All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for heat exchangers as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 171 heat exchanger manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked heat exchanger companies as of July, 2025: 1.THERMAL FLUID SYSTEMS, INC., 2.Barksdale, 3.Gaumer Process INC..
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Heat Exchangers
Engaged in research on nitride semiconductor growth using the MBE method at Waseda University Graduate School. After graduating from graduate school in 2016, he joined a non-ferrous metal manufacturer.
Engaged in equipment maintenance and engineering work at metal smelting plants. Moved to a chemical manufacturer in 2022. Engaging in similar tasks.
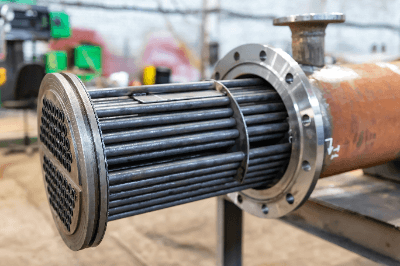 A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between fluids, such as air and water.
A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between fluids, such as air and water.
A typical device that uses a heat exchanger is an air conditioner, a machine that regulates room temperature by a heat exchanger between a refrigerant and air. Various structures have been developed, and appropriate selection is necessary according to the fluid used for heat exchange.
Heat exchangers are used in a variety of applications, from household appliances to industrial applications.
The following are examples of heat exchanger applications:
In the home, heat exchangers are used in air conditioners and refrigerators. They maintain the required temperature by transferring heat from the room or inside the cabinet. Heat exchangers are also used in water heaters and floor heating systems.
There are countless examples in industry. Factories with industrial furnaces use industrial water or seawater to cool their jackets in heat exchangers. Heat exchangers are also widely used in infrastructure facilities such as power plants, and condensers in steam power generation are also a type of heat exchanger.
Heat exchangers such as heat sinks are used to cool computers. This is a product with many heat sinks, which are installed directly on the heat-generating medium and use the ambient air as a cooling medium.
A heat exchanger consists of piping and fins.
Piping is the structure through which the medium to be heated or cooled flows. Generally, they are made of metal, and a variety of products are available, such as stainless steel and copper, depending on the application. When a fluid that serves as a heat source flows through it, it is called a heat medium pipe, and when a fluid that serves as a cooling source flows through it, it is called a refrigerant pipe.
A fin is a structure that efficiently dissipates heat. Aluminum is often used because of its excellent heat transfer characteristics. They are attached to the piping in the form of pleats.
Depending on the direction of flow of low-temperature fluid and high-temperature fluid, there are two types: countercurrent and parallel flow. When they flow in opposite directions, they are of the countercurrent type, and when they flow in the same direction, they are of the parallel flow type. Generally speaking, the directional flow type is more efficient for heat exchange.
Typical types of heat exchanger structures include multi-tube heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers, and spiral heat exchangers. Other types include air-fin type, fin-tube type, and coil type.
A multi-tube heat exchanger consists of a thick circular tube and many thin circular tubes inside the circular ring. The fluid to be exchanged flows into the thick tube, and the refrigerant or cooling water flows into the thin tube. Since each pipe is partitioned, the fluids do not mix and heat is exchanged between them.
This heat exchanger consists of a number of specially processed metal heat transfer plates that are stacked on top of each other, and the high-temperature fluid and low-temperature fluid flow alternately across the plates.
This heat exchanger easily achieves a turbulent flow effect and a high heat exchange rate. They also have the advantage of a compact design and are less likely to cause problems in terms of installation location. Because of the stacked structure of the heat transfer plates, the number of plates can be changed according to the process requirements. However, it is difficult to use this type of heat exchanger with fluids that have high viscosity or contain particles, as these fluids can cause blockage between the plates.
A spiral heat exchanger is a heat exchanger that exchanges heat between two fluids in a spiral-shaped flow path where the two fluids do not mix.
The inside of the channel is a single flow path, and even if a substance adheres to the walls of the heat exchanger, it can be peeled off from the walls. This is because the channel width is shortened and the flow velocity is increased. Therefore, it is suitable for the heat exchange of fluids containing impurities.
This heat exchanger consists of a tube and a fan. It is used for cooling. The fluid to be cooled flows through the tube and is cooled by air flowing through it using the power of the fan.
This type of heat exchanger has fins (heat-transfer plates) installed on tubular tubes to increase the heat-transfer area. This type of heat exchanger is used in air conditioner heat exchangers.
This is a heat exchanger in which the heat transfer tubes are coiled and the outside is surrounded by a cylinder or the like. A cooling or heating medium is inserted into the tube to exchange heat with the tube side.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Thermal Fluid Systems, inc. was founded in 1994 and is headquartered in Kennesaw, Georgia. The company is a designer, manufacturer, and complete system supplier of thermal fluid heaters and hot oil systems including heating, cooling, pumps, valves, and associated equipment. The company’s equipment is designed to run at very low pressure which increases reliability and operational efficiency, reducing the total cost of ownership. The company’s lineup includes thermal fluid heating systems, electric heating systems, fluid filtration systems, process skids, and waste heat recovery systems. These serve industries such as aerospace, textiles, automotive, and power generation.

CoorsTek, Inc., founded in 1910, is a family-run manufacturer of technical ceramic material formulations with products such as acetabular liners, baffle chambers, carbon brushes for power, focal plane array components, and precision fixed gauges used in transportation, food & beverage, electronic, chemicals, and semiconductor industries. The company in Golden, CO, USA, has research & development, custom manufacturing, and design assistance capabilities. The company's CIO- Matt Mehlbrech, was awarded the 2023 Colorado ORDIE Award for CIO of the Year.

Gamer Process was founded in 1962 and is headquartered in Houston, Texas. The ISO 9001 registered company is an electric heater manufacturer, providing engineering, design, and manufacturing of heating equipment and systems including control panels, liquid fuel conditioning, pumping, and other engineered systems for industrial, paper, marine, aeronautics, and defense industries. Some of the company’s heating solutions include indirect electric heaters, duct heaters, and process immersion heaters. The company’s non-heating solutions include pressure reduction stations, fuel gas scrubbers, and ammonia unloading stations.

ProSonix, LLC, founded in 2007, operates as a manufacturer and provider of process heating solutions. Based in the United States, the company specializes in steam injection heating systems and liquid heating technologies. It serves diverse industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power plant & boiler operation, pulp & paper, food and beverage production, among others. The company's cutting-edge solutions optimize heating processes, ensuring efficiency and cost savings for its clients.

Pick Heaters, Inc., established in West Bend, WI, in 1945 is a manufacturer of Direct Steam Injection Industrial & Sanitary Liquid Heaters. Their product portfolio includes sanitary liquid heaters used in the food and beverage industry, providing hygienic and precise heating for food processing, and industrial liquid heaters used for handling a wide variety of liquids, including water, chemicals, and food products. The company serves industries including Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology, Chemical and Petrochemical, Water and Wastewater Treatment.

Barksdale, established in 1949 and headquartered in Reichelsheim, Germany, is a manufacturer of industrial control and regulator products. The comprehensive product line includes pressure, transducers, switches, temperature, level, and flow controls that offer precise monitoring, efficient regulation, and enhanced operational safety. These products find application in industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing, energy, and transportation. The company's accurate monitoring instruments optimize processes, guarantee operational efficiency, and maintain safety standards, all of which add to the smooth running of complex industrial systems.

