All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for protective relays as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 45 protective relay manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked protective relay companies as of July, 2025: 1.NOARK Electric North America, 2.Beckwith Electric Co., Inc., 3.Ross Engineering Corp..
Table of Contents
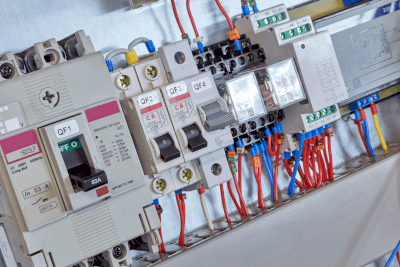
A protective relay is a device that instantly detects sudden changes in current and voltage occurring in power system equipment and sends a control signal to the circuit breaker to isolate the faulty point.
By quickly disconnecting the faulty part in the event of an accident in the power system, the protective relay not only prevents the spread of damage caused by overcurrents but also minimizes the duration of power outages and ensures a stable supply of electric power.
For this purpose, equipment fault elimination relays to isolate faulty equipment and accident spread prevention relays to prevent the spread of the effects of accidents are dispersed throughout the power system. A reclosing device for quick recovery from an accident is also treated as a type of protective relay.
Protective relays are used to prevent the effects of accidents such as lightning strikes from spreading throughout the power system and to ensure a stable supply of electricity. Protective relays are installed in various places in facilities that make up power systems, such as power plants, substations, and power transmission and distribution lines managed by power companies.
Private power generation facilities that are connected to the power company's power system are also required to install protective relays at the receiving points to protect the power system in the event of a failure of the private power generation facilities and to protect the private power generation facilities in the event of an accident on the power system.
In addition to power generation facilities, protective relays are also used to protect power receiving and transforming facilities in buildings, factories, hospitals, railroads, and other power-demand facilities.
The operational principle of protective relays varies depending on the type of protective relays.
Over Current Relay (OCR): Operates when the current value at the location where the protective relays are installed exceeds the set value. There are two types of elements that trigger the overcurrent protective relays: dimensional elements and instantaneous elements. The dimensional element operates when it detects that an overcurrent has flowed for a long period of time due to an overload. The higher the current value, the sooner the normal system is protected. The instantaneous element detects the instantaneous flow of a large current far in excess of the rated current due to a short circuit and protects the normal system.
Over Voltage Relay (OVR): Operates when the voltage at the location where the protective relays are installed exceeds the set value. Detects overvoltage on the power system side due to a generator or other failure and protects the system and equipment on the load side.
Under Voltage Relay (UVR): Operates when the voltage at the location where the protective relays are installed drops below a set value. Detects a drop in power due to a power failure or short-circuit failure, and protects the load-side system and equipment.
Ground Fault Protective Relays (GR: Ground Relay): Operates by detecting ground faults caused by cables contacting the earth. Ground protective relays use a zero-phase alternator (ZCT) to detect unbalanced current due to an imbalance in the three-phase circuit in the event of a ground fault. At this time, since a ground fault is detected only by the magnitude of the current, it is not possible to distinguish between an accident current in the power system and an accident current on the self-circuit side, which may result in false detection.
Directional Ground Relay (DGR): Operates by detecting a ground fault using the zero-phase current and zero-phase voltage between the line and the ground. It can detect only the fault current of its own line in the direction of the phase difference between the current and voltage.
Differential protective relays (DFR: Differential Relay): Operates when the differential current, which is proportional to the vector (current value and phase) difference between the input and output currents in the protective section, exceeds a certain value. Only when a short circuit occurs in the protective section, a difference is generated in the secondary current of the alternator (CT), and a differential current flows to the operating coil. With this method, the differential current does not reach zero during normal operation due to the characteristic difference of the CT, etc., and may malfunction.
Ratio Differential Relay (RDFR): To prevent malfunction of the differential protective relays, differential protective relays have a structure with an additional suppression coil that generates a suppression force when a current passes through it. When a large current due to an external accident passes through the relay, a large suppression force is applied to prevent malfunction.
Other types of protective relay systems include power protective relays, over-frequency protective relays, under-frequency protective relays, short-circuit protective relays, and short-circuit direction protective relays.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Danfoss was founded in 1933 in Nordborg, Denmark where it remains today. The company serves automotive, food & beverage, energy & natural resources, wastewater, and mobile hydraulics industries as a manufacturer of power systems and industrial hydraulics. The company operates through three business segments: Danfoss Power Solutions, Danfoss Climate Solutions, and Danfoss Drives. Danfoss Power Solutions produces electronic controls, hydraulic power units, and cylinders. Climate Solutions produces heat exchangers, burner components, hydraulic heating, and sight glasses. Drives produce gear motors, low and medium voltage drives, and various software solutions for operating drives.

