All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for gaskets as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 164 gasket manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked gasket companies as of July, 2025: 1.Gates Corporation, 2.Rees, Inc., 3.Gilson Company, Inc..
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Gaskets
1985-2014: Worked for Alstom Corporation, ABB Corporation, and Gadelius Corporation, designing Jungstrom air preheaters and mechanical design of diamond soot blowers. (ABB Corporation: https://new.abb.com/jp)
2014-2021: Worked as an engineering and project manager at Alvos Inc.
https://www.linkedin.com/in/yoichi-hiroki-92192394/
 A gasket is a part or material used in equipment, structures, piping, etc. to maintain airtightness and sealing to prevent internal fluids from leaking out.
A gasket is a part or material used in equipment, structures, piping, etc. to maintain airtightness and sealing to prevent internal fluids from leaking out.
In general, there are two types of gaskets and packings for sealing purposes. Gaskets are mainly used for "motionless" or "non-moving" parts. Gaskets are mainly used for "motionless" or "non-moving" parts, while packing is mainly used for "moving" or "movable" parts.
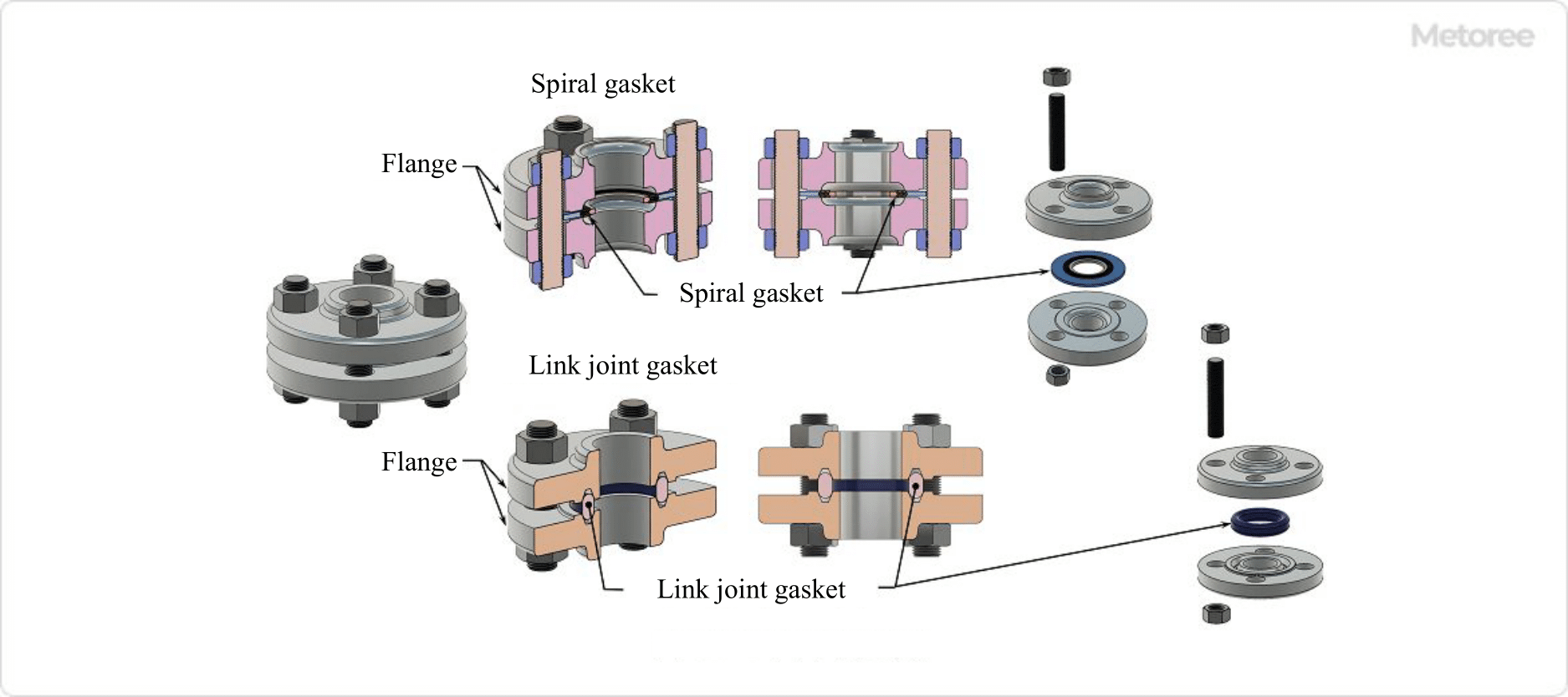
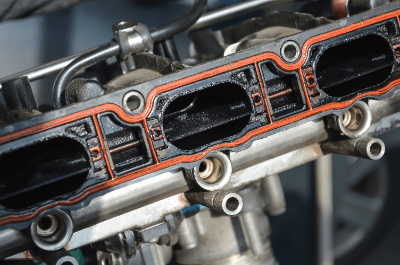
Figure 1. Example of gasket use (1)
Gaskets are used to fill and seal gaps in flat areas such as pipe flanges, machine joints, and covers. The main reason is to prevent leakage of internal fluids by maintaining and sealing tightness, but they are also used to prevent foreign matter from entering through gaps in joint surfaces.
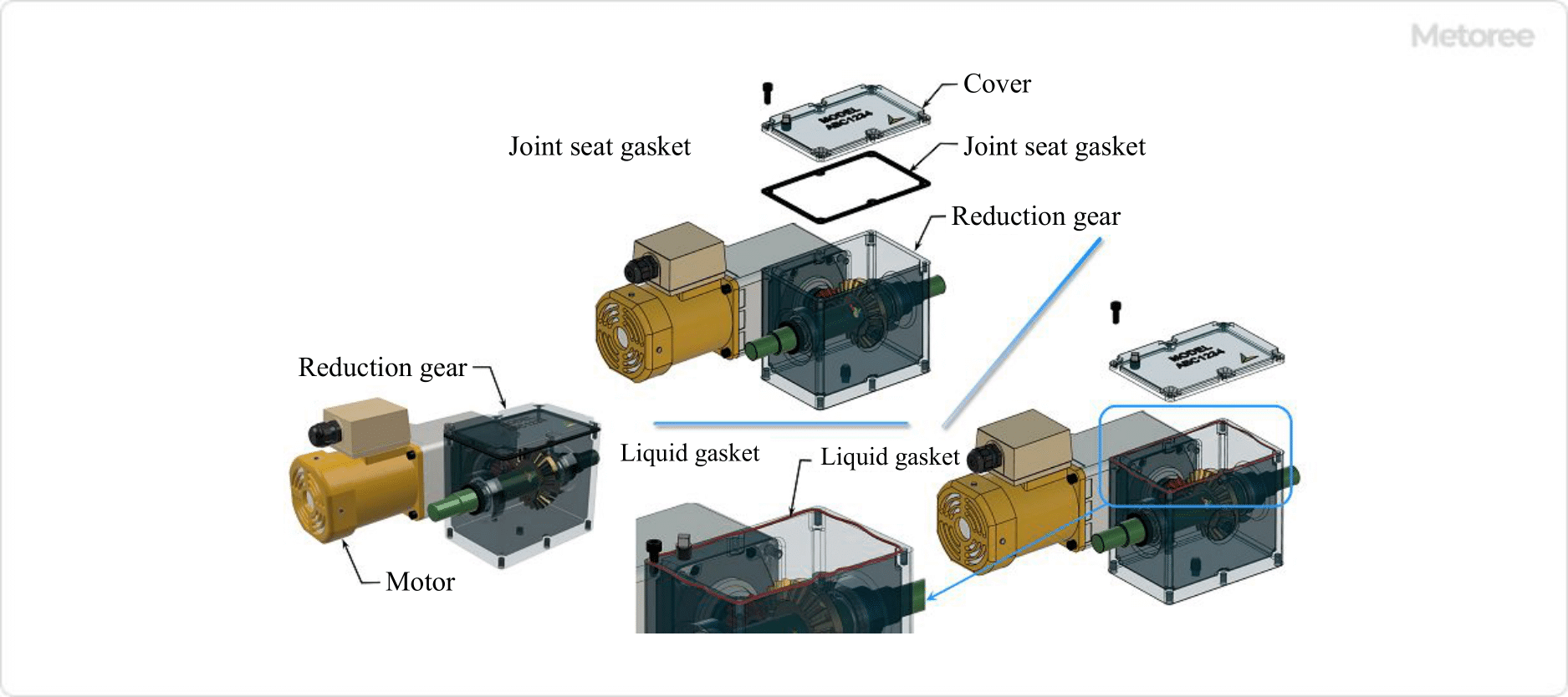
Figure 2. Example of gasket use (2)
Generally, gaskets are inserted between joint surfaces and tightened with screws or bolts to enhance sealing by the surface pressure.
Gaskets are inserted between joints of piping flanges or machine parts, tightened by screws or bolts, compressed to a certain thickness and shape, and sealed by the surface pressure. Therefore, the proper tightening method and tightening force of gaskets vary depending on the material, thickness, shape, structure and material.
In particular, for gaskets for pipe flanges and pressure vessel flanges, the following standards specify the tightening method and control method. It is necessary to refer to these standards and each manufacturer's proper tightening surface pressure for optimum tightening management.
In general, when used for flanges, the tightening force required to seal the fluid is the bolt load (tightening force) in service (Wm1) and the bolt load (tightening force) when tightening the gasket (Wm2), as specified in JIS B8625.
Liquid gaskets are applied to the joint surface and tightened to form a uniform, hardened, adhesive thin film that provides a tight seal.
There are various types of gaskets, depending on the material, shape, and structure. See the table below for the main types.
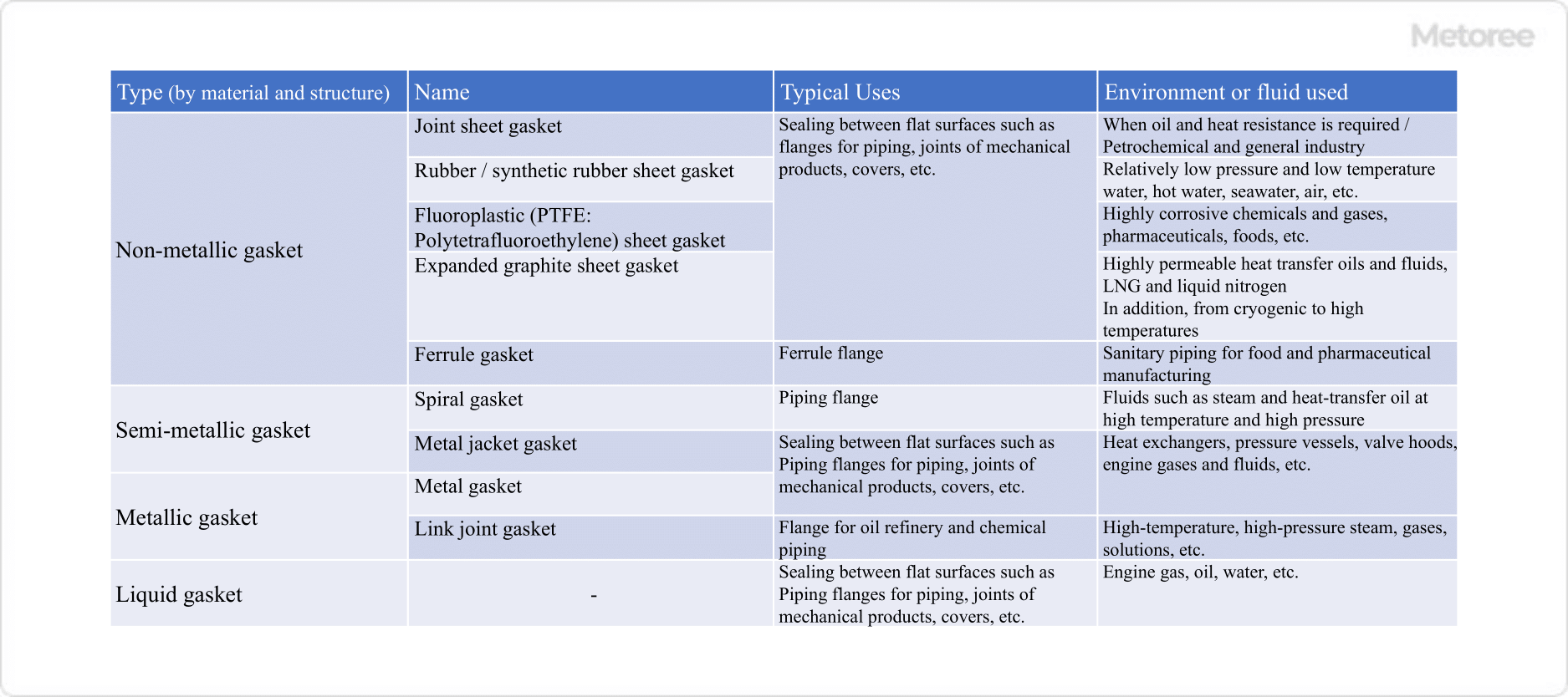
Figure 3. Types of gaskets
Joint Sheet Gasket
Joint sheet gaskets are gaskets made by adding rubber and fillers to glass fiber material, rolling, and vulcanizing to form a sheet. The sheet material is punched or cut to the size and shape of the joint surface of piping flanges and machine parts. They are used in a wide variety of situations, with a high degree of dimensional flexibility, and are used in a wide range of applications, from high and low temperatures to high and low pressures, and are also highly versatile with excellent oil and heat resistance.
Rubber and Synthetic Rubber Sheet Gaskets
Rubber and synthetic rubber sheet gaskets are sheet gaskets made of natural rubber, nitrile rubber, silicon rubber, and other materials. They are punched or cut to the required size and shape. They are used for relatively low-pressure and low-temperature fluids.
Fluoroplastic PTFE Sheet Gasket
This gasket is a sheet of fluoroplastic PTFE compression-molded gasket. Inorganic fillers and carbon-based fillers are added to improve heat resistance, chemical resistance, acid resistance, and alkali resistance. They are used for highly corrosive chemicals, food piping flanges, and equipment.
Expanded Graphite Gasket
These gaskets are made of graphite that has been treated with chemicals, heated to a high temperature for expansion, and formed into a sheet shape. They are punched or cut to the required size and shape. Since the sheet by itself has low strength, some are reinforced by sandwiching or laminating a thin stainless steel plate between them to increase strength.
It has excellent heat and chemical resistance, and is used for flanges and equipment in general-purpose piping. They are also used for flanges of piping for highly permeable fluids, cryogenic LNG and liquid nitrogen.
Ferrule Gasket
The Herule gasket is a standard gasket that conforms to the Herule flange for sanitary piping. Materials include ethylene-propylene rubber (EPDM), fluoroplastic (PTFE), and silicone rubber. These gaskets are used in flanges for food, pharmaceutical and chemical piping, and equipment.
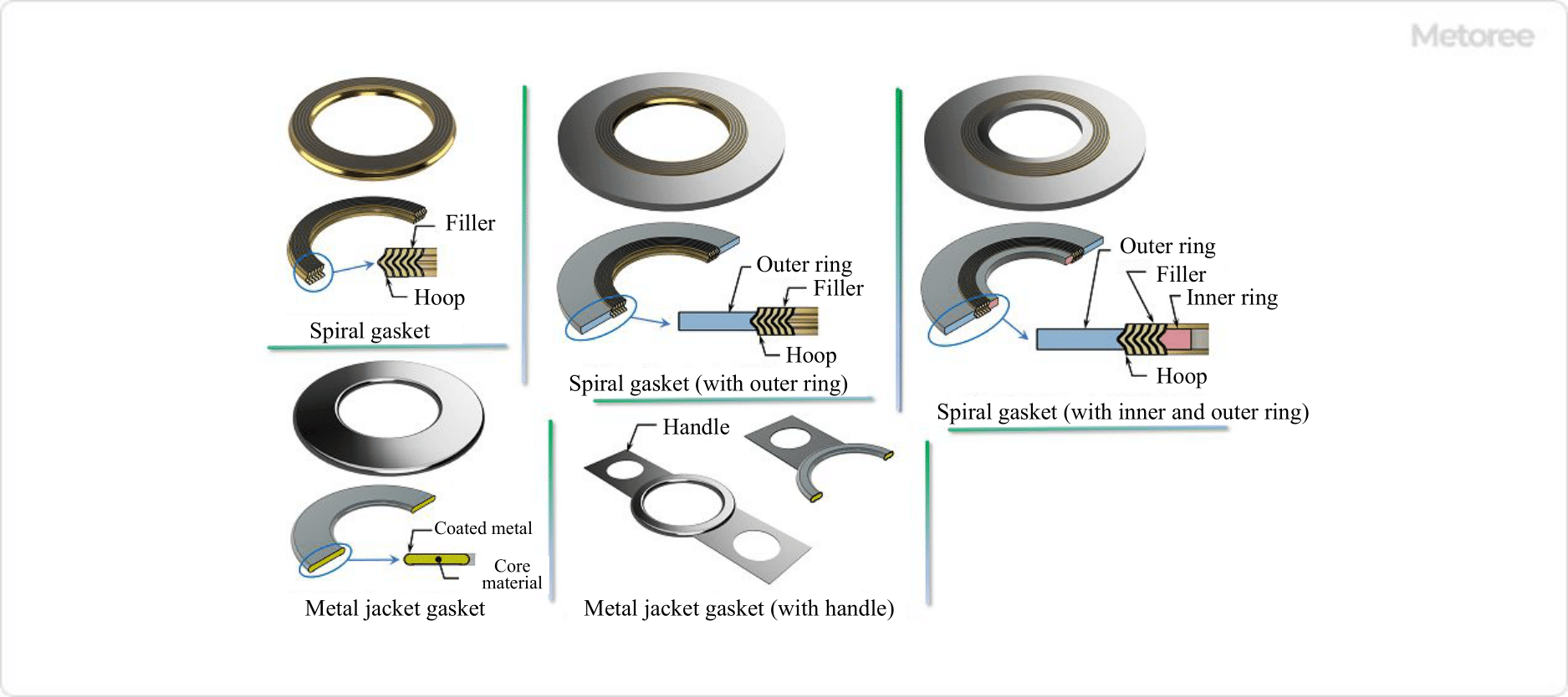
Figure 4. Semi-metallic gasket
Spiral Gasket
A spiral gasket is a gasket consisting of a hoop of thin iron or stainless steel sheet formed into a V-shaped cross section and a buffer material of the same shape, such as expanded graphite, fluoroplastic PTFE, or non-asbestos paper, alternately wrapped around the hoop.
The state consisting of hoop and filler is the basic form. In addition to the basic type, there are gaskets with an outer ring for proper positioning of the flange joint surface and with an inner ring to reduce deformation due to tightening force. These gaskets are used for flanges for fluid piping such as high-temperature, high-pressure steam and heat-transfer oil.
Metal Jacket Gasket
Metal jacket gaskets are gaskets consisting of a highly heat-resistant core material (cushioning material) wrapped around a thin coated metal plate of carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, or Monel (nickel-copper alloy). They are used for high-temperature, high-pressure, acid- and alkali-resistant piping flanges and equipment joints such as heat exchangers and pressure vessels.
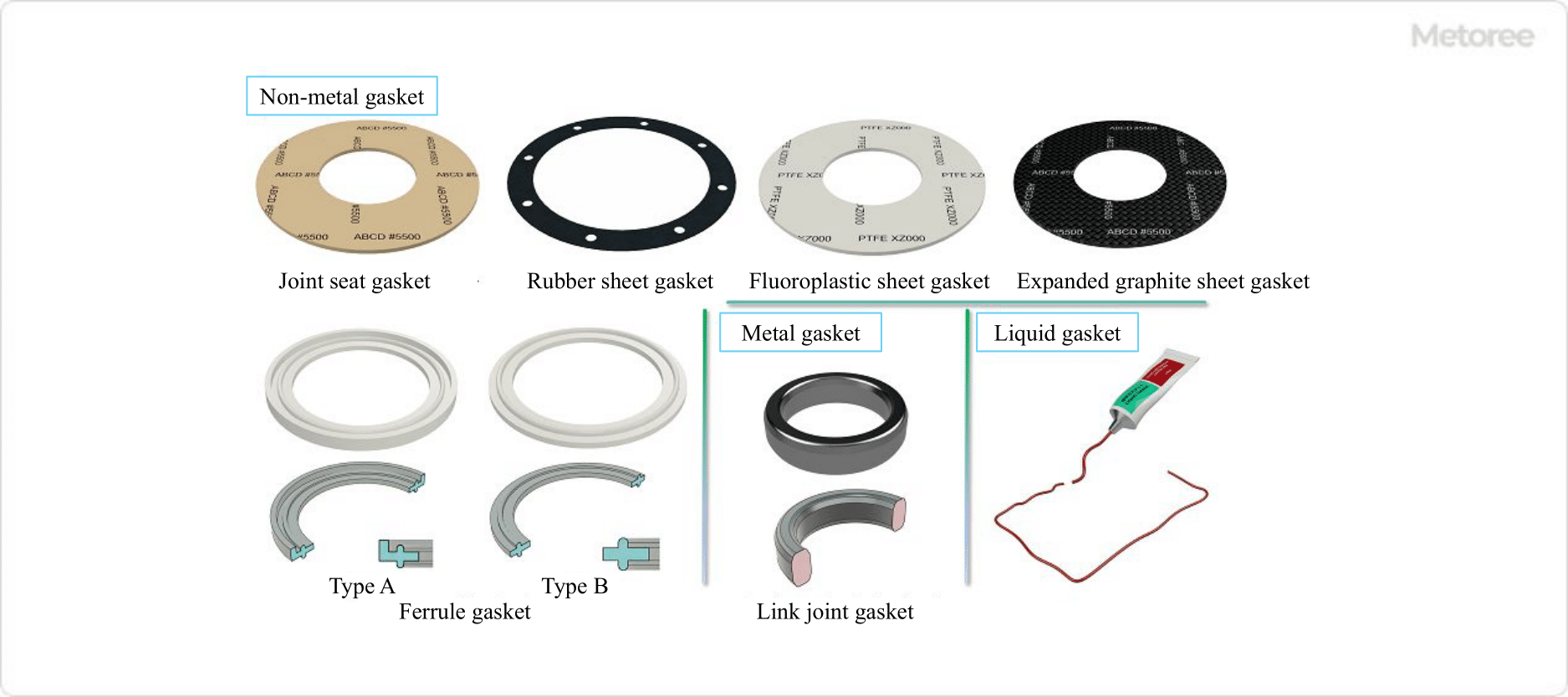
Figure 5. Non-metallic gasket, metallic gasket, and liquid gasket
Metal Gasket
Metal gaskets include "metal corrugated gaskets," which are thin mild steel or stainless steel sheets bent into a corrugated cross section and processed into a ring shape; "metal flat gaskets," which are single sheet rings of mild steel or stainless steel sheets; and "saw-tooth gaskets," which are circular V-shaped grooves processed on the back surface of a flat shape. These gaskets are used for cylinder block and cylinder head joint surfaces of engines and flanges for high-temperature, high-pressure piping.
Ring Joint Gasket
Ring joint gaskets are made by machining forged metal into a ring shape and fitting it into a ring groove on the flange joint surface. The cross section of the ring can be oval, octagonal, hexagonal diamond, triangular delta, or round.
Materials include mild steel, stainless steel, Monel (nickel-copper alloy), titanium and aluminum. They are used in equipment joints such as flanges for high-temperature, high-pressure steam, gas, and oil piping, and pressure vessels.
Liquid gaskets are used in a variety of situations, such as PVC pipes for rainwater drainage and engine joints. They are low-cost because they are effective even when applied in small quantities, and because they blend well with the joint surface, they provide good sealing even at low tightening surface pressure and relatively low machining accuracy, and they require no retightening, which makes them highly efficient in operation.
There are several types, including organic solvent (modified alkyd-based, fiber ester-based, synthetic rubber-based), solvent-free (phenolic-based, modified ester-based, silicone-based, acrylic-based), and water-based types (water-based acrylic-based).
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