Inproheat Industries Ltd., a company established in 1958, is based in North Vancouver, British Columbia, as a manufacturer and supplier of liquid heating and evaporation systems. It manufactures SubCom direct fire heaters, heat exchangers, industrial blowers and compressors, steam generators, and metallurgical sensors. Its products are utilized in evaporative, forestry, petroleum, mining, and chemical industries. Each of its products is equipped with patented Submerged Combustion technology for industrial liquid heating and evaporation applications. The company acquired ISO 9001:2015 certification and is a Class A (Guideline BRC-7025) Boiler Contractor licensed. It has partnered with Ask Chemicals, Belco, Bernoulli, Evapco, and Heraeus Group.


Caterpillar Inc., established in 1925 and headquartered in Irving, Texas, is a manufacturer of construction and mining equipment with a portfolio of about 20 brands. The company also produces engines, turbines, and locomotives, serving several industries, including agriculture, construction, and mining. It operates through its three primary segments — resource, energy, and construction — and has a financial products segment that provides financing and related services. The company operates approximately 150 primary locations worldwide, with its common stock listed on the New York Stock Exchange as well as on the stock exchanges in Switzerland and France.

Dry Coolers, Inc., established in 1985 is a manufacturer of industrial cooling solutions headquartered in Oxford, Michigan, USA. The company, which has on-site engineering and fabrication departments offers various cooling technologies and custom solutions such as evaporative cooling towers, mechanical chillers, pump stations, air-cooled heat exchangers, and accessories such as plate heat exchangers, bag filters, controls, sensors, and centrifugal separators. It has passed the ASME, CSA, CE, and UL standards and is ISO 9001:2015 certified to offer products to various industries including aerospace, canning, energy, data centers, and metal treatment.

Taco Comfort Solutions, founded in 1920, and headquartered in Cranston, Rhode Island, is a manufacturer of heating, cooling, plumbing, and irrigation products. Catering to residential, commercial, industrial, and institutional markets, offered products include lead-free shut-off flanges for pipe connections, domestic water booster systems enhancing water pressure, ECM circulators for hydronic systems, air-to-water heat pumps for heating and cooling, and commercial air & dirt separators. The company holds significant certifications including ISO 9001:2015 for quality management, Hydraulic Institute's Approved Pump Test Lab certification, and ASME certification for adherence to safety standards in product design and manufacturing.

Kooltronic, Inc., established in 1956 and headquartered in Pennington, New Jersey, USA, is a manufacturer of thermal management solutions for equipment and process cooling applications. It offers a range of products, including enclosure air conditioners, centrifugal and packaged blowers, and fans and fan trays. These products are used for controlling the temperature of equipment housed in electrical enclosures and rack enclosures, and are incorporated into Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) products. The company has been granted ISO 9001:2015 certification by DQS Inc., for its quality systems.

Wasco Switches & Sensors is a manufacturer and supplier of pressure and temperature vacuum switches. Established in 1963, the company is headquartered in Santa Maria, California, USA. The company specializes in producing a wide range of pressure and temperature switches for various applications. Its product portfolio includes pressure sensors, switches, and transducers, serving industries such as HVAC, semiconductor, medical and industrial, fire suppression, and defense as well as aerospace. Wasco Switches & Sensors offers services like technical support and customization.


John Crane, founded in 1917 and based in Chicago, Illinois, US, is a manufacturer of mission-critical flow control solutions for increased efficiency, emission reductions, and energy transformation. The company’s products include mechanical seals, seal support systems, seal face technologies, power transmission couplings, and bearing isolators among others. It serves a wide range of industries such as oil & gas, power generation, chemical, pharmaceutical, and polymers among others. The company also offers services like mechanical seals reliability programs, turbomachinery services, asset management solutions, and gas seal management program.

Xylem Inc. was incorporated in 2011 and is headquartered in Washington, District of Columbia. Xylem engages in the design, manufacture, and servicing of engineered products and solutions for the water and wastewater applications across global markets. Xylem operates through three segments: water infrastructure, applied water, and measurement & control solutions. Xylem’s water infrastructure segment offers numerous products such as water pumps, filtration, disinfection, and biological treatment equipment. Xylem’s applied water segment distributes pumps, valves, heat exchangers, controls, and dispensing equipment systems. Xylem’s measurement & control Solutions segment offers devices such as smart meters, networked communication devices, data analytics, test equipment, controls, sensor devices, and software and managed services.

Thermal Edge Inc., established in 1985 and based in Irving, Texas, is a manufacturer and designer of industrial enclosures and air conditioning units. The company specializes in producing cooling solutions for electrical enclosures and control panels in various industries, including manufacturing, automation, and telecommunications. Its main products include air conditioners, heat exchangers, filtered fans, and enclosure accessories. These units find applications in protecting sensitive electronic equipment from overheating. The company also offers a five-year warranty on all its products.

Sentry Equipment Corporation is a manufacturer and supplier of sampling and analysis equipment based in Wisconsin, USA. Established in 1925, the company's products include sampling systems, sample preparation equipment, and analyzers. These solutions are designed to cater to industries such as power generation, oil and gas, chemical, petrochemical, food and beverage, pulp and paper, pharmaceutical, and more. Its product offerings help ensure accurate and representative samples for quality control, process monitoring, and compliance purposes. The company holds the ISO9001:2015 certification.

Watlow Electric Manufacturing Co. was established in 1922 and is headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri as a manufacturer and designer of heating solutions. Their product portfolio includes electric resistive heaters, temperature sensors, temperature and power controllers, and supporting software. The industrial technology and thermal products offered by the company are crucial components in optimising thermal performance, decreasing design time, and improving the efficiency of products and applications. The company's sales offices span 16 countries, serving diverse industries like semiconductor processing, energy processes, environmental chambers, diesel emissions, and foodservice equipment, among others.

Kadant Johnson, established in 1930 and based in Three Rivers, Michigan is a manufacturer of rotary pressure joints and fluid handling equipment. The company manufactures and supplies various products, such as jet devices, condensate pumps, siphons, dryer bars, and system controls. The company also offers manufacturing services like testing, repairing, and installing components. Various industries that use the company products are plastic, rubber, chemical, and construction. The R&D department of the company develops and tests the products in natural conditions before installation.

JBT Corporation, established in 1894 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, is a manufacturer and designer of automated systems. Its diverse product portfolio includes airport ground support equipment, cargo handling systems, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), labeling machinery, evaporators, as well as brine-making equipment, and food processing machines. The company also offers comprehensive engineering, maintenance, and repair services, catering to industries such as automotive, food and beverage, healthcare, and paper. Its products are utilized for automating processes, increasing efficiency, ensuring product quality, and reducing manual labor.

Enerquip Thermal Solutions, founded in 1985, is an American manufacturer based in Medford, Wisconsin, specializing in sanitary and industrial heating and cooling solutions. The company’s product portfolio includes a range of shell and tube heat exchangers, such as off-the-shelf, industrial, pharmaceutical, and sanitary heat exchangers. It also offers an array of industrial heaters, ranging from single heating system components to custom thermal fluid systems. Furthermore, the company provides industrial heaters like asphalt, process, waste, and thermal fluid heaters. Custom vapor condensers and tank heating solutions are also available. The company serves various industries including chemical, food and beverages, pharmaceutical, and renewable fuel.