Sensata Technologies was originally founded in 1916 as General Plate Company and is now headquartered in Attleboro, Massachusetts. The company is a developer, manufacturer, and seller of sensors and sensor-rich solutions, electrical protection components, and other products used in automotive, industrial, energy, telecom, and construction industries. The company has 20 product categories including force sensors, tire management solutions, inverters & charges, and pressure sensors.The company’s next generation of products are designed to improve the efficiency of industrial pumps, fuel efficiency in ICE cars and energy efficiency in TVs, and facilitate usage of IoT devices.

Beckwith Electric Co., Inc. is a manufacturer of solutions that pertain to the production, transmission, and distribution of electric power, established in 1967 and based in Florida, United States. The company makes generator protection products, transformer protection products, and regulator control products. It also crafts capacitor bank control products, digital motor bus transfer systems, and DG/DER interconnection protection products. Its generator protection products provide customers with the ability to meet or exceed ANSI/IEEE C37.102 or Buff Book standards, plus give customers additional operational and security enhancements.

Littlefuse was founded in 1927 and headquartered in the United States. Littlefuse is a diversified industrial technology manufacturing company with customers globally. Littlefuse has products segments which are electronic, industrial, and transportation. Electronic segment products include fuses and fuse accessories, positive temperature coefficient resettable fuses, polymer electrostatic discharge suppressors, and varistors. Transportation products include blade, resettable, and high-current and high-voltage fuses, as well as battery cable protectors; fuses, switches, relays, circuit breakers, and power distribution modules. The Industrial segment offerings include contactors, transformers, and temperature sensors for use in renewable energy and energy storage systems, electric vehicle infrastructure, HVAC systems.

Schweitzer Engineering Laboratory, established in 1982, is a manufacturer of power systems protection based in Washington, USA. The company provides cutting-edge products and services that enhance the efficiency and security of electrical power systems. The company offers many products, including protective relays, communication devices, automation controllers, and software solutions. The advantage of the company's products is its robustness, which can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making it suitable for deployment in diverse settings, from substations to remote installations.

Baster Electric Co., established in 1942, based in Highland, Illinois, is a manufacturer that provides a wide range of products for the control and management of electric power. The company offers various products, including generator controls, plastic injection molding, and more. Its custom transformers are designed for application-specific electrical and thermal requirements using cost-effective materials. Its injection molding and LLC specializes in product development and other secondary service. It has achieved ISO 9001:2015 certification for quality management systems. The company has expanded its manufacturing capabilities by opening new plants in Taylor, Texas, and Suzhou, China.

Woodward Inc, founded in 1870, is a manufacturer and service provider of aerospace solutions and industrial products based in Colorado. The company manufactures aircraft control systems including compressors, safety systems, software, turbines, servo valves, and so on. It also offers industrial products such as valves, motors, and electromechanical components designed for any type of industrial engine application. In addition, the company’s services are extended to the military, transportation, and power industries.

