50205...
WIN SOURCE ELECTRONICS
380+ people viewing
Last viewed: 10 hours ago
■Summary Protection relays and systems are essential to protect electrical circuits and equipment from faults such as overcurrents, voltage abnorma...