Metalcraft Services of Tampa, Inc., founded in 1947, is a manufacturer of custom and specialty metal fabrications used in the energy, phosphate, entertainment, and construction industries. Based in Tampa, Florida, the company deals with products like phosphoric acid filtration systems and pressure vessels. They also produce chemical process equipment for the general chemical industry. Metalcraft has partnered with APEX Engineered Products to manufacture shell and tube, heat exchangers. The pressure vessels, reactors, and jacketed and industrial tanks they build meet the ASME Code.

Elanco, Inc., founded in Bear, Delaware, in 1978 is a manufacturer of Spiral Plate Heat Exchangers and Custom Heat Transfer Equipment. The company's product portfolio includes air cooled heat exchangers, Double Walled Tube Heat Exchangers, Encoils and Specialized Shell And Tube Heat Exchangers. The company serves industries such as Oil and Gas, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Construction, and Power Generation. They also provide services including product selection, installation, preventative maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.

Petro-Chem Industries, founded in Chicago, IL in 1969 is a manufacturer of heat exchangers for the petrochemical, steel, and power industry. The company's product portfolio includes Nuclear Power Plant Heat Exchangers, Air-Motor Coolers, Turbine Oil Coolers, Transformer Oil Coolers and Gas Coolers. The company serves industries such as Oil and Gas, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Construction, and Power Generation. They also provide services including product selection, installation, preventative maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.

STAFCO, founded in 1952 and located in Indiana, USA, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial storage tanks, serving diverse industries worldwide. They offer a wide range of storage tanks, including aboveground, underground, and mobile tanks. These tanks find applications in industries such as oil and gas, agriculture, manufacturing, and chemical processing. STAFCO's products are designed to store liquids such as petroleum, water, chemicals, and hazardous materials, ensuring safe and efficient storage solutions.

Exergy, LLC, founded in 1979 and headquartered in Garden City, New York, is a manufacturer and supplier of heat exchangers. The company caters to industries such as pharmaceutical, biotech, sanitary, industrial, and process, offering a comprehensive catalog featuring shell and tube heat exchangers, tube-in-tube heat exchangers, POU sampling systems, condensers, as well as reboilers, evaporators, and heat transfer accessories. Exergy, LLC is certified under ISO 9001:2015 industry standards for its quality management system.

Procedyne Corp. is an American manufacturer and supplier of thermal processing equipment that was established in New Brunswick, New Jersey in 1981. The company primarily produces fluid bed reactors, calciners, food processors, and dryers. It also offers heat treating furnaces, catalyst activators, waste to energy systems, and thermal cleaning equipment, as well as contract manufacturing services for unique customer projects. Procedyne mainly serves clients in the metalworking, chemical, and food processing sectors, including companies such as ExxonMobil and the Ford Motor Company.

ERG Aerospace is an American manufacturer of open-celled, solid ligament foams founded in 1967 and headquartered in Sparks, Nevada. Under the brand name Duocel, the company offers metal, ceramic, and carbon foams in materials such as titanium, phenolic resins, or silicon carbide. With features such as high-temperature and corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity or stability, or chemical inertness, these can be used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, biomedical applications, cryogenic tanks, or combustion chambers. ERG Aerospace also provides additional services to its clients including design, prototyping, testing, coating, and bonding for custom projects.

SUSSMAN Electric Boilers, a Div. of Sussman-Automatic Corp. (SEB) is a manufacturer of electric steam and hot water boilers originally established in 1917 before its acquisition in 2022 by Diversified Heat Transfer, Inc. (DHT). Based in Towaco, New Jersey, the company offers various boilers, generators, and heat exchangers. These include humidification boilers, electric steam generators, stainless steel electric steam boilers, and steam heat exchangers. SEB serves clients in a range of industries, including chemical processors, pharmaceutical manufacturers, biotechnology facilities, and dry-cleaning businesses.

Orca Marine Cooling Systems, established in Bellingham, WA, in 1973, is a manufacturer of marine heat exchangers and cooling systems. Their product portfolio includes engine cooling systems to ensure optimal temperature regulation and performance for marine engines, seawater desalination cooling systems, and engine cooling systems to ensure optimal temperature regulation and performance for marine engines. The company serves industries such as Commercial Shipping and Cruise Lines, Naval and Defense Vessels, Offshore Exploration and Oil Platforms.

TITAN Metal Fabricators is a designer, manufacturer, and supplier of corrosion-resistant process equipment for industries facing corrosion challenges in Camarillo, USA. Their expertise lies in reactive metals and corrosion resistant alloys such as Titanium, Tantalum, Zirconium, and more. TITAN offers a wide range of process equipment, including Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers, Columns and Towers, Condensers, Reactors, and Pressure Vessels. The company serves diverse industries like Oil and Gas, Pharmaceutical, Steel, and Chemical. Their subsidiary in Wuxi, China, also specializes in Reactive Metal Process Industry Equipment.

Thermal Care, Inc., established in 1969, is an ISO 9001-certified industrial water chiller and process cooling equipment manufacturer in Niles, Illinois. The company ships worldwide, and has domestic and worldwide sales offices in Canada, Mexico, Central, and South America. Its product lineup includes cooling towers, portable chillers, reservoirs, and temperature controllers. Further, Thermal Care produces standardized and customized cooling systems for a vast range of industries, from food and dairy, to aviation, medical, and industrial.

Fin Tube Products, Inc., established in 1993 and headquartered in Wadsworth, Ohio, is a manufacturer of both standard and custom helical-wound finned tubes and pipes. Its finned tubing comes in various standard sizes commonly used in applications such as heat exchangers, boiler economizers, coolers, and heaters. Its range extends to small diameter and miniature finned tubes (hypodermic), which find usage in military cryostats, cryogenic coolers, and medical cryoablation procedures. Utilizing an in-house brazing process, the company has the capability to affix stamped fins of diverse shapes and sizes to their products.

Heat Exchange and Transfer, Inc. was founded in 1968 and is headquartered in Carnegie, Pennsylvania. The company is a designer and manufacturer of custom, made-to-order heat transfer systems, serving industries such as aerospace, automotive, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and packaging. The company’s two product divisions are Direct Heating and Indirect Heating of Process Equipment. Direct Heating includes open coil heaters, flanged immersion heaters, unitary storage tank heaters, and stand-alone circulation heaters. Indirect Heating of Process Equipment includes extruders, mixers, ovens, dryers, and other equipment and machinery.

Pre-Heat, Inc. (PHI) is an American manufacturer of heat exchangers and heat recovery systems originally founded as Construction International Inc. in 1984 before its rebrand in 2000. Based in Oostburg, Wisconsin, the company designs and produces various heat exchangers including shell and tube, in-line wave plate, and dimple plate models, as well as various cooling towers. These are commonly used in metal fabrication, oil refining, food processing, and in the drying or curing processes involved in manufacturing wood products. PHI also offers repair, replacement, retrofitting and upgrade services, as well as custom design and engineering for demanding customer projects.