Wisconsin Oven Corporation has operated since 1973 and is located in East Troy, Wisconsin. Wisconsin Oven designs, engineers, and manufactures industrial ovens and other heating equipment for numerous applications including heat treating, powder coating, paper pulp drying, finishing, drying, and curing in the aerospace, automotive, composite, energy, finishing, foundry, heat treating, annealing, military, and pharmaceutical industries. Types of ovens and equipment include custom and standard batch ovens, conveyor ovens, pollution control equipment, and walk-in ovens.

Ross Engineering Corporation, founded in 1964 and based in Campbell, California, is a manufacturer of a wide range of high-voltage electronic and electro-mechanical devices and is ISO 9001 certified. It stocks over 25 lines of high voltage devices such as voltmeters, relays, and probes used in several fields such as industrial plants, communication transmitters, and power supplies with ranges from 0.01mV to 1,200,000 V. The company is ISO/IEC 17025:2017 certified and has a calibration lab for testing and calibrating dividers, relays, and probes up to 450kV.

ifm efector (ifm) is a subsidiary of ifm electronic, founded in Germany in 1969. ifm has developed, manufactured and marketed sensors and controls technology to industries that include assembly and robotics, automotive, material handling, metal forming, mobile equipment, plastics, and food and beverage. Ifm produces sensors, condition monitoring equipment, image processing, safety technology, industrial communication, IO-link, systems for mobile machines, displays, software, connection technology, voltage supplies, as well as other accessories.

Motor Protection Electronics, Inc. was founded in 1983 and is located in Apopka, Florida. The company is a manufacturer and designer of industrial controls for several industries including water and wastewater industries to customers around the United States through its distributors. Since its founding, the company has designed and manufactured all parts at its company headquarters in Apopka, Florida. The company’s 10 product segments include phase and voltage monitors, alternators, time delay relays, and intrinsically safe controls.

Industrial Electric Machinery, also known as IEM, was originally founded in 1988 as Northwest Motor Service. IEM serves industrial customers with products and services including motors, relays, transformers, UPS batteries, and more. IEM offers 4 primary product categories: Controls such as low voltage VFDs and transformers, gearboxes & couplings, motors, and power distribution including MCCs and automatic transfer switches. IEM also offers field service including 24/7 availability for troubleshooting, analysis, calibration, field testing, and repairs. Additional services such as training courses and warehousing of spare equipment is also available.

CBIONE founded in Grand Ave Vista, California, USA, in 1980, is a distributor of molded case circuit breakers and other electric products. Products offered by the company are circuit breakers, plugs, fusible switches, relays, and medium voltage contactors. It has completed 6,352 projects and has 864 returning clients. The company also provides services of AC repair, electronic equipment maintenance, and field support. It is a partner of the National Steel and Shipbuilding Company (NASSCO) and QUALCOMM.

National Switchgear Systems, Inc. is a distributor of power and control equipment, specializing in the sale and service of low and medium-voltage circuit breakers and other power distribution equipment. The company was founded in 1986 and is headquartered in Lewisville, Texas. It offers a comprehensive range of services to support critical power systems. These services include shop and on-site services, engineering support, remanufacturing of circuit breakers and switchgear, quality assurance, bus manufacturing, reverse engineering, field services, and training. The expertise extends to power system studies and disaster recovery operations, ensuring the reliability and safety of electrical systems.

Marsh Electronics, Inc. is a distributor of electronic components that was established in 1937 in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The company offers various passive, electromechanical, and power semiconductor products. These products include potentiometers for regulating current and voltage, capacitors for energy storage, and terminal blocks. The company chiefly serves clients in the food and beverage, energy, and medical sectors. Some of its notable customers include companies such as GE Healthcare, Harley-Davidson, and Rockwell Automation.

Air Rite Service Supply, founded in 1964, is a distributor which offers products in every category of air filtration for the commercial, industrial and institutional markets based in Lakewood, Ohio, USA. The company specializes in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), offers heating and cooling equipment, refrigerants, and ventilation solutions. They also manufacture special size, odd size and custom air filters to order, with a full line of air filtration products.