American Cast Iron Pipe Company, headquartered in Birmingham Alabama is a manufacturer of valves, fire hydrants, and pipes established in 1905. The pipes include spiral-welded steel and ductile iron pipes utilized in the waterworks sector. The firm produces high-frequency welded steel pipes for the energy and carbon capture sectors. Fire pumps, structural casing, piling, castings, and specialty rubber goods are manufactured. The goods are employed in pipeline dredging, structural facilities, mining, and mining, the goods go through finished pipe inspection, pipe stenciling, hydrostatic, ultrasonic, and lab testing before sell.

Frenzelit Inc., founded in 1881 and headquartered in Bad Berneck, Germany, is a manufacturer of gaskets, insulation, and expansion joints. The company produces and sells seals and sealing materials, insulation and insulation materials as well as expansion joints for global industrial customers. It develops products for a range of markets including renewable energies, electromobility, and fire protection. The company's management system complies with IATF 16949/ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 50001 for quality, environmental, and energy management systems.

Gilson Company, Inc. is an American manufacturer and supplier of construction material testing equipment based in Lewis Center, Ohio. The company was established in 1939 with a primary focus on manufacturing the testing screen, a laboratory-scale screening machine, to cater to the mining and highway construction industries' requirements. Over time, Gilson has expanded its product portfolio and now offers a wide range of equipment, including ovens and furnaces, scales and balances, general laboratory testing equipment, as well as material testing equipment for aggregates, asphalt, concrete, and soils.