Coastal Manufacturing, Inc., based in Watsonville, California, is a manufacturer of equipment for the food processing industry, beverage, pharmaceutical, and high-tech sectors. The company offers various products including specialty conveyors, produce chilling and washing units, high precision fabrication units, and heat exchangers. They also produce hydro chillers, inspection conveyors, paddle mixers, carrot sizers, and carton conveyors. All of their equipment is CAD-designed and CNC-cut. Coastal Manufacturing Inc. offers engineering solutions, covering the entire process from design to installation.

Pearse Betram+ was founded in 1947 in Bloomfield, Connecticut. Today Pearse Bertram+ is an end-to-end solutions provider for the manufacturing industry. Pearse Bertram+ is ISO 9001:2015 certified and also UL508A (industrial control panels), IPC 620 (wire harness assemblies), and IPC-A-610, J-STD-001, and IPC-7711 certified for soldering. Pearse Bertram+ operates in both contract manufacturing and engineering support. The manufacturing segment includes electrical, pneumatic, robotic, hydraulic, and process systems. Engineering support includes support for operation of robotics, machinery design and usage, industrial automation, value engineering, and auditing.

The Titus Company was founded in 1986 and is based in Morgantown, Pennsylvania. The Titus Company provides expertise for compressed air solutions for private companies in manufacturing, concrete, and chemical applications as well as government institutions such as the Royal Navy. Product offerings include blowers & vacuum products, chillers & coolers, compressors, dehydrators, dryers, dust collection equipment, energy management tools, filters, gas generators, pumps, and accessories. The Titus Company also offers maintenance, service, repair, system analysis, system dieting, monitoring, as well as installation services.

Advanced Thermal Solutions, established in 1989, is a global manufacturer and supplier specializing in thermal management of electronics, headquartered in Norwood, Massachusetts, USA. Their range of products includes heat sinks, thermal interface materials, heat pipes & vapor chambers, and liquid cooling systems, which are used to manage and control the temperature of electronic devices. These products are applied in industries such as electronics, automotive, Internet of Things, thermal management, military, and aerospace. Advanced Thermal Solutions, Inc.'s quality management system is certified according to ISO 9001:2015.

Custom Thermoelectric LLC was established in 2005 and is based in Bishopville, Maryland, United States, and is a manufacturer and supplier of thermoelectric devices and products for various industrial applications. The company provides thermoelectric generators and assemblies, water blocks, liquid cold plates, and thermal interface materials for thermal power generation applications based on solid-state semiconductor materials. The company specializes in custom-made and "customized" TE devices designed to optimally fit a customer's interests, such as physical size, thermal performance, power consumption, and environmental requirements.

Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., founded in 1956 and headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts, is a manufacturer and supplier of life science solutions, analytical instruments, specialty diagnostics, laboratory products, and biopharma services. Through its brand names, including Invitrogen, Fisher Scientific, Patheon, Applied Biosystems, and Gibco, among others, the company provides a wide range of products, which include chromatography systems, thermal cyclers, automated cell counters, fermenters, and DNA polymerases. The company’s annual revenue is over 40 billion USD, and it serves several fields, including customers working in clinical diagnostic labs, research institutions, hospitals, government agencies, and pharmaceutical/biotech companies.

Orange Research Inc. is a manufacturer and supplier of high-precision fluid measurement and control instrumentation. The company was established in 1963 and is based in Milford, United States. The company product range includes Differential pressure flow meters, flow switches, and mini-transmitters. The company equipment used in various industries such as aerospace, industrial, pharmaceutical, and more. The company offers customer support services which encompass technical assistance, troubleshooting, installation guidance, and maintenance support.

ENERVEX, established in 1990 and based in Alpharetta, Georgia, is a manufacturer and supplier of draft control and mechanical draft solutions. The company introduced the industry's first mechanical draft fan in 1958 and delivers custom-built, comprehensive venting systems from boiler outlet to chimney termination. These are engineered to optimize exhaust and air quality while reducing energy consumption and CO2 emissions3. The company serves North and Central America as well as the Middle East, operating from its 80,000-square-foot facility.

SPX Cooling Tech, LLC was established in 1957 in Overland Park, Kansas, specializing as a manufacturer and supplier of cooling solutions such as cooling towers and evaporative fluid coolers. Located in Kansas City, their R&D Center stands as the technological cornerstone for various product lines. With a network extending to over 150 global locations, SPX Cooling Tech offers localized solutions across HVAC, industrial cooling, and refrigeration sectors, covering everything from system design to maintenance.

TruStop Inc. created in 1999 is a manufacturer and distributor of CODE Stamped Pressure Vessels, and precision machined products located in Tempe, AZ. The company has heat exchangers and tube bundles, filter vessels, and skid systems which serve a wide range of companies where precision-engineered and manufactured products are needed. The services provided by Trustop Inc include engineering and design, cable and wire harness assembly, and contract manufacturing. Their products serve the Oil and gas, filtration, Fluid processing, Aerospace, and medical industries.

Metafin Supply company was founded in the 1980s and is headquartered in Volo, Illinois, and is a distributor of metal finishing and electroplating equipment and supplies for the surface finishing industry. Metafin Supply offers a range of machines and parts. Machine listings include pumps, filtration systems, centrifugal dryers, and heaters. Parts and components include cartridges, individual chemicals, tank magnets, and dipping baskets. Items or parts not present on the website may be available upon request by email or phone.
Potter Associates, Inc. was founded in 1964 and is based in Rochester, New York. Potter Associates is a manufacturer and distributor industrial materials, tools, and machinery. Manufacturing capabilities include V packaging sets, O-rings, gaskets, sheet material, rubber extrusions & sheet material, heat exchangers, compression braided packing, non-asbestos brake linings, urethane molding, and PTFE machining. Other product offerings include valve packing, pulp and paper packing, soot blower sets, copper packing, metallic packing, and wastewater treatment packing.

TAM Metal Products Inc., established in 1969 and headquartered in New York, USA, is a manufacturer and supplier of oilfields and energy industrial solutions. The company’s product range includes a wide variety of offerings, including drilling fluids, wellbore cleanup tools, and cement additives. These solutions cater to the oil and gas sector, enhancing efficient drilling, well-maintenance, and production. TAM International is devoted to providing quality products and services that meet industrial standards and exceed customer expectations. With decades of experience, they continue to play a crucial role in supporting the energy company's operations and technological advancements.

IEA Cooling, established in 1993 and headquartered in Kenosha, Wisconsin, USA, is a manufacturer and supplier of custom industrial radiators and heat exchangers. The company's product range includes custom radiators, heat exchangers, cooling towers, condensers, and air-cooled heat exchangers, catering to diverse industries such as standby power generation, co-generation, marine, oil & gas, and heavy vehicle.The company’s services encompass design and engineering, testing and certification, supply chain management, and technical support. The company is devoted to providing quality custom industrial radiators and heat exchangers to its customers. This determination is reflected in their ISO 9001:2015 certification.

Process Solutions, based in Rehoboth, Massachusetts is a manufacturer and service provider of heat exchangers used in industrial settings including factories and material handling facilities. The company has four product divisions and offers replacement parts and services for each. Shell and tube heat exchangers are the most versatile standard. Plate and frame heat exchangers are the most efficient and easy to service and modify after-market. Spiral plate heat exchangers are the most durable in demanding thermal applications. Finally, industrial coil heat exchangers are useful in niche applications.