Franklin Electric Europa GmbH, founded in 1944 and headquartered in Fort Wayne, Indiana, is a manufacturer of systems and components used in the movement of water and automotive fuels. Its products include submersible pumps, motors, and surface pumps, and the company is ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certified. Its submersible motors portfolio includes encapsulated and rewindable motors in the range of 0.25kW up to 400kW. The company serves customers in commercial, solar, and agricultural sectors and is present in over 50 worldwide locations. It owns brands like LittleGiant, FPS, and Hydropompe and has a sales turnover of 1.1 billion Euros.

YUEQING RUNEASY ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD., founded in China, is a manufacturer of electricity meter components. The company's product range includes current transformers for smart metering, AC current transformers with fly-leads, current transformers with busbar-y series, DC immune current transformers for energy meter series, and PCB mounting current transformers for energy meters. Its factory has ISO9001 quality system certification and its products conform to domestic and international standards JB/T10665-2016 and IEC 62055-31.

E-T-A Circuit Breakers, founded in 1955 and headquartered in Mt. Prospect, USA, is a manufacturer of circuit breakers for equipment protection and circuit protectors. The company's product portfolio includes circuit protection devices, power management systems, and solid state remote power controllers (SSRPCs). Its circuit breakers are available in more than 150 models and 350,000 different configurations. It also develops intelligent power distribution systems for power distribution and overcurrent protection for industrial applications, watercraft, and vehicles. The company has acquired ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certifications and complies with the RoHS and REACH standards.

Siemens began in 1847 and is headquartered in Munich, Germany. Siemens focuses in automation and digitalization technology and operates globally. Siemens’s 5 operating segments are digital industries, smart infrastructure, mobility, Siemens Healthineers, and Siemens Financial Services. Siemens Financial Services provides debt and equity investment as well as financing solutions. Siemens Healthineers is a medical devices company that provides products and consulting. Mobility includes passenger and freight transportation. Smart infrastructure includes full solutions for electrification. Digital industries offer both software and hardware for industries and production efficiency.

Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corporation is a division of Toshiba focusing on providing designs for end-product developers as well as semiconductor and drive equipment for automotive, industrial equipment, green energy, and consumer and personal electronic devices. Toshiba’s storage products include cloud-scale and enterprise-level products, and PC hard drives. Semiconductor products include Si Cower devices, MOSFETs, IGBTs, IEGTs, isolators, solid state relays, power management and intelligent power ICs, diodes, bipolar transistors, microcontrollers, automotive devices, ICs for wireless communication equipment, general purpose logic ICs, radio-frequency devices, sensors, and linear image sensors.

ERL Phase Power Technologies Ltd., founded in 1993 and headquartered in Winnipeg, Canada, is a manufacturer of digital fault recording systems and protective relays. The company makes TESLA power system recorders, relay test blocks, portable recorders, protection relays, and transformer protection relays used in wind farms, distribution systems, system planning, communications, and industrial systems. It is ISO 9001:2015 certified and provides services like testing, configuration, training, troubleshooting, and updates for the products.

Nissin Electric Co., Ltd., established in Kyoto, Japan, in 1917, is a Supplier of electrical energy by substation equipment, and grid connection technology. The company provides factories and office buildings to realize the optimal operation of energy and technical support. They also provide industrial infrastructure, with an emphasis on power system and energy equipment. Their product range includes gas insulated switchgear, storage battery system, vehicle recognition system, high voltage test product and multiple environmental sensors.

Meiden Europe is a German manufacturer of electrical equipment and systems established in 1996 as a wholly-owned subsidiary of Japan’s Meidensha Corporation, which has been in operation since 1897. Headquartered in Unterschleissheim, Bavaria, the company produces various electrical equipment including surge arresters, inverters, and motors, as well as electrical systems for railway power supply and substation automation. These are utilized in a wide range of industrial processes, such as in power transmission or distribution, water treatment and robotics. Meiden Europe has sales offices and facilities across the European Union, including in France, Switzerland, Slovakia, Austria, and the United Kingdom.