Roettele Industries, Inc. is an ISO 9001:2015-certified manufacturer of non-metallic connectors, seals, and diaphragms for the industrial sector established in 1979 and located in Chino, California, USA. The company’s products include washers and gaskets fabricated from thermoplastic elastomers, plastic, and rubber. It also offers seals and diaphragms made from plastic compounds such as polyethylene (PE), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and polystyrene (PS). The company’s products are commonly used in medical device manufacturing, automotive production, and irrigation operations.

DuraTech Industries, founded in 1977, is a manufacturer of custom graphics and die-cut components in Commerce Street, La Crosse, WI. The company is Thomas-certified and produces graphic overlays, touch screens, printed electronics, in-mold decorating, and structural electronics. It also manufactures membrane switches, flexographic labels, fills nameplates, and keypads used in appliances, automotive, electronics, industrial, and medical industries. The company offers bin stocking, prototyping, engineering, product development, and large program management services.

Gates Industrial Corporation began in 1911 in Denver Colorado where the company remains today, with additional headquarters in Europe and Asia. The company is a manufacturer of power transmission and fluid power solutions to customers around the world in industries such as agriculture construction, automotive, mining, and heavy-duty industrial equipment. The company’s products include CVT transmission belts, serpentine kits, hydraulic hoses, electric water pumps for electric vehicles, and rubber synchronous belts used in material handling applications.

3M Company was founded in 1902 and is headquartered in St. Paul, Minnesota. 3M provides diversified technology services globally. 3M operates through four segments: Safety and Industrial, Transportation and Electronics, Health Care, and Consumer. The Safety and Industrial segment offerings include industrial abrasives, masking, and natural and color-coated mineral granules for shingles. The Transportation and Electronics segment offerings include ceramic solutions, light management films, and electronics assembly solutions. The Healthcare segment offerings include wound care, dentistry and orthodontia solutions, and filtration and purification systems. The Consumer segment offerings include consumer bandages, picture hanging, and stationery products.

AutoVac Industrial Vacuum & Air Systems, generally known as AutoVac, was founded in 1989 and centered in the town of Lake Tahoe, Nevada. AutoVac serves automotive, aerospace, medical, dental, and industrial manufacturing industries. AutoVac is a designer for manufacturing and production vacuum systems. AutoVac uses CAD to design systems such as factories and industrial production factoring in material cost, installation and operation labor, and electrical usage. Autovac can install or provide installation supervision, commissioning support, and new product development and prototyping.

FedTech was founded in 1996 and is headquartered in Mounds View, Minnesota. The ISO 9001:2015 certified company is a manufacturer and value-added service provider of machining services for several industries including automotive, aerospace, medical, and manufacturing industries. The company’s vertically integrated machining services include laser and waterjet cutting, CNC machining, metal fabrication, and finishing services. Services include assembly and sub-assembly, heat treating, liquid and powder painting, packaging & kitting, and custom material procurement.

Aavolyn Corp. was established in 1996, and is a manufacturer and supplier of compressor replacement parts. The company specializes in providing sealing products for customers' need. Their compressor replacement parts include piston and rider rings, rod and wiper packing, pistons and rods, bushings, and pump packings. Additionally, they offer compressor packing assemblies and custom machine parts. This company also provides various services, including natural gas service, specialty gas service, process service, and air services, as well as offering industrial machined parts.

Rees, Inc. began in 1929 and is based in Fremont, Indiana. The company is a designer and manufacturer of electromechanical and industrial control switches that serve the automotive, conveyor, material handling, food processing, and other manufacturing industries. The company manufactures its parts in the United States in ISO 9001:2015 certified facilities. The company’s product categories include various types of switches, control units, contact blocks, and push buttons. The company offers modification options on most parts available upon request.

Thomas A. Caserta, Inc, is an American-based manufacturer of rubber products and parts since 1948 whose headquarters are in Robbinsville, New Jersey. The company’s product portfolio includes washers, bushings, gaskets, cords & tubing manufactured from materials such as EPDM, neoprene, nitrile, SBR, silicone, and Viton. The company uses manufacturing methods such as high-speed on-demand cut, lathe cut, guillotine cut, die cut, and hand cut processes depending on size, tolerance, and material required. The company offers services such as designing, prototyping, compounding, cutting, and extruding.

Based in Bayville, NY, SAE Manufacturing Specialties Corp. is an ISO-certified supplier and manufacturer of industrial equipment, chemicals, components, ordinance, electronics, and systems for industries ranging from aerospace to high tech to law enforcement. Examples of product offerings include raw materials, chemicals, and lubricants for industrial purposes to finished products such as security helmets for law enforcement, and military ordnances. SAE also provides research and development as well as technical support for other companies in similar industries.

PennEngineering, established in 1942 in Danboro, Pennsylvania, USA, is a manufacturer and supplier of fastening solutions. The company's main products include self-clinching nuts, studs, and standoffs, as well as inserts, spacers, and access hardware, used in various industries such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive. PennEngineering's fastening solutions play a crucial role in providing secure joining of components, ensuring structural integrity and performance. PennEngineering collaborates with clients to provide efficient solutions for their fastening needs. The company's aim for quality and precision has made them a dependable partner for businesses seeking good performance in fastening solutions.

Atlantic Gasket Corporation (AGC) is an American manufacturer of custom and standard gaskets founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1947. The company produces various gaskets, as well as cushioning, insulation, and vibration damping tapes, cork and rubber molded products, and cabinet bumpers. These are used extensively in the manufacturing processes of the construction, automotive, electrical, and appliance sectors. AGC also offers material selection, waterjet and die cutting, and lamination services for contract production of gaskets according to customer specifications.

Pure Rubber Products Co., established in Rockaway, NJ in 1935, is a manufacturer of Precision Molded Parts custom rubber parts in Natural & Synthetic. Their product portfolio includes Pump components such as diaphragms, valves, and gaskets, Packaging cups & caps, Switches, Dampers and Odd-shaped O-rings. The company serves industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, consumer goods, and industrial equipment. They also provide services including product selection, installation, preventative maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.

Clippard Instrument Laboratory, Inc. was founded in 1941 in Arkansas and is now located in Cincinnati, Ohio. The company is a manufacturer of miniature pneumatic valves, specializing in ultra low leak, precision pressure control, and high-resolution flow control. Categories of Clipard Products include electronic valves, proportional valves, isolation valves, electronic controls, custom solutions, ppressure regulators, control valves, directional control valves, air pilot valves, air preparation equipment, and fittings hose, and tubings.

AGE Nameplate is an American ISO 9001 certified membrane switch manufacturer that was established in 1973. Based in Santa Fe Springs, California, the company primarily designs and produces custom membrane switches, as well as nameplates, graphic overlays, decals, and rubber keypads. These have various applications including in weapons systems, production machine controls, medical instrumentation, and gaming consoles. AGE Nameplate products serve clients in the aerospace, military, consumer electronics, medical, and industrial markets.

Orca Marine Cooling Systems, established in Bellingham, WA, in 1973, is a manufacturer of marine heat exchangers and cooling systems. Their product portfolio includes engine cooling systems to ensure optimal temperature regulation and performance for marine engines, seawater desalination cooling systems, and engine cooling systems to ensure optimal temperature regulation and performance for marine engines. The company serves industries such as Commercial Shipping and Cruise Lines, Naval and Defense Vessels, Offshore Exploration and Oil Platforms.

Alan Manufacturing Inc. was founded in the year 1952 and has been involved in producing products in the HVAC industry. They reside in the United States of America in the state of Ohio in the city of Wooster. The products the company provides are parts for HVAC equipment such as dampers as well as products for ducts. They cater to their customers needs and provide products based on their specifications.

Woods Manufacturing Co. established in 1978 and headquartered in Wood Dale, Illinois, is a manufacturer of precision screw machine products and components. Their product range includes screw machinery equipment, CNC swiss screw machines, and components. These products are utilized in sectors such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and medical. Woods Manufacturing Co. ensures the quality of their products through relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, meeting industry standards. Their offerings enhances efficiency and productivity in industrial applications such as in manufacturing and assembly processes.

International Crystal Laboratories, ICL, was founded in 1962 and is based in Garfield, New Jersey. ICL serves the spectroscopy, applied spectroscopy, and analytical chemistry industries and end users. ICL’s product categories include transmission windows & optics, FTIR calibration films, sample cards, powders, cuttings, IR, UV, optical spectroscopy sampling, laboratory presses, die sets, laboratory supplies, and spectro-optic lab supplies. Examples of ICL’s products include circular disks, magneto crystals, crystal cuttings for grinding, Gemini FTIR gas analysis cells, liquids, and solids, polishing kits, and laboratory grinding mills.

Polar Hardware Mfg. Co., Inc. is a custom manufacturer of door and truck body hardware for industrial applications. It is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, and was established in 1959. The company offers a wide range of door and truck body hardware, including spring bolts and handles, hinges and latches, bars and locks, rope rings and steel rods, as well as cams and lugs, retainers, spacers and gas springs. Polar Hardware also offers several finishes, including zinc-plated, stainless steel, and chrome-plated. The company's customers include truck manufacturers, trailer manufacturers, and industrial equipment manufacturers.

Industrial Magnetics Inc (IMI) was established in 1961 and is based in Boyne City, Michigan. IMI is a producer for magnetic products used in various industries such as fabrication, automotive, conveying, recycling, stamping, welding, mining & aggregate, and grain. Product offerings include magnetizers, demagnetizers, conveyor systems, magnetic conveying rail, manhole cover lift systems, raw magnetic material, lift devices, conveyor and pneumatic line magnets, magnetic inspection probes, as well as numerous magnetic tools.

Aero Rubber Company began in 1973 and is a family-run business based in Tinley Park, Illinois. Aero Rubbery Company is a custom manufacturer of rubber components such as tubing, sheeting, seals, and gaskets. Aero also offers fabrication services including die cutting, water-jet and lathe cutting, slitting, and vulcanized splicing. Aero Rubber is an ISO 9001:2015 certified company. Aero Rubber manufacturers use materials such as Viton, Neoprene, EPDM, silicone, and rubber materials. Aero Rubber manufacturing includes molded parts such as gaskets, extruded parts, sheeting, fabricated parts, and mandrel-made parts. Value-added capabilities are also offered.

Thermwood is based in Dale, Indiana, and operates as a multinational diversified CNC machinery manufacturer that markets its products and services globally through offices in 11 countries. The company primarily serves the woodworking, aerospace, plastics, and composites industries but also serves almost every major industry from medicine to entertainment. The company’s products include both hardware and software. Hardware includes 3-axis and 5-axis CNC routers and LSAM machines. Software offerings include Mastercam, Moldplus, and THM Desktop among others.

Dymax Corporation was founded in 1980 and is headquartered in Torrington, Connecticut. The company develops and manufactures rapid and light-curable materials and light-curing systems for the medical, consumer electronics, wearables, aerospace, and automotive electronics industries. The company’s product segments include Light Curable Materials, Light-Curing Equipment, and Dispensing Equipment. Light Curable Materials include masking, gasketing, and activators. Light-Curing Equipment includes conveyor systems, flood-curing systems, and radiometers. Dispensing Equipment includes dispense valves, syringe dispensers, and material reservoirs. The company also offers application engineering, equipment, and system integration services.

California Sealing Solutions, established in 2014, is a manufacturer of custom and standard parts, including door & dam gasket kits, pump repair kits, mechanical seals, leveling vials, and cable slings from materials such as rubber, silicone, polyurethane, ethylene propylene, and PTFE. The products are used in machinery, construction, and manufacturing sectors. The Irvine, CA-based company offer services such as metal stamping, rubber & plastic extrusion, plastic injection molding, aluminum die casting, and O-rings creation of international standards as the company is ISO 9001:2008 certified.

H&S Manufacturing Co., Inc., established in 1968 and headquartered in Garland, Texas is a custom manufacturer specializing in precision sheet metal fabrication, machining, assembly, and testing. Its product portfolio encompasses enclosures, chassis, panels, brackets, cabinets, as well as racks, and frames. The company is proficient in managing Covered Defense Information (CDI), adhering to DFARS Clause 252.204-7012. Additionally, its comprehensive services also extends to engineering design, prototyping, testing, and quality control of the products.

Wisconsin Foam Products (WFP) is an American manufacturer of flexible foam products and accessories founded in 1985 and based in Madison, Wisconsin. The company offers wood crates and pallets, foam solutions for applications like bedding, filtration, packaging, as well as shipping boxes and various laminated items such as protective covers and fabricated products. These are primarily used in the furniture, medical, and marine sectors, as well as in the packaging industry. WFP also provides their clients with additional design, logistics, and OEM services.

Anti-Seize Technology Inc (AST) was founded in 1971 and is headquartered in Franklin Park, Illinois. AST is a global manufacturer and supplier of anti-seize compounds for petroleum, food processing, steel, paper, transportation, earth moving, agriculture, mining, fire protection, plumbing, and construction industries. Product offerings include anti-seize compounds, thread sealants, anaerobic thread lockers, casketing, sealing-caulking and adhesives, food grade products, plumbing specialties, lubricants-penetrants, protectants, coatings, greases, aerosol cleaners-degreasers, hand cleaners, and lubricant application equipment.