Johansing Iron Works, established in 1982, is a manufacturing and service company offering engineering, fabrication, and repair services for heat exchangers and pressure vessels. The company, based in Benicia, was established by acquiring Bender’s Machine, UNICO Services, Inc., California Centrifugal Pump, and Johansing Iron Work by the Potters’. They are also outsource partners offering ASME engineering and designs, welding, and repair services. They also offer process piping, instrumentation, and assembly of skid-mounted systems.
Oji Industrial Materials Management Co., ltd. filter business division is a part of Oji Holdings.Oji Holdings, founded in 1873, is the largest paper manufacturer in Japan. With its history spanning some 150 years, the Oji Group has cultivated challenging manufacturing based on insight gained from paper making and forest development. Filter technologies based on wood resources are one such example. Our mission is to conserve energy and improve air quality. To shape a livable future, we will harness nature's gifts to provide innovative products.

Thermofin, established in 1993, is a designer and manufacturer headquartered in Candiac, Canada, specializing in creating heat exchange solutions. Its product range encompasses ten segments: hydroocool, Electra, powerfin, caleos, and T-rex. These products find application in hydropower, electrical substations, and industrial and petrochemical industries. The company's heat exchangers are utilized in thermal power to enhance thermodynamic gain and reduce resistance in naval applications. It also offers various services, including onsite repair, maintenance, engineering, and performance diagnosis.

Sulzer Ltd. is a fluid engineering and chemical processing solutions manufacturer originally founded in 1775. The company has been headquartered in Winterthur, Switzerland since 1834, maintaining a network of 180 manufacturing facilities and service centers around the world. The company has an expansive product portfolio including distillation and absorption columns, agitators, reactors, crystallizers, and polymerization systems. These supply clients in the metals, plastics, chemicals, power, and pharmaceutical industries. Sulzer Ltd. also offers a range of services, such as testing and diagnostics, prototyping, retrofitting, and upgrades, including technical training with long-term support for their customers.

SUNKAIER Industrial Technology Co. Ltd. is a Chinese manufacturer of process equipment and technology established in 1999 and based in Yixing, Jiangsu. The company produces various reactors and mixing agitators, as well as polymer processing and heat transfer equipment. Aside from its products, the company offers engineering services including project planning and commissioning, installation, and maintenance. The company's products are mainly used by its clients in the petrochemical, energy, and pharmaceutical sectors.

Danfoss, established in 1933 and headquartered in Nordborg, Denmark, is a manufacturer specializing in Climate Solutions, Drives, and Power Solutions. The company's solutions find applications in various sectors such as refrigeration, heating, and both off- and on-highway equipment. It also offers solutions for renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, alongside district-energy infrastructure for urban areas. Its digital displacement pump received both the Powertrain Product of the Year and Achievement of the Year in the 2022 Diesel Progress Summit Awards.

Pfannenberg, Inc., established in 1954 and located in Lancaster, New York, is a global manufacturer and supplier specializing in thermal management, liquid cooling solutions and signaling technologies. The company’s product line includes filter fans, air to air heat exchangers, chillers, visual signaling devices, and more. These products cater to various applications, including machine tooling and food and beverage equipment. The company offers pre-sales consulting, engineering support, and after-sales maintenance services such as on-site repair, parts and training. With headquarters in Germany and the US, and locations worldwide, the company serves various industries globally including manufacturing, food, energy and automative.

HRS Heat Exchangers is a manufacturer of heat transfer products located in Watford, Hertfordshire, and was founded in 1981. The company's product line includes plate heat exchangers, aseptic fillers, hydraulic piston pumps, multitubular heat exchangers and CIP packages. It serves a wide range of industries, including the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, Industrial, and environmental Industries. The company provides food processing, environmental, and product and process trial systems. Its systems are designed to maximize energy efficiency and reduce waste.

Coperion was founded in 1879 and is headquartered in Stuttgart, Germany. The company is a manufacturer of the machines and systems used in the recycling, food, pharmaceutical, plastics, and other industries. The company has five business platforms: Extruders & Compounding Machines, Process Equipment, Plants & Systems, Service, and C-Beyond. Extruders & Compound Machines include conveying systems, palletizers, and extruders that sort and dry materials for pharmaceuticals, food, and recycling. Process equipment includes valves, mixers, and product feeders. Plants & Systems include larger machines and complete plants. Services and C-Beyond help customers maximize product, machine, and system utility.

HT S.p.A., founded in 1978 and now a subsidiary of NIBE Industrier AB, is an Italian manufacturer based in San Vendemiano, Treviso, producing cartridge electric heaters. The company obtained its first patent for cartridge heaters in 1980 and has since designed these products for various domestic applications, including towel rails and radiators. These heaters, equipped with built-in thermocouples and leads suitable for high temperatures, cater to a wide range of industries such as food and health technology, plastics, and transportation. In addition to cartridge heaters, HT S.p.A. offers an array of heating solutions, including air, immersion, and tubular heaters.

Energest is a Portuguese manufacturer of thermal engineering products that was established in Lisbon in 1998 as a subsidiary of Energias de Portugal SA. The company’s product portfolio includes heat exchangers, burners, and boilers for heating as well as cooling processes. It also offers solar panels and thermal oil systems, along with design and engineering, installation, and upgrade services. The company’s products are used mainly by clients in the chemical, energy, and pharmaceutical industries, including by companies such as Sonae and Pfizer.

Evoguard GmbH, founded and owned by Krones AG in 2014 and headquartered in Nittenau, Germany, is a manufacturer of valves and pumps used in beverage plant operations. The company's products include hygienic valves, vessel dome fittings, and Evotube heat exchanger systems. Due to its product innovation and independent operations, apart from being used in beverage filling plants and dairy processing plants manufactured by Krones AG, it has expanded its product range to serve the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors.

Bondioli & Pavesi Inc. is a manufacturer of hydraulic and mechanical products established in 1980 and located in Ashland, Virginia, USA. The company offers gearboxes for mechanical drives, power take-off (PTO) drive shafts for transmitting power in industrial machinery, and axial piston pumps and motors for converting mechanical energy to hydraulic energy. It also offers directional control valves, gear pumps and motors, and heat exchangers for transferring heat between fluids. The company is ISO 50001 and ISO 14001-certified, and mainly serves clients in the energy, construction, and industrial automation sectors.

Kamui Co., LTD., established in 1960 and headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is a manufacturer that manufactures and sells heat exchangers. The company offers a range of products that are designed to keep hydraulic fluid, compressors, and gas turbine generators. It also provides a wide range of maintenance and support after product delivery. Its products can be used with any equipment in any environment and have short lead times. The company has received an award from the Inspector of Chiba Prefectural Labor Standards. It serves various industries such as Industrial equipment, Construction equipment, Chemical devices, and more.

Rittal is a German manufacturer of electrical enclosures and related products that was established in Herborn, Hesse in 1961 as part of the Friedhelm Loh Group. The company primarily produces standard and modular enclosures for various electronic and electrical components, such as servers, switchgear, or control panels. It also offers automation, power distribution, IT infrastructure, and climate control systems for use in industrial facilities. Rittal products are mainly used by clients in the telecommunications, energy production, automotive, maritime, and logistics sectors.