Schneider Electric S.E. is headquartered in Rueil-Malmaison, France, and has been operating since 1836. Schneider Electric provides a number of products and services including electrical car charging, energy management software, surge protection devices, load banks, servers and HMIs, valve and valve actuators, feeder automation, grid automation, and SCADA software products, data center cooling and software, home automation and security, light switches, motion control and robotics, signaling units, solar and energy storage, RFID systems, as well as other hardware, services, and software.

Pilz is headquartered in Ostfildern, Germany. Pilz designs components, systems, and services to assist industrial plant and machinery customers globally. Customers include many industries such as metals, pharmaceutical, food, presses, and robotics. Pilz serves customers through 4 venues: products and industries, services, support, and training. Products and services include everything from sensor technology and small controllers to robotics to software and operation monitoring. Services include machinery and workplace safety and international compliance. Support is offered 24/7. Training is available through courses and qualification programs.

TE Connectivity Ltd., started in 2007 and headquartered in Schaffhausen, Switzerland, is a designer and manufacturer of sensor and connectivity solutions for harsh conditions. It operates three primary segments, namely transport, industrial, and communication solutions, and its product portfolio includes automotive connectors, fiber optic connectors, analog power meters, RTD sensors, and circuit breakers. It serves customers in approximately 140 countries and several industries, including aerospace, automotive, rail, IoT connectivity, and E-mobility. The company manufactures 192 billion products annually and has invested over 610 million USD in research development and engineering.

Omron Corporation, started in 1933 and headquartered in Kyoto, Japan, is a manufacturer of automation components, equipment, and systems, and it developed the first contactless proximity switch in 1960. It has four domains, including industrial automation, electronic components, healthcare, and social systems, and it provides products and services in around 120 countries and regions. Some of its products include microsensing devices, access control systems, industrial robots, surveillance cameras, and blood pressure monitors. In 1971, it developed the first online cash machine, and in 1972, it established Japan’s first welfare factory.

WEG S.A. is an ISO 9001-certified manufacturer of industrial engineering products founded in 1961 and based in Jaraguá do Sul, Brazil. The company produces equipment and products for power generation, control, and coating metal or wood. These include powder coatings for decorative or protective purposes, gas turbines, and dry-type transformers. The company primarily serves clients in the oil and gas, wastewater processing, and mining industries. It also offers maintenance, engineering, and automation services to its customers.

U.S. Tsubaki Power Transmission LLC., founded in 1971 and based in Wheeling, Illinois, is a manufacturer and supplier of motion control and power transmission products and is ISO 9001 certified. Its products include sprockets, conveyor chains, and roller chains used in several industries, including automotive, primary metals, and forest products. It’s a subsidiary of the Tsubakimoto Chain Company, and it has several manufacturing facilities in the United States, including Milwaukee (WI), Sandusky (OH), and Chicopee (MA). The company sells its products through distribution channels but can sell directly to qualified OEMs.

NOARK is based in Pomona, California, and is a global manufacturer of low-voltage electrical components for industrial applications. NOARK specializes in motor controls and protection for original equipment and manufacturers with products covered by five-year limited warranties. NOARK parts are used in numerous solutions such as HVAC and refrigeration, industrial food equipment, panel builders, digital storage, and engine generators. NOARK’s main product lines include low-voltage power circuit breakers, molded case circuit breakers, miniature circuit breakers, overload relays, and circuit control devices.

Celduc Inc. through Celduc Transfo was founded in 1960 as a manufacturer of transformers. Celduc Inc. is based in, France. Celduc Inc. was officially created in 2020 and headquartered in Centerport, New York. Celduc creates electronics and customized products for industries including railway, plastic, packaging, medical, and electronics. Celduc’s main product lines include solid state relays, magnetic proximity sensors, reed relays & switches, and customized products. Customized products are versions of other products adapted for use in industries with special needs such as nuclear power, aircraft, and agriculture.