Morris Coupling is a family-owned company that was founded in 1941 and is headquartered in Erie, Pennsylvania. Morris is a manufacturer of compression coupling and components for pneumatic conveying and industrial vacuum systems. Morris Coupling has additional manufacturing facilities in Tennessee and Georgia, as well as distribution centers in Mexico, Europe, and Asia for international customers. Morris Coupling 7 product lines include couplings, flex hose, bends, and installation components. Most products are available in multiple configurations.

AmeriStar Manufacturing, Inc. was established in 1908 and headquartered in Mankato, Minnesota. The company is an ISO 9001:2015 certified full-service metal manufacturing company capable of on-site tool making. The company’s services include metal stamping, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, electro-mechanical assembly, and engineering & tool building. The company provides support for SMI, VMI, and Kanban programs to support customers’ inventory management as well as other contract manufacturing services including warehousing and shipping.

Century Rubber was founded in 1973 and is headquartered in Bakersfield, California. The company is a manufacturer of precision custom elastomer components such as rubber seals & die cut gaskets for aerospace, defense, electronics, medical, and other industries. The company’s fabrication methods include homogeneous molding, die cutting, rubber-to-metal and rubber-to-plastic vulcanizing. The company is ISO 9001 and AS9100D certified and works with such materials as silicone, ferrosilicon, Neoprene, Nitrile, and millable urethanes.

CS Hyde, Company was founded in 1996 and is headquartered in Lake Villa, Illinois. The company is a manufacturer of high-end materials including adhesives, films, and rubber for customers from numerous industries including automotive, electronics, and large batteries. The company’s main products include pressure-sensitive tapes, silicone rubber sheets, threading, and 3D printing surface materials. The company also provides numerous services such as slitting, die and dieless cutting, sheeting, and belting. Other services include material conversion such as applying adhesives to films.

Fluoro-Plastics, Inc., founded in 1951, is a manufacturer of fluoropolymer products, with its headquarters also located in Bristol, Pennsylvania. Their extensive product range includes PTFE sheets, films, rods, tubes, and custom-molded parts, as well as PTFE coatings for various substrates. These products exhibit chemical resistance, thermal stability, and electrical properties, and are utilized in industries such as chemical processing, food and beverage, medical, aerospace, and electronics. The company hold ISO 9001:2015 certification for their quality management, and USP Class VI certification.

Precision Associates, Inc., founded in 1955 and based in Minneapolis, Minnesota, is a manufacturer of custom rubber seals, molded rubber parts, and rubber o-rings. Some of the products that the company offers are standard and metric o-rings, quad rings, backup rings, oil seals, gaskets, and custom molded rubber parts. These products are used for sealing, cushioning, vibration damping, and noise reduction in various devices and systems. The company has ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 13485:2016 certifications, which show its adherence to quality standards and customer requirements.

Wisconsin Oven Corporation has operated since 1973 and is located in East Troy, Wisconsin. Wisconsin Oven designs, engineers, and manufactures industrial ovens and other heating equipment for numerous applications including heat treating, powder coating, paper pulp drying, finishing, drying, and curing in the aerospace, automotive, composite, energy, finishing, foundry, heat treating, annealing, military, and pharmaceutical industries. Types of ovens and equipment include custom and standard batch ovens, conveyor ovens, pollution control equipment, and walk-in ovens.

Minnesota Rubber & Plastics was founded in 1946 and is headquartered in Minneapolis, Minnesota as a subsidiary of Trelleborg Group. The company is a designer and manufacturer of rubber and plastic components for medical devices, water, food, & beverage, specialty industrial, infrastructure, and automotive markets. The company’s core solutions include custom and standard parts. Standard parts include assemblies, inflatable and compression seals and gaskets, and Pawling Engineered Products. Custom parts include custom molded rubber, LSR injection molding, and molded plastics.

Tricomp, Inc. is a manufacturer providing sealing and gasketing solutions, headquartered in Pompton Plains, New Jersey. Their product range includes weather strippings, shower door magnetic strips, and flexible magnetic strips. These products are designed to create a tight seal, preventing leaks, providing insulation, and protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and noise. They also offer double bulb seals and options with or without pressure-sensitive adhesive. Tricomp, Inc. uses NSF, FDA, and UL approved materials, guaranteeing compliance with industry standards.

Nadco Tapes and Labels, Inc., headquartered in Sarasota, Florida, is a manufacturer and supplier of adhesive tapes and labels. The company serves various industries including packaging, automotive, electronics, and logistics. Their product range includes pressure-sensitive tapes, custom labels, and specialty adhesive solutions, which are used for packaging, branding, product identification, and sealing applications. Nadco holds certifications such as ISO 9001, ensuring compliance of products to industry standards, while providing effective adhesion, durability, and functionality for efficient operations and brand integrity in industrial settings.

Johnson Bros. Metal Forming Company was founded in 1947 in Chicago, Illinois as a manufacturer of roll-forming machines. Today the company is based in Berkeley, Illinois, and has a much-expanded product line serving industries such as agriculture, communications, glass, sports products, and woodworking. The company’s roll-forming capabilities include compatibility with materials such as brass, aluminum, titanium, and other metals. The company is capable of manufacturing products as varied as framing, hats, wireways, tubing, and cable trays.

Chambers Gasket & Manufacturing Co., founded in Chicago, Illinois, in 1937 is a manufacturer of gasket materials. The company's product portfolio includes Custom Die Cuts, Gaskets & Seals, Waterjet Cuts, and cutting tables. The company serves industries such as Oil and Gas, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Construction, and Power Generation. They also offer custom packaging, Bar-Coding for tracking materials Lean Manufacturing Support, warehousing and distribution services, and customer support.

Edgewater Products Co. (EPC) is an American contract manufacturer of non-metallic products specializing in design and fabrication services since 1947. Located in Chicago, Illinois, the company fabricates items from various materials such as rubber, silicone or plastic using processes like lathe, die, and water jet cutting, as well as stripping and molding. EPC manufactures products such as gaskets, expansion joints, and plastic spacers for clients including Intex Technologies, Pulver Packaging, and Polymer Contours, Inc.

MCMILLANCO, LLC is a manufacturer that provides custom component manufacturing solutions, based in West Liberty, Ohio. The services provided by MCMILLANCO, LLC are primarily focused on manufacturing processes. They offer services such as aluminum sand casting foundry, machining, metal stamping, injection molding, and vapor deposition coating. These services are utilized in the manufacturing industry to produce components, parts, and finished products such as in medical device manufacturing, steel fabrication, natural gas, defense, and film production.

Vanguard Products Corporation is headquartered in Danbury Connecticut. The company is an ISO 9001:2015 certified full-service manufacturing and engineering company providing the industry with precision elastomeric fabricated goods, producing all custom and standard goods in the United States. The company offers custom rubber and silicone products, as well as standard products including food-grade silicone tubing, rubber tubing, and fabricated EMI and RFI shielding products. The company also offers a materials configurator for customers to design with their own materials based on preference for qualities and resistance to various elements.

Gasket Express, established in Worcester, Massachusetts is a manufacturer of Die Cutting, Gasket Material, and Machined plastic products. The company's product portfolio includes sheet and roll gasket material, vulcanized o-rings, molded rubber products, fabricated gaskets and plastic die cutting. Their products are used in industries such as Electronics and Telecommunications, Automotive, Transportation and aerospace and Defense. The company also provides services including national distribution, product selection, customized services, technical support and customer service.

Stockwell Elastomerics, Inc., established in 1919, is a manufacturer of silicone gaskets, cushioning pads, seals, and elastomeric components used in technology, medical, air & space, electrical, and defense fields as they can perform in temperature extremes. Based in Philadelphia, PA, the company is a member of GFA, ARPM, and The Chamber business associations and partnerships with companies such as Rogers Corporation, Saint-Gobain, SPP, and 3M. Stockwell Elastomerics is ISO 9001:2015, NQA certified, an ITAR-registered rubber components supplier to the U.S. defense sector.

Southern Rubber Co. Inc. was chartered in 1925 and is headquartered in Greensboro, North Carolina. The company is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer and fabricator of rubber-based products. The company’s product segments include gaskets, extrusions, industrial hoses & tubing, adhesives, and O-rings & seals. The company provides both stock and custom offerings compatible with military and various commercial standard requirements. The company also produces prototypes of various components from customer drawings.

Phelps Industrial Products LLC is based in Laurel, Maryland. The company is a manufacturer and fabricator of custom products for domestic and global customers from industries such as oil & gas, shipbuilding, petrochemicals, utilities, and water treatment. The company’s primary product lines revolve around standard and custom gaskets, O-rings, marine products, mechanical seals, and additional products. The company provides expansive online resources and support to assist customers in both product selection and correct product usage.

Allstates Rubber was founded in 1968 and has operated in the Chicagoland area as a family-run business. The company manufactures, designs, and offers custom solutions for rubber machined parts for customers in the United States as well as overseas. The company offers specific custom capabilities including molding, rubber extrusions, rubber fabrication, and thermoplastic extrusions. The company offers both civilian and military-grade products, tools, and accessories. Standard product lines include rubber balls, bumpers, grommets, and suction cups.

Lusida Rubber Products, Inc. was founded in 2000 and is based in Rosemead, United States, is a manufacturer of plastic and rubber products that have applications in the Construction, Automotive, Food Processing, HVAC, and appliance industries. The company produces conveyor belts, diaphragms, extruded seals, fabric-reinforced hoses, and, molded products, as well as ring gaskets, seals, rubber sheets, silicone heater hoses, and timing belts that are used in Furniture manufacturing, Electronics, Metal fabrication, and, Aerospace arenas. They offer molding, extrusion, rubber-to-metal bonding, engineering, and prototyping services that find uses in research institutes, the medical sector, and, the computer-accessory manufacturing industry.

ACE Seal was founded in 1982 and is headquartered in San Jose, California. The company serves industries including aerospace, biotech, semiconductor, medical, and solar with custom rubber products, seal accessories, and other sealing components using a variety of elastomers. The company offers standard and custom products. The company offers four product categories of standard products: O-ring products, O-ring materials, gaskets, and barrel bungs. Custom products include custom O-rings, rubber components and extrusions, plastic components, and customized accessories. Custom molding services such as compression molding, injection molding, and multi-cavity molding are also available.

XTO Incorporated was founded in 1978 and is headquartered in Liverpool, New York. The company is a manufacturer of and service provider of machined parts finishing. The company partners with companies such as Parker Chomerics, Aeroflot, Rogers Corporation, Saint-Gobain, and others to provide water jet cutting, EMI, and RFI shielding, lamination, and gluing services. The company works with several materials including silicone, PORON, thin gage plastics, and foam. 3M conversion services for VHB tape, pressure-sensitive adhesives, and double-coated tapes are also available.

Economy Die & Gasket, Inc. (EDG) is an American manufacturer of custom die-cut gaskets and parts that was established in Baltimore, Maryland in 1948. The company primarily produces various die-cut parts such as thermal batteries, washers, spacers, and gaskets, as well as steel rule dies for die-cutting applications (e.g. corrugated boxes or packaging). These are used by client manufacturers and OEMs in a broad range of industries, including in the appliance, automotive and HVAC sectors. EDG also offers CAD product design and planning services, as well as quality control and inspection for customer projects with unique applications.

Mercer Gasket & Shim, Inc. established in Bellmawr, New Jersey in 1919 is a manufacturer of gaskets and expansion joints. that are used in refining industries. Their product portfolio includes Metallic Gaskets, Jacketed Gaskets, Kammprofile Gaskets, Spiral Wound Gaskets, and non-Metallic Gaskets. The company has 7,000 square foot facility with 25 employees and has ISO 9001-2015 certification. They also provide cutting machines, including Knives, Laser, Waterjet, and Die cutting that can cut any material from thin plastic to thick steel. The company has a national distribution network and a customer support center.

Southco Inc. is based in Pennsylvania, USA, and is a manufacturer and supplier of access control hardware that was established in 1899 before its acquisition by TouchPoint, Inc. in 2012. The company specializes in engineered access hardware solutions, including latches for doors or panels, fasteners for secure attachment of components or panels, and hinges for allowing controlled rotation or positioning. It also offers a variety of handles for doors or panels, and electronic locking or access systems. The company mainly serves clients in the data center, telecom, and medical industries.

J.G. Finneran was founded in 1977 and headquartered in Vineland, New Jersey. The ISO 9001:2015 certified company is a manufacturer and distributor of sample preparation consumables and equipment used in laboratories and educational facilities. All company products are built in the United States in ISO 9001-certified facilities. The company has five primary product divisions: chromatography, lab equipment, microplates, environmental, and sample prep equipment. The company also provides preventative maintenance and equipment service contracts for new and existing equipment.