Bitzer is a manufacturer of refrigeration condensing units and compressors that was established in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, in 1934. The company offers screw compressors, reciprocating compressors, and scroll compressors for refrigeration or air conditioning units. It also offers pressure vessels, condensing units, and heat exchangers for models with different capacities or refrigerants. The company provides maintenance and repair services for its clients in Europe’s transportation, refrigeration, and HVAC industries. It is certified to ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 operating standards.

Zeltwanger, founded in 1982 and based in Tübingen, Germany, is a manufacturer of products in the leak testing, thermal management, and mechanical engineering fields and consists of eight independent companies. Its contract manufacturing business manufactures prototypes, machine components, and 3D molded parts. The thermal management business manufactures systems for producing and functional testing efficient heat exchangers like those used in heat pumps, radiators, and conditioning units. The company also makes leak-testing products and serves the packaging, medical technology, and optical industries. All its companies are ISO 9001 certified, and its calibration laboratory is ISO/IEC 17025 accredited.

Peter Huber Kältemaschinenbau SE, established in 1968 and headquartered in Offenburg, Germany, is a manufacturer of temperature control systems and solutions for research and industry. The company's products include dynamic temperature control systems, baths and circulators, and heat exchanger systems, catering botanical extraction, chemicals, and semiconductor industries. It provides high-precision thermoregulation solutions for research and industry, ensuring precise temperature control from -125°C to +425°C in laboratories, pilot plants, and production processes. The company also offers circulators, classic heating and cooling thermostats, and customized special equipment, providing factory and on-site calibrations, dynamic temperature control systems, and chiller services.

Parker Plant Ltd., established in 1911 and headquartered in Leicester, United Kingdom, is a mining, quarrying, and demolition equipment and solution designer and manufacturer. It's products include industrial vehicles, equipment, and plants for bitumen handling, wet and dry concrete mix batching plants, and bulk material handling conveyors used in harsh mining environments and infrastructure construction projects. The company works directly with end users to supply turnkey industrial equipment and plants, as well as partnering with original equipment manufacturers. As of 2007, it became the Phoenix Parker Group after being acquired by its then-current owner.

Pfannenberg Holding Group, established in 1972 and headquartered in Hamburg, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial electro-technology. The company's solutions include thermal management, signaling technology, and liquid cooling systems. Its products include thermostats, air-to-air heat exchangers, and obstacle lights. These products are used in disaster warning and hazardous area applications, light art, and illumination projects. Its services include the planning of individual thermal management solutions, comprehensive plant audits, and maintenance programs.

Teralba Industries, established in 1976 and based in New South Wales, Australia, is a manufacturer of heat transfer systems and stainless-steel pressure vessels. The company creates various solutions such as plate heat exchangers, dimple Flo tube-in-tube and shell and tube heat exchangers, and thermal processing equipment. It serves multiple sectors, including food and dairy, pharmaceutical, and environmental industries, and is known for its proficiency in installation, maintenance, and heat exchanger assessments. The company offers a complete engineering service encompassing customized systems' design, supply, and installation.

Armstrong Fluid Technology, founded in 1934 and headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, is a manufacturer of intelligent fluid-flow equipment and control solutions. The company develops integrated solutions that incorporate fluid flow, heat transfer, variable speed, and demand-based control to meet the fluid flow system needs in HVAC, plumbing, gas transmission, and fire safety applications. Among these offerings are packaged fluid management and plant control systems, as well as various pumps and circulators seamlessly integrated through the design envelope technology. The company received a queen's enterprise award for sustainability in 2021, in recognition of its energy efficiency, carbon footprint reduction and environmental stewardship.

Moon Environment Technology Co. Ltd., established in 1956 and based in Yantai, China, is a diversified manufacturer of refrigeration, central air conditioning, and environmental heating equipment. Its other business areas include hydrogen energy development, chemical equipment, and precision castings. The company has research, production, and service centers in over 40 countries worldwide and provides products to more than 120 countries and regions. It has 263 national patented technologies and has participated in the making of 32 industry and 20 national standards. It has also won two national awards, including the National Technology Invention Award.

Taisei Kogyo Co., Ltd., established in 1957 and headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is a manufacturer of oil filters and heat exchangers for industrial machinery and related sectors. Its product line includes hydraulic filters, suction strainers, suction line filters, as well as in-line filters, and duplex filters, designed to remove contaminants and enhance system stability, ultimately extending component and system lifespans. The company has achieved ISO 13485 medical management system certification in 2019.

Valsteam ADCA Engineering S.A. is a manufacturer of industrial fluid and steam handling equipment that was established in Guia, Pombal, Portugal in 1986. The company’s products include control valves for pressure or temperature regulation, steam traps for removing condensate from industrial processes, and heat exchangers. These are marketed under the brands ADCATrol, a product line optimized for automation, and ADCAPure, a product line optimized for high purity standards. The company’s products are commonly used by clients in the pharmaceutical, petrochemical, and food and beverage industries.

DE DIETRICH SAS, founded in 1684 and headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is a manufacturer of process equipment and solutions for the fine chemical, pharmaceutical and allied industries. The company offers a range of solutions in reaction, mixing, heat transfer, filtration and drying operations, proprietary processes such as acid concentration and solvent purification, as well as FDA and cGMP compliant multi-purpose synthesis plants. It also engineers and installs turnkey processing systems along with providing field service for the installation and maintenance of glass lined equipment. The company offers a range of equipment that can be rented to perform product tests.

Henry Group Industries, established in 1914 and based in Harbour City, Tsim Sha Tsui, Hongkong is a manufacturer of components for the commercial refrigeration and air conditioning industry. The company is international, with operations in Australia, China, Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The company's products include automatic controls, fan motors, filters and dryers, heat exchangers, and safety devices. Its pressure vessels meet CE, UL/ASME, AS1210, and TSG codes. The goods of the company are fully compliant with ISO 5149 certification. Each component has a unique QR code for identification.

EJ Bowman, founded in 1919 and headquartered in the U.K., is a manufacturer of shell and tube heat exchangers and oil coolers. The company's offerings include marine heat exchangers, exhaust gas heat exchangers, and swimming pool heat exchangers. Its product range comprises charge air coolers, engine jacket water coolers, and transmission oil coolers, which cater to the needs of diverse industries, such as automotive testing, co-generation, and marine propulsion. The company's products are utilized in applications from Antarctic winters to Australian summers, highlighting its versatility and adaptability across different environments and industries.

ElringKlinger Kunststofftechnik GmbH, established in 1971 and located in Bietigheim-Bissingen, Germany, is a manufacturer of optimal-performance engineered plastics. The company offers a broad range of products, including gaskets, PTFE materials, seals, shielding components, and custom-engineered plastic parts. It holds quality certifications like ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 for meeting stringent quality standards. Its engineered plastics are used in industries for robust mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making them ideal for applications in the automotive, aerospace, industrial, and energy sectors.

Polyfluor, established in 1983 and headquartered in Breda, Netherlands, is a manufacturer of a wide range of fluoropolymer products. The company manufactures various plastic products, including PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene), PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy), PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride), PEEK (Polyetheretherketone), and other optimal-performance polymers. It holds ISO 9001:2015 certification and offers benefits such as chemical resistance, optimal-temperature stability, electrical insulation, and low friction, making them ideal for various industries, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, electronics, automotive, and aerospace, that thrive in challenging environments across diverse sectors.