ABB E-mobility provides electric vehicle charging solutions for customers around the globe. ABB E-mobility offers DC fast chargers as well as AC chargers with focus on reliability and uptime. Since 2010, ABB E-mobility has sold over 50,000 DC fast chargers and over 1 million total AC chargers. ABB E-mobility offers home single and multi-charge units, retail, workplace, and hospitality charge units, electric vehicle fleet sales, as well as public transportation. Additionally, numerous digital solutions and software services are available.

COMITRONIC BTI, established in 1981 and based in Canéjan, Nouvelle-Aquitaine, France, is an ISO9001-2015 certified manufacturer and supplier of safety switches and sensors. The company's product range includes safety switches & safety sensors, pressure switches, safety modules, multi-purpose safety systems, and Atex Gamme. These products are used to ensure safety and monitoring in industries like appliances, electrical, and electronics manufacturing. The products are used in safeguarding machine operators and maintenance personnel from potential injuries. The company offers services such as ISO 13849-1 safety of machinery consultation and SYTCOM - assessment of ISO 13849-1 parameters.

Established in 1992, Fanox is a famous manufacturer and supplier of safe and dependable protection relays headquartered in Pais Vasco, Spain. The company's concept is centered around research and innovation, with a significant allocation of resources towards design engineering. One of the intentions of the energy transition in the power business is to promote and integrate Renewable Energies. This phenomenon results in the developing of a more adaptable and distributed electrical infrastructure, necessitating a digital transformation of the business to manage it effectively.

Fuji Electric Equipment Control was established in 2008 in Saitama-ken, Japan is a manufacturer of power distribution and control equipment. The company boasts an extensive and diversified product portfolio including motor controls, MV distributors, energy control equipment, LV distributors, and industrial control relays. These products find applications in construction as magnetic contactors, automotive as manual motor starters, home appliances as air circuit breakers, health care devices as sensors and switches, and in environmental management for quality assurance and protection of high-voltage electric power and management of low-voltage consumption rate.
Electric Motor Center, Inc. is a distributor of electric drives and motors established in 1978 and based in Arkansas, USA. The company primarily stocks products from global manufacturers such as WEG, Baldor, and Worldwide Electric. These products include AC motors and controls, DC motors and controls, and gear products for utilizing AC or DC power. It also offers motion controls and servos for controlling the position, velocity, or torque of motors. The company mainly markets to its clients in the power generation, public utilities, and metalworking sectors.

Auburn Armature was founded in 1946 and headquartered in Auburn, New York. Auburn Armature is a distributor of electrical products and was recently purchased by Power-Flo Technologies of New Hyde Park, New York. Services that Auburn Armature provide include training, testing, rebuilding, repair, troubleshooting, and training. Parts that Auburn Armature specialize in include automation systems, AC and DC drives, motor controls, motors, motion controls, connectors, wire, boxes, cables, sensors, relays, transformers, panels, struts, terminal blocks, lighting supplies, and conduits.


SCLE is a high-tech company based in Toulouse, France, and was established in 1973. The company is a provider of IT and electronics for energy and rail systems. It includes manufacturing of electronic and computer equipment for high voltage and rail substations for clients working in electricity and rail transport. The company’s principal clients are energy producers, and energy transport/distribution network operators. The services offered are engineering, manufacturing and integration, onsite commissioning and operation, and technical support.

Yaskawa America Inc., started in 1967 and based in Waukegan, Illinois, is a manufacturer of machine controllers, industrial robots, and variable frequency drives and is part of Yaskawa Electric Corporation. Some of its products include industrial AC drives, machine controllers, and IEC programmable robots. The company incorporates the Kaizen method of continuous incremental improvements and Total Quality Management processes to prevent manufacturing defects, and its distributors must be certified and re-certified every two years. It is ISO 9001 certified and is the only industrial drives and motion control manufacturer to win the Deming Medal.