Seal Fast, Inc. was founded in 1933 and is headquartered in Houston, Texas. Seal Fast is a distributor of sealing and fitting products. Seal Fast product categories include couplings, fire protection, gauges, pipe fittings and valves, hose and hose protection, and sheet rubber. Couplings include cam and groove, dry disconnect, shank, ring lock, foot valves, brass fittings, hydraulics, clamps, and banjo couplings. Fire protection equipment also includes gaskets, and industrial ground monitors. Gauges include siphons, oxygen, and thermowells. Pipe fittings and valves include combination nipples and flanges. Hose and hose protection include Fire hoses and industrial rubber. Sheet rubber includes skirt board and cloth insert neoprene.

TVI Valves was originally founded in 1986 and is currently headquartered in Emmaus, Pennsylvania. The company is a distributor of valves and accessories to numerous industries ranging from amusement parks to health care to photography to water purification. The company’s four primary product lines are Plastic Valves, Metal Valves, Instrumentation, and Valve Accessories. Examples of valves include ball, butterfly diaphragm, and plug valves. Valve accessories include actuators, stem extensions, gears, fasteners, and other devices.

C.W. Swift & Associates, Inc. was founded in 1958 in Van Nuys, California where it still stands as a family-run business. The company is a distributor of standard and non-standard RF and microwave electronics. The company’s line card includes products from manufacturers such as RF Industries, M Wave Design, Connectronics, and Johanson Manufacturing. The company’s product list includes coaxial connectors, precision grade adapters, and many other items, each organized according to the manufacturer.

Plastixs, LLC was founded in 1999 and operates out of Shrewsbury, Massachusetts. Plastixs is a distributor for industrial, plastics processors, process companies, and equipment manufacturers as well as a producer of custom water manifold assemblies and accessories to equipment such as plastic processors, semiconductor equipment, x-ray machines computer servers. Plastixs’s offerings include AIRTECT plastic leak alarm aystem, ATI quick-change robotic automatic tool changers, Bunting magnets, Crizaf conveyors, and Moditec low speed granulators among many more.

SC Fastening Systems hailing from Macedonia, OH is an industrial and construction supply distributer that provides value-added services. Product lines include fasteners, concrete anchors, abrasives, cutting tools, safety, janitorial, welding, paints and chemicals, material handling, tools and equipment, electrical, hydraulics and pneumatics, and lifting and rigging. Additionally, SC Fastening Systems offers specialty parts for niche industries such as laundry chute parts and custom hinges. SC Fastening Systems also offers services including inventory management and supply chain solutions, modified parts, kitting, assembly and special packaging, and fire protection products and services.

ESPE Mfg. Co., Inc., founded in 1941, is a custom manufacturer and distributor of electrical insulation materials and fabricated plastic parts, headquartered in Schiller Park, Illinois. They offer materials such as Formex, Vulcanized Fibre/Fishpaper, and Nomex, used for electrical insulation in industrial and consumer electronic equipment, serving industries including computers, telecommunications, medical equipment, automotive components, and consumer products. ESPE Mfg. Co., Inc. is ISO 9001:2008 compliant and operates from a 30,000 sq. ft. facility.

Allied Metrics was founded in the 1990s and is headquartered in Naples, Florida. The ISO 9001:2015-certified company is a full-service manufacturer and distributor of hydraulic seals, oil seals, and pneumatic seals. The company’s product offerings include O-rings, seals, V-rings & V-ring seals, X-rings & square rings, and wear bands & guide rings. The company’s service offerings include on-demand delivery with short cycle times, custom-designing to customer specifications, prototype parts, and emergency repairs.

Thermal Products Company, Inc. has been a manufacturer, fabricator, and distributor of high-temperature products since 1981. The company is certified with ISO 9001 & 9002 and specializes in offering high-temperature ceramic fiber insulation materials applicable to temperature ranges from 1000°F to 3000°F. Additionally, the company distributes fiberglass and silica textiles, along with heating elements and crucibles. Its fabrication capabilities are comprehensive, ranging from manufacturing modules of varying sizes to die-cutting gaskets, slitting insulation products into strips, producing machined shapes, and even adding foil to specific insulation products.

RubberMill was founded in 1987 and is headquartered in Liberty, North Carolina. The ISO 9001:2015 certified company is a manufacturer and distributor of rubber, plastic, ceramic, and other non-metallic materials used in automotive, manufacturing, and other industries. The company offers standard gaskets, seals, insulation parts, and molded rubber parts and custom manufacturing of molded rubber parts according to customer drawings from materials including Nitrile, silicone, natural rubber, and urethane. The company also provides contract and lamination services and in-house cuttings of non-metallic and flexible materials.

Asahi/America was born in 1971 to be the distributor for Asahi Yukizai Corporation products on the East Coast of the United States. Asahi/America serves the aquarium & entertainment, chemical processing, data center, metal finishing, and the water/wastewater industries. The company offers a selection of valves and actuators including many types of valves, high purity piping, air & gas handling, double containment, and welding equipment. The company alos offers a wide assortment of custom fabrication of parts and components.

US Rubber Supply Company is headquartered in Brooklyn, New York. The company is a manufacturer and stocking distributor of standard and custom rubber goods and other services for OEM, military, and various commercial industries. The company’s product lineup includes bumpers & fenders, expansion joints, hose & fittings, snow plow blades, and window products. The company offers complete die-cutting and molding extruding services and offers custom fabrication capabilities to customer specifications. Just-in-time delivery on all rubber goods is also available.

Industrial Vacuum Equipment Corporation is headquartered in Ixonia, Wisconsin. Industrial Vacuum is a distributor, service, and repair provider for industrial vacuum systems used in a variety of industrial settings including painting, asbestos abatement, abrasive blast recovery, hazardous waste removal, and shipyards. Industrial Vacuum’s product categories range from vacuum systems to dust collectors and blowers. Additionally, Industrial Vacuum offers individual parts and accessories. Industrial Vacuum’s offers rental service for industrial vacuums and dust collectors and also offers used equipment service.

Web Seal Inc. was founded in 1960 and is headquartered in Rochester, New York. Web Seal is a manufacturer and distributor of custom sealing solutions for business and industries including agricultural equipment, electronics & lighting, filtration, food processing, life sciences, pumps, waster & wastewater treatment, and government contracting. Web Seal’s product lines include custom gaskets & die cuts, O-rings & backup rings, hydraulic & pneumatic seals, custom molded seals, EMI & RFI shielding, thermal management, and related sealing products. Custom services include color coding, kitting and assembly, supply chain management, and custom packaging.

Production Materials Inc. was founded in 1981 and headquartered near Chicago in Wheeling, Illinois. The company is an ISO 9001:2015 certified distributor of fasteners and related components such as nuts, washers, and bolts to manufacturers as well as individuals. The company provides option types such as material, coating, and threading. The company also prototypes and designs parts and offers customization options on many of the parts available. The company also assists customers in the consolidation and standardization of existing parts along with inventory management assistance.


Seal Science Inc. (SSI), a subsidiary of Rubbercraft, is an American manufacturer established in 1992 and based in Long Beach, California, producing components for sealing applications. The company's products include fabric and rubber aircraft seals, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)/Teflon seals, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) conductive gaskets and seals. It also provides various types of seals, such as hydraulic, pneumatic, and rod models. Certified with ISO 9001:2015, the company has been one of the United States government's aerospace and defense subcontractors for over thirty years. It also serves customers in the semiconductor, medical, and various industrial sectors.


A 3M™ Preferred Converter and world-class die-cutter, JBC Technologies provides innovative die-cut solutions that enable our customers to convert their design concepts into reality. But the impact of what we do goes far beyond converting flexible materials into custom parts. Our customers benefit from our strong engineering focus and emphasis on providing value during the full product lifecycle. This includes everything from a prototype and quick react program that helps you solve last-minute production problems fast to high volume production with lead time strategies tailored to your specific needs.

North American Signal manufactures truck, auto, and industrial warning lights and accessories. Established in 1962 by Julius Newman and partners, NASAG was originally based on North Pulaski Road, Chicago, but is now based in Wheeling, Illinois, with a 45,000-square-foot warehouse. From LEDs, strobe, and battery-powered portable lights to revolving and specialty options, NASAG designs and manufactures warning lights to suit nearly any application. Besides truck and automotive, North American Signal Company also serves industrial markets such as construction and law enforcement.

H&O Products Corporation is a company that specializes in manufacturing precision components and assemblies for various industries, including aerospace, defense, and medical devices. The company was established in 1971 and has since built a renown for producing high-precision, complex, and critical components that meet the most demanding customer requirements. The company has won several awards for its products and services, for its unique quality, on-time delivery, and customer service. The company's consistent aim on continuous improvement, lean manufacturing, and technological creativity has helped it establish a strong position in the precision manufacturing industry.

Jefferson Rubber Works, Inc. was founded in 1979 in Worcester, Massachusetts. The company is a producer of custom rubber products in a wide variety of markets including the medical, liquid injection molding, construction, hydronics, and automotive markets. The company’s rubber molding capabilities include rubber injection and compression molding, liquid injection molding, transfer molding, and composite molding with prototyping services available. The company’s products include rubber molded parts including grommets, EMI shielding, hoses, vibration isolators, and gaskets. Custom molded rubber components are also available.

Accurate Products was founded in 1958 and is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. The company manufactures and distributes rubber products for the agricultural, manufacturing, and automotive industries. Its die-cutting operation in Chicago provides custom die and rubber molding services for Neoprene, EPDM, silicone rubber, as well as plastic injection molding. The company’s standard products are divided into molded rubber parts and injection molding. Molded rubber parts include SBR, Bun-N, natural rubber, and other parts and products. Injection molding parts include button bumpers, grommets, extrusions, and leg tips.

Custom Gasket Manufacturing is based in Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey. Custom Gasket serves several industries such as power generation, lighting, transportation, water & air filtration, food processing, pump & valve, electronics, cryogenic equipment, oil & gas, construction, agriculture, pharmaceutical, pulp & paper, HVAC, as well as others including OEMs. Custom Gasket Manufacturing produces many types of custom products including rubber elbows, rubber diaphragms, insulators, seals, extrusions, and as per their namesake, gaskets. Custom Gasket also offers rubber extrusion, die cutting, rubber molding, water jet cutting, laser cutting, and flash cutting services.

Qosina Corp., established in 1980 by Stuart Herskovitz, supplier of OEM medical device components to the medical, pharmaceutical, and bioprocessing industries headquartered in Ronkonkoma, New York. Their product portfolio includes sterilization supplies, needles, guide wire & catheter accessories, containers, and single-use sensors used in different applications including urology, vascular access, neuraxial, bloodline, cardiology, and respiratory. The company is ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 13485, ISO 45001, and ISO 22301 certified and offers brands such as Merit Advance, Nordson Medical, NRFIT, OETIKER, and SMARTSITE.

Technical Specialties Company, Inc. (TSC) has been a supplier of die-cut, extruded, and molded parts since 1949. Their team consists of decades of experience led by President and CEO Donald Schutz, who has been with the company since 1996. The company’s plant managers, partners, and vendors have an average tenure of 20+ years in the industry. As a full-service provider of non-metallic components, they specialize in custom fabricating, extruding, molding, and die-cutting plastic and rubber parts. Their technology is applied across a broad spectrum of industries and applications.

R.L. Craig Company, Inc. was founded in 1955 and is headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky. R.L. Craig Company is a distributor of HVAC and related products for residential, commercial, and industrial customers. R.L. Craig Company’s product lines include air distribution such as displacement ventilation and clean room exhaust systems, louvers and dampers such as fire & smoke dampers, vibration & noise control such as floating floor systems, duct systems such as acoustical duct, dust & filtration systems such as oil mist collectors, heating & cooling equipment such as gas unit heaters, fans such as utility set fans, and other equipment such as laboratory air flow controls.

Central Diesel, Inc was founded in 1972 by Martin R. Wittersheim and is located in Richmond, Virginia. Central Diesel is a distributor of marine, construction, mining, rental, industrial, military, state government, federal government, transportation, and agriculture industries. Central Diesel product categories include diesel engines, diesel engine electrical components, diesel engine filtration systems, diesel engine maintenance & repair, diesel engine turbocharger assemblies, diesel exhaust systems, fuel injection systems & parts, generators, and hydraulic hoses & fittings.

Henning Gasket of Chicago, Illinois, has a 100 year history of serving industries including agriculture, power generation, transportation, construction, electronics, pharmaceutical, and food processing as a distributor for gasket materials, seal materials, gaskets, seals, and related tools. Hennig Gasket also offers gasket manufacturing, of over 30 varieties including roll and sheet gasket material, and cutting services. Custom gasket manufacturing includes many types such as paper gaskets, ceramic fiber gaskets, pipe seals, flame resistant, neoprene gaskets, and chiller gaskets.