ATTSU Térmica is based in Girona, Spain, and is a manufacturer of industrial heaters and boilers that was established in 1993 following the merger of the companies Tecnivap, Teyvi, and Arcones. The company produces thermal oil boilers for heating thermal fluid systems, electric steam generators for sustainable steam-powered systems, and steam boilers for standard industrial applications. It also offers co-generation plants for simultaneous production of heat and electricity, along with equipment rental and maintenance services. The company is certified to ASME S and CE standards, and serves a wide range of clients throughout Spain’s industrial sector.

Comporato Nello S.R.L, established in 1968 and headquartered in Liguria, Italy, is a manufacturer of motorized valves, hydraulic interface units, and components for heating plants. The company offers a wide range of products, including a Sintesi 2-way ON/OFF motorized valve, FUTURA HP hydraulic interface unit, and strainers. It also offers Diamix PR and Compamix PR mixing/thermoregulating motorized valves and manual interception valves. Its motorized valve can help reduce energy costs for heating systems. Additionally, the company has achieved ISO 9001:2015 certification. It serves the heating and plumbing industries.

Bosch Industriekessel GmbH is based in Bavaria, Germany, and is a manufacturer of industrial boilers that was originally established as Loos in 1865 before its acquisition and rebrand by Bosch Thermotechnik GmbH. The company’s product lineup includes heating boiler systems for public facilities or buildings, steam boilers for commercial or industrial use, and hot water boilers for standard heating operations. It also offers thermal and process heating system solutions for customers requiring additional assistance. The company serves clients in the industrial and commercial sector, as well as German public utility companies.

HISAKA WORKS, LTD., a company established in May 1942 and based in Osaka, Japan, is a manufacturer of industrial machinery. The company specializes in providing a wide range of products and services for various industries, including petrochemicals, oil and gas, power generation, and food processing. The company provides products such as heat exchangers, pressure vessels, and other related equipment used for efficient heat transfer and fluid control. Their products play a crucial role in processes such as cooling, heating, condensation, and evaporation. The company also offers comprehensive customer support, including pre-sale consultation, product selection assistance, and after-sales support.

Advantage Engineering, Inc. is a manufacturer of industrial heat transfer products, established in 1977, and is headquartered in Greenwood, Indiana, USA. Their products include water chillers, temperature control units, and evaporative cooling towers, which provide energy-efficient process cooling, and reduce manufacturing time by controlling the temperature of equipment, materials, or the environment in industrial processes. Their facility in Indiana consists of a campus of three manufacturing buildings and one warehouse with over 100,000 square feet under the roof, annually producing more than 1,200 portable chillers, 120 central chillers, and 3,500 temperature control units.

Greenheck Fan Corporation, established in 1947 and headquartered in Schofield, Wisconsin, is a manufacturer that specializes in providing air movement, control, and conditioning equipment. The company's product line includes fans, dampers, louvers, kitchen ventilation systems, energy recovery, and more. It also offers make-up air units, indoor air handlers, fan coil units, dedicated outdoor air systems, and duct heaters. Its ventilation systems are engineered for low noise levels, providing a quiet and comfortable environment for building occupants. The company has achieved ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 certifications. It serves industries such as healthcare, education, hospitality, retail, and commercial.

New York Blower Company, founded in 1889, is a manufacturer of industrial fans and blowers made from fiberglass, stainless steel, and aluminum with special coatings. The products include incline fans, centrifugal ventilators, custom fans, axial ventilators, and silencers/flex connectors for applications such as cooling towers, sewer & water tunnels, pollution control, spray booth exhaust, and spark-resistant construction. The company in Willowbrook, Illinois, serves the railroad & locomotive, snow-making, food & beverage, thermal power generation, and microchip industries. The company provides services such as repair & rebuild, engineering analysis, preventive maintenance, aftermarket retrofit, and testing capabilities.

Solid State Cooling Systems, founded in 1994 and headquartered in Wappingers Falls, NY, is a manufacturer of precision temperature control products using thermoelectric technology with cooling capacities ranging from 160 watts to over 14000 watts. The company produces compact chillers, cold plates, semiconductor chillers, thermal control stages, and air-cooled rackmount chillers. The products produced are used in analytical equipment, lasers, semiconductors, aerospace, and defence industries. The company offers custom system development, repair, electrical design, assembly, and manufacturing services.

Cleaver-Brooks Company is a manufacturer of boiler room products and related equipment that was established in Thomasville, Georgia, USA, in 1929. The company primarily produces steam and hot water generation products. These products include water- and firetube boilers, waste heat boilers for recovering wasted heat from exhaust gasses, and electric boilers for low-noise and clean applications. It also offers low-NOx burners and economizers for improving boiler efficiency. The company’s products are used mainly by biofuel refineries, chemical processing plants, and power generation facilities.

Founded in 1885 at Cork, Ireland, Johnson Controls Inc is a manufacturer of smart building solutions and safety systems for commercial and domestic needs. The company with their OneBlue product focuses on producing blueprints for advanced and healthy technologies associated with schools, commercial buildings, hospitals and residences. The products comprise HVAC systems, building automation, security systems, energy storage, and automotive batteries. These products are used for their effectiveness in offering energy efficacy, safety, comfortability and sustainability for the dwellers. Their AI based intelligence functioning offers more productivity while being sustainable and environment friendly.

Ralston Metal Products Ltd, established in 1960 and headquartered in Guelph, Canada, is a manufacturer of electrical enclosures. The company provides both European and North American electrical enclosures and related accessories in stainless steel and non-metallic lines. It offers to modify its standard enclosures or build a custom enclosure to suit the customer's needs. It also provides online resources such as brochures and catalogs with its product dimensions and other technical information.

Tecai Innova S.L. is a Spanish manufacturer based in Logroño, La Rioja, producing duct cleaning equipment. The company's product range includes the Covix line of disinfection equipment that targets bacteria, fungi, and viruses, such as cold nebulizers, portable ozone generators, and intelligent disinfection systems. It also develops cleaning equipment for industrial kitchen exhaust and ventilation systems marketed under the Tegras brand. The Tecai line is the company's heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) cleaning solution. The ICS industrial cleaning equipment is designed for duct cleaning, among others, in atmosphere explosible (ATEX) zones, conveyor belts, and chimneys.

Pirobloc, S.A., established in 1977 and headquartered in Barcelona, Spain, is a manufacturer of thermal oil boilers and related industrial heating equipment. The company’s products include thermal oil heaters, electric steam boilers, and gas recovery boilers. It offers turnkey solutions, managing all aspects from design to commissioning. Its products are used in resin reactors, solar thermal power plants, and printing machines. Te company’s services cover thermal engineering, heat transfer fluids, and maintenance of boilers and circuits. It also facilitates indirect heating processes for steam, hot air, or hot water using heat exchangers.

Aerre Inox S.r.l., founded in 1990 and based in Lombardia, Italy, is a manufacturer of stainless-steel valves and devices. The company offers a range of aseptic and process valves, magnetic stirrers, and custom-made heat exchangers. It also produces fittings and sampling devices for various industrial sectors, such as pharmaceutical, biotechnological, and cosmetic. The company's products utilize CAD-CAM technology and numerical control machines, and they comply with FDA, USP Class VI, and ATEX certifications, ensuring conformity to strict industry standards.