DEIF A/S, founded in 1933 and headquartered in Skive, Denmark, is a supplier of safe power control products for decentralized power generation on land and sea. The company offers products such as single genset controllers, protection relays, HMI control panels, and pitch battery chargers. The company's products are used in land power, whitepapers, webinars, wind power, and marine sectors. It has ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 quality management certifications and also offers training, repair, and consultancy services.

Grid Solutions, established in 1892, is a global producer and distributor of GE Renewable Energy solutions headquartered in Boulogne-Billancourt, France. The company is a part of GE Vernova with over 12,000 employees offering equipment, systems, and services to power utilities and industries, ensuring efficient power delivery from generation to consumers. These include Power Electronics, High Voltage Equipment, Automation & Protection, Software Solutions, and Projects & Services. Addressing the challenges of the energy transition, Grid Solutions provides safe integration of renewable and distributed energy into the grid using HV/MV equipment, gas-insulated substations, and more.

Hybrid Electronics is a global distribution specialist of electronic components, with access to over 50 million unique components. Among the markets HE serves are the aerospace, automotive, communications, defense, industrial, medical, national security, and test & measurement industries. In addition to components, HE also provides quality and compliance testing, counterfeit detection, upscreening, and other forms of quality control. Examples of component subtypes that HE offers include ICs, batteries, capacitors, semiconductor products, sensors, circuit protection, interconnectors, filters, optoelectronics, relays, switches, power supplies, and cables and cable assemblies.

AutomationDirect.com was founded in 1994 to provide solutions for the industrial automation market and has been growing its list of offerings ever since. AutomationDirects’ extensive catalog includes individual components such as cables, various controls, I/O devices, relays, gauges, fittings, and sensors to complete systems. Many parts and devices, especially PLC units are customizable. AutomationDirect.com also provides support via video instructions, online manuals, a learning library, an active community forum to further assist customers.
Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | NOARK Electric North America |
7.0%
|
| 2 | Beckwith Electric Co., Inc. |
5.5%
|
| 3 | Ross Engineering Corp. |
4.6%
|
| 4 | Wisconsin Oven Corporation |
4.6%
|
| 5 | Schweitzer Engineering Laboratory |
4.2%
|
| 6 | Basler Electric Co. |
4.2%
|
| 7 | WOODWARD INC |
3.8%
|
| 8 | Fanox |
3.4%
|
| 9 | Pilz GmbH & Co. KG |
3.1%
|
| 10 | ERL Phase Power Technologies Ltd. |
2.9%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the protective relay page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
16 | 53.3% |
 Germany
Germany
|
4 | 13.3% |
 Japan
Japan
|
2 | 6.7% |
 France
France
|
2 | 6.7% |
 China
China
|
1 | 3.3% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 3.3% |
 Canada
Canada
|
1 | 3.3% |
 Spain
Spain
|
1 | 3.3% |
 Austria
Austria
|
1 | 3.3% |
 Denmark
Denmark
|
1 | 3.3% |
36 products found
36 products
Irie Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Features ・When a voltage drop occurs, servos, etc. are safely stopped with DC backup. ・Maintenance free ・Half the size and cost for AC output v...
Irie Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Features ・Outlet type that can be easily replaced with UPS ・Capacity 800VA (desktop type, rack mount type) ・Maintenance free ・High efficiency ...
Irie Co., Ltd.
250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
■Features Protects against instantaneous voltage sags and instantaneous power interruptions. This is a device designed specifically for instantaneo...
WIN SOURCE ELECTRONICS
160+ people viewing
Last viewed: 17 hours ago
■Summary Protection relays and systems are essential to protect electrical circuits and equipment from faults such as overcurrents, voltage abnorma...
Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd.
130+ people viewing
Last viewed: 19 hours ago
■High capacity cutoff relay ・400V DC high voltage switching possible. Lineup with current capacity up to 300A ・Main applications: Solar power gen...
Panasonic Industry Co., Ltd.
120+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
■High capacity cutoff relay ・400V DC high voltage switching possible. Lineup with current capacity up to 300A ・Main applications: Solar power gen...