Circle Valve was founded in 1986 and headquartered in Harleysville, Pennsylvania. Circle Valve is a value-added distributor and manufacture rep of industrial valves, fittings, filters, and measurement control devices for a variety of industries and applications. Among Circle Valve’s product listings are check valves, relief valves, vacuum & high purity fittings, circle seal solenoid valves, Jefferson solenoid valves, Atkomatic solenoid valves GO regulators, cryogenic valves & equipment, hoke valves, Gyrolok Tube Fittings, Circle Seal Control Valves, and various measurement devices.

Founded in 1993, Liquidyne Process Technologies serves the dairy, brewery, distillery, biotech, pharmaceutical, & cannabis industries. Liquidyne offers a full line of sanitary and single-use products including process equipment components, sanitary equipment, single-use pumps and valves, single-use fittings and connectors, custom single-use assemblies, sanitary hose assemblies, sanitary valves, and single-use bioprocessing systems. Liquedyne produces all equipment in an ISO14644 Class 7-certified cleanroom has also attained 9001:2015, USP Class VI Testing, ASME Bioprocessing Equipment, and EHEDG certification status. Liquedyne also offers process optimization and on-site process audit & evaluation services.

N.T. Ruddock Company was founded in 1951 and is located in Cleveland, Ohio. N. T. Ruddock is ISO 9001:2015 registered and is a distributor off industrial equipment. Product lines include blast cleaning abrasives, equipment and replacement parts, primary and secondary aluminum ingot, aluminum and copper master alloys, and pure metals. Abrasive options include glass beads, corn cob, crushed glass, steel shot, copper slag, and more. Metal options include aluminum alloys, aluminum master alloys, copper master alloys, ferro alloys, alloy additions, and beryllium alloys. Additionally, N.T. Ruddock also sells many types of parts such as nozzles, guns, and valves, in addition to larger equipment such as blast cabinets and blast pots. NT. Ruddock offers installation, cleaning, repair, custom bagging, and in-house blending of abrasives, and repair.

Robert McKeown Co., Inc., established in 1937, and headquartered in Brunchburg, New Jersey, is a fabricating distributor of electronic assembly materials and equipments. The company specializes in providing application assistance for the design of new products and the redesign of existing products. Their range of products encompasses of electronic tapes, EMI gasket, adhesives, and ESD shields. These products play a crucial role in ensuring proper functioning, and safety of electronic assemblies in industries such as aerospace, medical, and electronics.

Arizona Sealing Devices, Inc. is a sealing products distributor located in Chandler, Arizona that was established in 1989. The company began as an O-ring supplier but has since expanded its product range to caps, plugs, gaskets, and customized and prepackaged kits. The products are available in a variety of materials, such as various kinds of rubber, plastic, and silicone. The company services a range of industries, including automotive, aviation, electronics, medical, and industrial.

Pacific States Felt & Mfg. Co., Inc., established in 1920, is a supplier of standard and custom sealing devices and industrial products such as gaskets, washers & pads, seals, O-rings, and molded bumpers made from felt, cork, rubber, fibre, and plastic. The products are used in decorative, lighting, medical, utility, and sciences industries. The Hayward, CA-based company has die cutting, tape slitting & adhesives, laminating & fabricating, extrusion, and rubber molding capabilities. The company has projects such as assembling silicone sponge housing gaskets for the lighting sector.

Sealing Specialties, Inc. established in Souderton, Pennsylvania in 1985 is a distributor of seal components that are used in automotive, chemical, communication, energy, food & beverage/ Their product range includes O-Rings, Mechanical Seals Engineered Seals, Gore Sealant Products and Perfluoroelastomers. The company has a global distribution network and provides customer service. Their products are also used in industries such as instrumentation & controls, life sciences, medical, pharmaceutical, pulp & paper, and semiconductors.

Blucast, established in 2007 and headquartered in Vilnius, Lithuania, is a manufacturer that specializes in providing a range of ductile iron valves and fittings. The company offers a range of products that include ductile iron valves and fittings, as well as castable resins for the jewelry industry. It also offers other items such as copper vacuum insulated bottles. Its resin is shrinkage-free, ensuring dimensional stability over time. It serves two different industries, the jewelry industry and the water supply sector.

COMPELMA was founded in 1989 and is a developer and manufacturer specializing in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and thermal management located in Les Ulis, France. Its product list covers radio frequency shielded glass (CEM), spacer/nut for PCB, high frequency and microwave absorber, as well as heat sinks, thermal interface, and thermoelectric modules. Likewise, 90% of the company's products are custom-designed to meet the client's specific needs. The company is a member of the ICE Group, a federation of 19 industrial companies. It also holds ISO 9001 certification, serving the needs of diverse sectors, including automotive, medical, defense, and telecommunications.

Novagum S.r.l., headquartered in Schio, Italy, is a manufacturer of a vast array of machinery and equipment intended for jewelry. The company produces electric rotary-board burnout furnaces, industrial ovens, magnetic tumblers, enameling machines, and jewelry silicone rubber. It also makes perforated cylinders for lost wax casting, aluminum mold frames, steam generators, and silicone rubber for spin-casting. Its electric rotary-board burnout furnaces have special insulations that give their precious contributions to reducing fuel consumption compared to other furnaces.

Texpack, born in 1993, is a manufacturer of tapes, braids, fabrics, threads, and socks for thermal insulation for dynamic use in pumps and valves in Via Galileo Galilei, Adro, Italy. The company produces sealing rings, natural fibers, paper mills, flange covers, and dimensional tables. It also produces metallic gaskets, graphite products, textile artifacts, silica, and tables used in process, construction, energy production, fire protection, and transportation industries. The company has certifications such as ISO 45001:2018, ISO 9001:2015, CRIBIS, and ESA members.

Shenzhen In-Sail Precision Parts Co. Ltd., established in 2008 and headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is a special fastener manufacturer and supplier. The company's product range includes electronic hardware, fasteners for sheet metal, and plungers. It also provides threaded fasteners, self-tapping inserts, and power elements. These products are used for flow cytometry instruments, car battery compartments, and PCB production. The company serves wholesale buyers and also offers original equipment and original design manufacturing services, including the production of custom fasteners.

Elite Gomma International S.r.l., founded in 1999, is a manufacturer of rubber products based in Reggio Emilia, Italy. The company’s manufacturing facility, equipped with compression, deburring, and injection machines supplied by ENGEL Austria GmbH, produces a range of standard and custom rubber items. These include protection bellows (cone, cylindrical, and rectangular), shock absorbers, and shock absorber feet. Other products include grommets (cylindrical and symmetrical), painting caps (conic, square, and round), and vibration dampers. It also manufactures flat gaskets, floating balls, and rubber frictions. The company serves various sectors, including automotive, agriculture, and water treatment.

Schlegel Electronic Materials, Inc. is an EMI shielding and thermal management material manufacturer. Pioneering conductive fabric over foam shielding gaskets in 1987, it's a premier electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding provider. The company delivers advanced EMI containment and thermal management solutions.Offering Fabric Over Foam Gaskets, Conductive Elastomers, RF Absorber Materials, and enclosure gaskets, serving computing, telecommunications, military, medical, and electronics sectors. Its EMI shielding gaskets come in varied profiles, with attachment options. With a global operations in the U.S., Europe, and Asia, the company ensures unmatched support and service.

Precision Polymer Engineering Ltd. is based in Lancashire, England, United Kingdom, and is a manufacturer of rubber molding and elastomer seals that was established in 1975 before becoming a part of the IDEX Sealing Solutions group of companies. The company’s product lineup includes various sealing solutions such as X-rings, O-rings, and T-seals. These can be fabricated from a range of elastomer materials including Kimura, Detectaseal, and Perlast. It also offers component designing services for unique projects. The company’s products are commonly used in industrial processing, such as in chemical refining and wastewater treatment operations.

Xiamen Landee Industries Co. Ltd., established in 1994, is an industrial components manufacturer based in Xiamen, China. It releases a new flow control model on a monthly basis and produces over 50 types of compononts, including pipes, valves, flanges, pipe fittings, and gaskets, in over 20 materials and 400 sizes. The company's products are used in the oil rig, gas, chemical, pharmacuetical, and paper-making industries, and it complies with API, CE, and ISO 9001:2008 certification requirements.

Kowa Kasei Co., Ltd. was founded in 1969 and is a manufacturer and supplier of profile extrusion molding products, electric wiring member, and EMC components based in Nagoya, Aichi, Japan. The company's product portofolio including wiring ducts, birdie cutters, wiring protection tubes, noise protectors, and EMC protective tubes. The products have been certified to be RoHS compliant. The company have obtained the ISO 9001 certification in 2002 and ISO 14001 certification in 2003.

KJ Laser Micromachining, founded in 2001 and located in Toronto, Canada, is a manufacturer of advertising and promotional products. They offer precision laser micromachining services, including laser cutting and engraving for various materials like metals, plastics, and composites. This enables the precise and efficient creation of complex shapes, patterns, and permanent markings such as logos and serial numbers. Their product portfolio includes laser cut custom Gauge, ornaments cut from steel, laser engraved acrylic, and stainless steel medical implants.

E-SONG EMC Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer EMI shielded & absorbed products and thermal interface products, founded in 1991 and headquartered in South Korea. The company provide ingenious products and services that ensure seamless electronic interactions, minimizing interference and enhancing performance. E-SONG EMC., Ltd expertise spans across industries which offers tailored EMC test, consult, and design services. They are indebted to excellence; they empower clients with dependable solutions that meet regulatory standards and optimize operational efficiency.

TennVac Inc. is a manufacturer headquartered in Taipei Hsien, Taiwan, specializing in electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and thermal management. The company offers various shielding materials, including molded gaskets designed for mechanical structures with limited space, overmolded gaskets for seamless integration into mechanical structures, and dispensed gaskets tailored to fit plastic or metal housings. TennVac also provides thermal interface materials for efficient heat transfer between objects, such as conductive dispensable jelly, gap filler pads, multilayer pads, and insulation pads. The company is registered with the Department of State and supplies these products to the defense and aerospace sectors of the US government.

Metal Textiles Corporation, established in 1974 and headquartered in Edison, NJ, United States, is an engineered materials and component designer and manufacturer. The company specializes in providing solutions for automotive, aerospace, and military market segments worldwide. Its solutions include extreme environment solutions in sealing, vibration damping, and filtering. It has experience in complex products and components, such as electronic shielding innovations for critical aerospace applications, gasket reinforcement for the space shuttle cargo door, and pneumatic tool mufflers for the automotive industry. The company's notable clients include Lockheed Martin, General Motors, and Boeing.

Kemtron Ltd., founded in 1980 and currently a subsidiary of TE Connectivity, is a British manufacturer headquartered in Braintree, Essex, producing valves and fluid control equipment. The company's valve range includes ball, butterfly, and check valves. It also offers other variants including control, needle, and safety relief valves. In addition, the company produces manual, electric, and pneumatic actuators to operate valves. Pipe fittings, like flanges, elbows, and couplings, are also available for fluid handling systems. These products find applications in various fields, including food and beverage production, chemical and pharmaceutical processing, and water treatment plants.
IDT GmbH, founded in 1984, is a manufacturer based in Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, specializing in sustainable sealing solutions. The company offers a range of products, including non-metallic, semi-metallic, and metallic gaskets, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) molded and press-sintered parts, as well as various composite parts made from metal and perfluoroalkoxy (PFA). It offers other sealing solutions for critical applications and non-standard requirements, such as line blanks, expansion joints, and stuffing box packing. The company serves international clientele with the support of subsidiaries in Spain and China and distribution partners in over 40 countries.

Rezingom S.R.L. is a manufacturer of rubber gaskets and seals established in 2007 and located in Castelli Calepio, Italy. The company’s products include gaskets customized for a range of connectors, and application-specific rubber seals including for automotive assemblies and piping systems. It also offers o-rings in different sizes and materials for standard industrial applications. The company is ISO 9001 and ISO/TS 16949-certified, and chiefly serves clients in the industrial processing and manufacturing sectors.

Zhongding Group is an ISO 14001, ISO 16949, and ISO 45001-certified manufacturer of automotive parts established in 1980 in Ningguo, Anhui Province, China. The company offers environmentally friendly engine products such as exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems, and mechanical basic parts such as shafts and springs. It also offers plastic and rubber parts such as o-rings, belts, and gaskets. The company's products are used mainly by client manufacturers of standard automobiles and electric cars.

Hi-Tech Seals Inc. is a manufacturer of sealing and gasket components established in 1990 and headquartered in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. The company’s products include a wide selection of o-rings, seal kits, and gaskets. It offers products fabricated from BoKure urethane, KasPex PEEK, and RyFlor compounds. The company primarily serves clients in the oil and gas, water treatment, and aerospace sectors. It also offers custom molding services, in-house rapid prototyping, and optical measurement inspections.

Trelleborg AB, a company founded in 1905 and headquartered in Trelleborg, Sweden, is a manufacturer that provides solutions for extreme cold, heat, pressure, or the tremendous power of nature. The company offers a wide range of products, including Cassette Seal CSL 1500, Pneumatic seals, O-rings, and more. It also has a shop called Seals-Shop that offers various products, such as Rod and Piston Seals. It provides rubber wear liners with synthetic rubber and chemical resistance. It has received the Excellence in Quality 2018 Award and Certificate of Merit from Hyster-Yale Group. It serves various industries, including Aerospace, Agriculture, and more.

Davlyn Group, founded in 1980 and headquartered in Spring City, USA, is a manufacturer of technical textiles and composites. The company manufactures engineered materials including heat and cut resistant textiles and composites, gaskets, and seals that help keep heat in its place, improve safety, and increase productivity. These products are used for high-temperature applications across many industries including home appliances, energy, and transportation. The company is ISO 9001 certified for its quality management system, and complies with the RoHS and REACH standards.

Media Valve Co. Inc., founded in 1968, is a butterfly valve manufacturer based in Fort Worth, Texas, United States. The company produces various Mosites butterfly valves and gaskets, using corrosion and erosion-resistant rubber blends specially developed by Mosites Rubber Company. The company also provides specialty items, including automated fiber placement (AFP) rollers and custom mold metal forming bladders. These products are used in various applications, such as power plants, flue gas desulfurization facilities, and the transportation sector.

National Guard Products Inc., founded in 1935 and headquartered in Memphis, Tennessee, United States, is a manufacturer of commercial door hardware. The company's products include continuous hinges, floor shields, and sliding hardware. It also offers GapGuard, a gap solution for excessive fire door and frame clearances; Sportsguard flooring transitions and flooring assemblies used in event centers and sports arenas; and finger guards (also known as door edges and astragals). The company's products are widely used in hospitality, cold storage facilities, and commercial buildings.

Saint-Gobain Tape Solutions, established in 1963, is a manufacturer of tapes, including adhesive, bonding, gaskets, and spacer tapes targeting the automotive, energy, building & construction, industrial, and electrical markets. Saint-Gobain Tape Solutions offer custom solutions, with 139 projects opened in the last twelve months and three new projects each week. The company in Bengaluru, Karnataka, India, has gasketing foams that eliminate the sticky problems that come with sealants, elastomeric foam tapes are also available with or without adhesive.

Technetics Group is a sealing and critical component solutions manufacturer founded in 2006 as a subsidiary of EnPro Industries based in Columbia, South Carolina. The company offers a range of products including metal and polymer seals, rupture discs, accumulators and bellows. They also custom design polyether ether ketone (PEEK) rods, plates, disks, and other components. With 13 global manufacturing locations that offer engineering, manufacturing, testing, and prototyping services, Technetics Group serves clients in various markets including energy, life sciences, semiconductors, and aerospace.

Laird Performance Materials, also known as Laird PM, specializes in heat and EMI protection for advanced electronics in automotive, aerospace and defense, telecommunications, data infrastructure, precision and computing, medical, and consumer electronics industries. As a global organization, Laird PM, focuses on developing, manufacturing, selling, and supplying precision-engineered materials used by manufacturers to serve their electronic markets. Laird PM designs and develops products test and measurement instrumentation to create models and product performance simulations to improve product performance, reliability, and flexibility while reducing development time and cost.

Garlock, headquartered in Palmyra, New York, is a global manufacturer of sealing solutions for diverse industries worldwide. Offering over 100,000 sealing solutions, its products cater to demanding fluid-handling equipment in sectors such as chemical processing, food & beverage, brewing & bottling, and mining. Its product range includes GYLON for superior leak prevention, BLUE-GARD enhancing torque retention and emission reduction, MIll-RIGHT for abrasion resistance and extended seal life, and MULTI-SWELL for tight seals in water and oil applications.

MBK Tape Solutions was founded in 1971 and currently operates out of Chatsworth, California under the Boyd Corporation umbrella. MBK is an ISO 9001-2015 certified manufacturer and fabricator of adhesive tape and flexible material that offers bonding, surface protection, sealing, and thermal management solutions. The company specializes in the healthcare, electronics, and industrial industries. The company offers several customer services including die cutting, printing, sheeting, and packaging. In addition, the company offers product development, cleanroom manufacturing, and contract manufacturing to customers.

Quick Cut Gasket & Rubber Corporation (QGR) is an American manufacturer of various rubber products that was established in Lancaster, New York in 1974. The company produces o-rings fabricated from a range of rubber materials such as nitrile, silicone, or neoprene, as well as gaskets fabricated from various materials (e.g. cork, felt). It also offers rubber profiles, extrusions, and custom handmade products including grommets, anti-vibration pads, and bumpers. QGR products are primarily used in the medical, chemical processing, automotive, and marine industries.

Omnisafe, headquartered in San Diego, CA, is a manufacturer of torque-suppressed fittings including torque elimination fittings, metal face seal fittings, and micro weld fittings that are used in various industries and space research organizations. The company produces torque elimination fittings from 316 L grade stainless steel and Hastelloy® alloys. The company's products include caps, plugs, adapters, nuts, and torque eliminators which have applications in research institutes, NASA organizations, aerospace, semiconductor, and nuclear equipment industries.

Polymer Extrusions, Inc. was founded in 1994 and is headquartered in Oshawa, Ontario. The ISO 9001:2015 certified company is a custom manufacturer of extruded rubber profiles and molded polymer products, servicing a diverse market including automotive, architectural, construction, and OEM customers. The company works with materials including various elastomers, Nitrile, EPR, and Neoprene and designs many types of components including die-cut gaskets, molded rubber products, sheet rubber, and specialty hoses. The company offers customization services to meet customer needs for length, angles, materials, and specific grading standards.

Precision Wire Products, Inc., founded in 1913, is a manufacturer of filter wire cages and other wire products including racks, rings, 3D wire formed parts, spun metal items, and stamped flat-stock used in the medical, oil and gas production, chemical, and food and agricultural processing industries. The company on East Brown Street in Blairsville provides CNC wire forming, metal spinning, and metal stamping services. Precision Wire creates replacement cages for new and existing collector systems, and all manufactured parts are inspected hourly during manufacturing.

UIP International was founded in 1992 and operates out of Houston, Texas. The company is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer of custom-built hose and rubber-based materials for industries such as petroleum, chemical, water treatment, aerospace, and material handling. The company has 10 primary product lines including sheet rubber, gaskets, marine hose, expansion joints, and metal hose & pump connectors. Additionally, custom-cut rubber, rubber stripping, gaskets, and seals are also available for order.

Oil-Rite Corporation was founded in 1933 and is based in Manitowoc, Wisconsin. Oil-Rite is a designer and manufacturer of lubrication equipment used in industries as diverse as automotive, machining, and baking, as well as hydroelectric dams. Oil-Rite’s featured products include constant level lubricators, level gages, feed valves, and oil systems. Additional products include grease and oil dispensers, various valves, and sights. Oil-Rite also offers support including usage, lubrication levels, maintenance, and product selection for specific needs.

Budnick Converting, Inc. was founded in 1952 and is headquartered in Columbia, Illinois. The company is an adhesive coating converter, converting adhesive-coated tapes, foams, films, foils, and other specialty materials from other major manufacturers. Many customers are in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, energy, and marine industries. The company offers a host of other converting services including precision and die cutting, spooling and finishing, laminating and coating, and printing. The company also provides process audit, prototyping, and inventory management assistance.

Crafter Plastics, Inc. (CP) is an American contract manufacturer specializing in plastic fabrication and extrusions that was established in 1982. Based in Sheboygan, Wisconsin, the company offers various plastic fabrication services such as 3D printing filament disposition modeling (FDM), CNC routering of sheet stock, plastic extrusion, and plastic tubing. It can work with a wide range of materials including acrylic, thermoplastic elastomers, polyurethane, and wood. CP primarily serves client manufacturers of consumer products (e.g. sports equipment, toys), furniture, and packaging materials.

Lansco Manufacturing Services, Inc. was founded in 1986 and is headquartered in Chagrin Falls, Ohio. The company is a manufacturer of equipment ranging from Swiss machined components to complete factory automation. The company’s service offerings include prototyping and R&D services, concurrent engineering, and Kansan stocking programs. Machining capabilities include custom metal fabrication, precision stamping, assemblies, adjustable ergonomic workstations, and more. The company works with many types of plastics and metals including aluminum, high-temperature alloys, carbon steel, and more.

Fabri-Tech Components, Inc., established in 1993, is a manufacturer and supplier of custom assemblies for industrial, medical, automotive, telecom, and electronic devices. The company manufactures a vast range of products like EMI gaskets, protective films, thermal management systems, and more. They have a team that offers personalized service to create tailored solutions without exorbitant prices. They are ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 13485:2016 certified. With a global network of facilities, in Singapore, the USA, China, Vietnam, Thailand, and Taiwan, they have customers on a global scale.

New Process Fibre Company, Inc., established in 1927, is a manufacturer of teflon, nylon, plastic, fiber, and other non-metallic components. The company, based in Greenwood, Delaware, manufactures products for the automotive, military, and defense industries through standard and custom non-metallic component fabrication. Their gaskets, spacers, tags, insulators, and discs are used in processes that require corrosion-resistant and versatile materials. They can also customize products for matching colors, core sizes, materials, and tolerances per customer specifications. New Process Fibre is an ISO 9001-certified manufacturer which earned its certification in 2015.

Laird Technologies, now known as Laird Connectivity, established in 1991 at Missouri, USA is a manufacturer of advanced electronics and wireless products. The company offers a diverse range of products, including antennas, IoT modules, Bluetooth modules, Wi-Fi modules, and wireless IoT gateways. These products enable robust and secure wireless communication in applications such as industrial automation, medical devices, transportation, agriculture, and smart cities. Their solutions facilitate seamless connectivity, data transmission, and remote monitoring, enabling businesses to achieve enhanced efficiency, productivity, and connectivity in the fast paced world of wireless technology.

Ezi-Dock Systems Ltd is a manufacturer and supplier of life science products and equipment established in 2003 and located in Nottinghamshire, England, United Kingdom. The company offers flexible intermediate bulk container (FIBC) dust-free handling systems for maintaining sterility of transported materials, and high-containment transfer systems for handling pharmaceutical ingredients or catalysts. It also offers single-use valves and related fittings for Flexitank or Bag-in-Box applications. The company’s products are commonly used in the laboratory, pharmaceutical, and healthcare industries.

KLINGER was established in 1886 in Gumpoldskirchen, Lower Austria, as a manufacturer and supplier of industrial sealings, fluid control systems, and fluid monitoring systems. The company's product list comprises KLINGER CNAF gaskets, KLINGER ball valves (INTEC Range), and Reflex level gauges, among others. The products provide sealing solutions for critical applications requiring chemical resistance and temperature management, precise flow control and shut-off functionality in industrial processes, and essential liquid level monitoring for safe operations. The company serves various industries, including general manufacturing, automotive, infrastructure, marine, and food and beverage.

Praher Plastics Austria GmbH is a manufacturer and distributor of industrial piping system products made from technical plastics that was established in Schwertberg, Austria, in 1971. The company produces unplasticized PVC (PVC-U) pipes, fittings, and accessories for a range of industrial applications. It also offers various valves, such as diaphragm, check, and multiport models of different sizes and series. The company is certified to ISO 9001 standards, and chiefly serves clients in Austria’s industrial chemical, water treatment, and biotech industries.

Vital Parts, established in 1993 and headquartered in Maidstone, Kent, UK, is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic, rubber, and metal components. The company's product range includes a wide range of components such as plugs, furniture, chair feet, and cable management solutions. It serves a diverse array of industries including automotive, aerospace, construction, engineering, and the food and beverage sector. The company’s emphasis extends to offering technical support, on-site training, fast delivery, and custom molding services. It also emphasizes quality and customer satisfaction. The company stands as a dependable supplier in the UK and worldwide.

Tai Sam Hardware Corporation is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial cabinet products established in 1999 and located in New Taipei City, Taiwan. The company offers cylinder type cabinet locks used to secure railway maintenance or automation equipment, electronic locks for use in communication or power distribution facilities, and rotary handle cabinet locks for use in electronic or data center facilities. It also offers standard latches and panel locks for common industrial facilities. The company’s products are mainly used in the industrial manufacturing and public utilities sectors.

Ningbo Sunwell Sealing Materials Co., Ltd, established in 2010 and based in Zhejiang, China, is a manufacturer and supplier of gaskets and sealing products. The company's product portfolio includes spiral wound gaskets, testing equipment, and glass fibers. These products find applications in various industries, including renewable energy, manufacturing, and the food and beverage industry. The company is ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14000, and ISO 18000 certified, with a global network that spans various countries, including the United States.

EagleBurgmann, a company founded in 1884 and headquartered in Wolfratshausen, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in industrial sealing technology. The company's range of sealing technology includes mechanical seals, carbon floating ring seals, and seal supply systems. These products find applications in various industries, including the petrochemical industry, renewable energy generation, and shipbuilding. The company also offers services, including technical support, product training, and customized solutions to meet the specific requirements and applications of individual customers. The company has sales offices and service centers in various countries, including the United States, India, and China.

Seiwa Electric MFG Co., Ltd is a manufacturer of information display systems, lighting and noise countermeasure equipment, based in Kyoto, founded in 1945 (Samsung Electric Co., Ltd.,) and established in 1949. Their products include: electromagnetic noise countermeasure (EMC), waterproof and shockproof LED information display, their own blue light-emitting diode and white light-emitting diode, tunnel disaster prevention system and road & tsunami information display system. Seiwa Electric acquired ISO14001:2004 certification at all offices. Outside of Japan, they have offices and subsidiaries in Thailand, Vietnam and China.

Kitagawa Rubber Industries Co., Ltd., established in 1963 with headquarters in Japan, is a manufacturer and distributor of electronic components and equipment. The company’s products include EMC noise suppression components, thermal pad components, a plastic component series for holding PCBs, and plastic component ties. Kitagawa Rubber Industries is also involved in the technologies and services fields, providing components for the new energy products, biotechnology, industrial robots, semiconductors, and medical markets. The company has international offices located in the USA and China and also maintains ISO 9001 certification.

GKM Siebtechnik GmbH, established in 1998 and based in Waibstadt, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of tumbler screening machines. The company's product portfolio includes vibrating tumbler screeners, pneumatic screening machines, and ultrasonic discharging systems. These products are used in various industries, including chemical processing, food and beverage, and the plastics and rubber industry. The company offers services including spare parts supply and replacement of worn or damaged screens on screening machines, and it sells its products to the United States, Australia, and China.

Kuriyama of America, Inc. is based in Illinois, USA, and is a manufacturer and distributor of thermoplastic hoses and accessories established in 1968 as a subsidiary of Japan’s Kuriyama Holdings Corporation. The company offers industrial rubber hoses for hydraulic or pneumatic applications, thermoplastic tubing for chemical or beverage processing, and suction material handling hoses for agricultural purposes. It also offers hydraulic fittings and crimpers, and couplings for its hoses in stock. The company provides custom hose fabrication and assembly services, along with additional technical support for client projects.

Pegasus Glass established in Cambridge, Ontario in 1968 is a distributor and manufacturer of borosilicate glass products that are used in chemical, industrial, lighting, and optics. Their product range includes glass rods, glass tubing, sight glass, lampworking supplies, and processed glass. Their products are also used in industries such as Medical Devices Artistic Glass Chemical Pharmaceutical Biotech. The company has a warehouse with 375 standard sizes of glasses and also produces recycled or re-used galasses to have zero waste.

Parker Hannifin Corporation was founded in 1917 and is headquartered in Cleveland, Ohio. Parker Hannifin is a manufacturer and distributor of motion and control technologies and systems for markets including mobile, industrial, and aerospace. Parker-Hannifin operates through two segments: diversified industrial and aerospace systems. Diversified industrial offers sealing, shielding, thermal products and systems, adhesives, diagnostics solutions, and hydraulic, pneumatic, and elctromechanical components and systems or industrial machinery and equipment. The aerospace segment offers control actuation systems and components, engine exhaust nozzles and assemblies, pilot controls, as well as others.

Ningbo Baodi Plastic Valve Co., Ltd., founded in 1994 and headquartered in Beilun, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China, manufactures plastic valves, pipes, and fittings. The company offers a range of products, including plastic ball valves, diaphragm valves, butterfly valves, check valves, and globe valves, along with various plastic pipes and fittings. These products are constructed from materials like FRPP, PVDF, UPVC, CPVC, and PPH. It holds an ISO9001 quality system certification and possesses over 20 valve patents.







Ultrafab, Inc, a company founded in 1970 and based in Farmington, New York, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in weatherstripping products. The company's range of products includes adhesive backed weather seals, polypropylene leaf seals, and specialty brushes. These products find application in various sectors, including OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), fabricators, and the window and door industry. The company offers technical support to its customers while being ISO 9001:2015 certified for its quality management. Some of the company's partners include Lincoln Sentry, Collins Toker Agencies, and Central Plastics.





Alpha Technologies, established in 1976 and based in Bione, Brescia, Italy, is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer and supplier of fluid power products. The company's product range includes fittings and connectors, automatic couplings, automation equipment, compressed air networks, and fluid valves. These products are vital for operations involving fluids, compressed air, inert gases, and vacuum control. It serves industries such as manufacturing, pneumatics, hydraulics, and industrial automation. In addition to its products, the company offers services like BIM, My Aignep, Aignep Scan, and Infinity Air Planner.

4B Plastics, founded in 1978, is a supplier of compression molded unfilled and filled Polytetrafluoroethylene(PTF )and various other speciality thermoplastics such as lantern & compressor rings, bushings & bearings, valve repair kits, and gaskets to serve the chemical plant, petrochemical and paper industries. The company in South Choctaw, Baton Rouge, LA, has nozzle liner sleeves, threaded bottle adapters, PTFE witch hat strainers and UHMV skimmer guide blocks. The company sells bellows that offer flexible connections in a glass-lined piping system with a chemical resistance of up to 500 degrees Fahrenheit or 260 degrees Celsius.

Solar Biz Inc. began in the 1970s in Ft. Atkinson, Wisconson. Solar Biz offers complete solar panel systems for residential and commercial customers ranging from under 5 watts to over 400 watts. Systems include solar panel components with racking and mounting, inverters, power centers, solar charge controllers, batteries, and accessories, AC and DC enclosures, circuit protection, hydro and wind generators and accessories, water pumps and water filtering, tanks, heaters, hot tubs, rain catchments, and appliances such as fans, gas ranges, refrigerators and freezers.

Guenther Supply Inc. began in the 1940s and officially founded in 1956. Guenther Supply Inc. offers products and services. Product offerings include pipe and tubing across carbon steel, stainless steel, alloys, copper, and PVC, fittings and flanges, valves, pipe support and hardware, hose and tubing products, piping specialty products, pipe insulation, plumbing and heating products, chemicals, and tools including threating, cutting tools, and drain cleaning equipment. Service offerings include valve actuation assemblies, air, water, and hydraulic hose assemblies, along with tool rentals.
Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rees, Inc. |
1.5%
|
| 2 | Gates Corporation |
1.5%
|
| 3 | Gilson Company, Inc. |
1.4%
|
| 4 | AutoVac Industrial Vacuum & Air Systems |
1.3%
|
| 5 | Fedtech, Inc. |
1.3%
|
| 6 | Frenzelit Inc. |
1.2%
|
| 7 | Aavolyn Corp. |
1.2%
|
| 8 | Thomas A. Caserta, Inc. |
1.2%
|
| 9 | KLINGER |
1.1%
|
| 10 | Atlantic Gasket Corporation |
1.1%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the gasket page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
93 | 79.5% |
 China
China
|
5 | 4.3% |
 Japan
Japan
|
4 | 3.4% |
 Italy
Italy
|
3 | 2.6% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
3 | 2.6% |
 Austria
Austria
|
2 | 1.7% |
 Lithuania
Lithuania
|
1 | 0.9% |
 France
France
|
1 | 0.9% |
 Hong Kong
Hong Kong
|
1 | 0.9% |
 Canada
Canada
|
1 | 0.9% |
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
|
1 | 0.9% |
 Taiwan
Taiwan
|
1 | 0.9% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 0.9% |
450 products found
450 products
Hamamatsu Gasket Co., Ltd.
300+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
It is attached to the heart of the engine and must withstand the explosion pressure inside the cylinder, as well as have a strong seal that prevent...
Sowa Industries Co., Ltd.
250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 23 hours ago
A sheet gasket material made of biosoluble inorganic fiber as the main raw material, inorganic fiber and inorganic filler added, and reinforced wit...
E-SONG EMC CO., LTD.
970+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
■Summary ・SMT EMI gasket (automatic mounting gasket, PCB ground contact) is a PCB ground component that reduces electromagnetic noise generated fr...
3 models listed
Technetics Group
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■It is a metal seal with elasticity. Groove, RF/FF, T&G, NW/KF, 3-end contact type, ICF/conflat, irregular shapes, and rectangular shapes are also ...
Muramatsu Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 23 hours ago
■White sheet gasket that can be used for a wide range of purposes. ・Clean and has excellent chemical resistance. ・Can be used at high temperature...
Hamamatsu Gasket Co., Ltd.
380+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
Mainly required is oil/cooling water sealing. Various necessary functions are required depending on the rigidity of the engine and the intended use...
Sowa Industries Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
Heat and oil resistant joint sheet/S-2500 oil swelling type sheet. ■Features A heat-resistant and oil-resistant sheet that swells appropriately wi...
E-SONG EMC CO., LTD.
720+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Summary ・EMI Shielding Spiral spring gaskets have excellent electromagnetic shielding effects and are ideal shielding materials for equipment tha...
3 models listed
Muramatsu Co., Ltd.
470+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 hours ago
■Features ・A gasket with a corrugated shape that concentrates surface pressure and improves sealing performance. ・Can be processed into special s...
Hamamatsu Gasket Co., Ltd.
350+ people viewing
Last viewed: 23 hours ago
Combustion gas sealing is required. Since the combustion gas is high temperature, the gasket material must also have heat resistance. ■Main uses S...
Sowa Industries Co., Ltd.
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
This sheet is mainly made of expanded graphite and reinforced with biosoluble inorganic fibers and aramid fibers. Oil-resistant synthetic rubber wi...
E-SONG EMC CO., LTD.
780+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Summary ・EMI Shielding Spiral spring gaskets have excellent electromagnetic shielding effects and are ideal shielding materials for equipment tha...
6 models listed
Technetics Group
340+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Can be used on damaged ring joint flanges. It has the elastic properties of a Helicoflex seal. ・Omicron Seal HLO is for ring joint grooves and us...
Muramatsu Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
A gasket made of V-shaped metal hoops and cushioning material called filler, which are alternately layered and wrapped in a spiral shape. There is ...
Hamamatsu Gasket Co., Ltd.
340+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Seals oil, cooling water, and combustion gases. ■Main uses Seal between engine guide exhaust and oil pan ■Main product specifications Like head g...
Sowa Industries Co., Ltd.
220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
A low surface pressure gasket made by punching out various synthetic rubber sheets. ■Features Excellent wear resistance ■Applications Gaskets for...
E-SONG EMC CO., LTD.
490+ people viewing
Last viewed: 23 hours ago
■Summary ・Ground foam gasket is an electromagnetic shielding material whose outer skin is made of conductive fiber or metal foil, and can provide ...
2 models listed
Green, Tweed & Company Japan Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Highly versatile sealing for harsh environments MSE® (Metal Spring Energized) seals are custom designed with a dual lip body for superior performa...
Muramatsu Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
This is a semi-metallic gasket made by laminating expanded graphite sheets or PTFE sheets on both sides of a metal ring with a special groove shape...
Muramatsu Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
A gasket made of inorganic heat-resistant cushioning material covered with a thin metal plate. They are manufactured in various shapes and coating ...
Technetics Group
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
■Vacuum rubber O-ring Want to eliminate gas permeation and gas release. It is possible with Delta Beta HNRV. Delta Beta HNRV is a combination of De...
Nitto Shoji Co., Ltd.
470+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
We design various sealing materials such as O-rings, gaskets, and packing according to the application, and supply them to a wide range of applicat...
Hamamatsu Gasket Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Main uses Seal between engine cylinder head and exhaust pipe ■Main product specifications Like head gaskets, beads are formed on the base materia...
Sowa Industries Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
A gasket made of EPDM rubber that is pressure-molded into a cross-sectional shape. ■Features Suitable for piping lines where surface pressure cann...
Muramatsu Co., Ltd.
300+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Structure A gasket made of forged metal with an octagonal cross section. ■Features ・Provides sealing performance through surface contact between...
Eco Transfer Japan Co., Ltd.
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 10 hours ago
■Summary The gasket ``Carflex'' at the wiring point tightly adheres to the thin cable and leaves no gaps. A reliable gasket that quickly completes ...
Hamamatsu Gasket Co., Ltd.
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 18 hours ago
A seal that prevents oil, cooling water, and (combustion gas) from escaping is required. ■Main uses Water pump passage seal ■Main product specifi...
Sowa Industries Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
Last viewed: 10 hours ago
This is a gasket made by pressurizing and heating a PTFE film onto an EPDM rubber molded product and bonding it together. ■Features Suitable for p...
E-SONG EMC CO., LTD.
620+ people viewing
■Summary ・EMI Shielding Finger strip gaskets use beryllium copper (BeCu) as their main material, are resistant to metal fatigue, have excellent el...
10 models listed
Muramatsu Co., Ltd.
340+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
Metal O-Seal is a gasket that seals using the reaction force caused by crushing (compression). The perforated type is recommended for high pressure...