Fbr-Elpo S.p.A., established in 1963 and headquartered in Parma, Italy, is a niche food production and antiseptic equipment designer and manufacturer. The company's production range includes tomato processing, fruit processing, and antiseptic plants. Its products include juice extractors, eco-saving pre-concentrators, and antiseptic filling installations. The company has installed over 700 aseptic fillers and over 100 of its food processing plants worldwide. Its after-sales services include technical and mechanical assistance as well as operator training.

Founded in 1890 in Missouri, Emerson Electric Co., is a technology and engineering company that provides various solutions for customers in industrial, commercial, and consumer markets globally. Business segments include automation solutions, AspenTech, and commercial & residential solutions segments. The Automation Solutions segment offers measurement and analytical instrumentation, industrial valves and equipment, and process control software and systems. The AspenTech segment provides asset optimization software for enhancing performance through a combination of modeling, simulation, and optimization capabilities. The Commercial & Residential Solutions segment offers residential and commercial HVAC products, system protector and flow control devices, and IoT thermostats.

Honeywell, founded in 1906, in Wabash, Indiana is manufacturer of automotive parts, building technologies, and performance and safety materials for aerospace, The company's product portfolio includes electronic guidance systems, cockpit instrumentation, lighting, automotive parts, and primary propulsion and secondary power turbine engines. The company serves industries such as Oil and Gas, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Construction, and Power Generation. Their headquartere is located in Carolina and they have global sales offices and distributions channels.

Astim, established in 1980 and headquartered in Kocaeli, Turkey, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial liquid and gas mechanical equipment and machinery. The company's products include containerized treatment plants, pressurized tanks, and water flow control equipment. These products are used for wastewater treatment systems, water intake structures, and sludge treatment. It welcomes inquiries for custom turnkey systems, and its services include installation and maintenance. It has completed large-scale projects for WTE Germany, Strabag Austria, and Waterleau Belgium.

Onda S.p.A., established in 1989 and headquartered in Mussolente, VI, Italy, is a designer, manufacturer, and supplier of heat exchangers. The company's products include air heat exchangers, brazed plate heat exchangers, and marine bronze condensers. It also produces custom heat exchangers for industrial clients and supplies its own software to manage and control its products. Its products are used in industrial HVAC systems, food processing systems, and chemical processing systems. It serves industries that include marine, consumer product manufacturing, and automotive.

TIRA GmbH, founded in 1947 and headquartered in Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany, is a manufacturer of testing and measuring technology. The company's products include vibration testing systems, head expanders (load bearing platforms), and material testing machines with various testing functions such as tensile strength, tear resistance, and shear strength. It also offers individual customized solutions according to client requests and can modify existing machinery; for example, it can create derivations that include longer, wider, and shorter material testing machines. It serves industries that include consumer product manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive.

VULCANIC, founded in 1973 and based in France, is a manufacturer of electrical heating and cooling systems for various industrial and commercial applications. The company's product line encompasses heating elements, screw immersion heaters, flow heaters, heating panels, and electrical industrial radiators, all of which play a critical role in industries such as aeronautics, oil & gas, marine, food & beverages, and petrochemical sectors. The company holds ISO9001:2015 quality management system certification and provides a range of services, including hardware and software implementation, temperature measurement, hydraulic design, automation, and communication protocols.

MBK Tape Solutions was founded in 1971 and currently operates out of Chatsworth, California under the Boyd Corporation umbrella. MBK is an ISO 9001-2015 certified manufacturer and fabricator of adhesive tape and flexible material that offers bonding, surface protection, sealing, and thermal management solutions. The company specializes in the healthcare, electronics, and industrial industries. The company offers several customer services including die cutting, printing, sheeting, and packaging. In addition, the company offers product development, cleanroom manufacturing, and contract manufacturing to customers.

Conair, founded in Cranberry Township, PA, in 1959 is a manufacturer of resin drying, blending, feeding, and conveying/material handling equipment. The company's product portfolio includes Gravimetric Batch Blenders, Blending Accessories, Self-Contained Vacuum Loaders, Compressed Air Material Loaders and Vacuum Pumps/Dust Collectors. The company serves industries such as Oil and Gas, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Construction, and Power Generation. The company also provides services including national distribution, product selection, customized services, technical support and 7/24 customer service.

BV Thermal Systems, Division of Budzar Industries, Inc. founded in the United States in 1980, is a manufacturer of recirculating chillers and fluid to fluid heat exchangers. The company offers a line of recirculating chillers that provide precise temperature control for various applications that are used in laboratories, industrial processes, and medical equipment cooling, ensuring consistent and reliable cooling performance and fluid-to-fluid heat exchangers that find applications in HVAC systems, industrial machinery, and renewable energy systems, helping clients maintain optimal operating temperatures.

Trox GmbH, established in 1951 and headquartered in Neukirchen-Vluyn, Germany, is a manufacturer of air handling and climate control systems. The company offers air diffusers, shut-off devices, and filtration units. Its industry solutions cater to diverse sectors such as education, healthcare, and hospitality, providing ventilation and air conditioning solutions. Its x-cube compact unit integrates adjustable jet angles and noise-reduction technology features. The company offers concept development, architectural design, and performance testing services, complemented by digital services for remote operation and energy monitoring.

CRC Progetti S.r.l., founded in 1978, is an Italian manufacturer based in Flero, Lombardy, specializing in electrical heating elements and thermal treatment equipment. The company's resistance heaters include armored heating elements, cartridge heaters, wire mesh heaters, and heating elements for specific applications. Its thermal treatment equipment includes distension heaters, fluid heaters, and industrial ovens. It further provides metal fusion equipment and specialized thermal treatment equipment. The company serves various sectors, including woodworking and furniture manufacturing, recycling, and plastic processing.

Baker Hughes Co. (BHC) is an American service provider and manufacturer of industrial oilfield equipment that was established in 1987 following the merger of Baker International and Hughes Tool Company. Based in Houston, Texas, the company produces several categories of oilfield products including drilling equipment, pipe and subsea production systems, generators, and storage systems. It also offers process control components and actuators such as pumps, valves and regulators. BHC provides various services for oilfield and liquefied natural gas (LNG) operations, including regasification, well construction, transportation, and storage.

Heatsystems GmbH & Co. KG, established in 2000 and headquartered in Germany, is a manufacturer of electrical heat components. The company’s products include insulation, heat exchangers, and heating element storage systems. Its electrical flange heaters are ideal for liquids and gases, while tank heaters maintain proper temperatures. It also offers electrical process heaters for flowing fluids, heavy-oil preheaters to manage viscosity, and ceramic heating elements for heat exchange. The company customizes heat exchangers such as tubular, spiral tube, or plate types according to specific technical requirements. Its products are used in industrial, life science, and plant engineering.

Rono Maschinenbau GmbH (RONO), founded in 2005, is a manufacturer based in Lübeck, Germany, designing and producing equipment for the food industry. The company's food technology solutions include safety, security, health, and environment (SSHE) products, crystallizers, and emulsifying systems. Its machines include surface heat exchangers, pin worker units, and high-pressure plunger pumps catering to various food processing needs. It also manufactures vacuum process systems, emulsifying systems, and universal cookers or mixers. The company offers after-sales services like spare parts, maintenance, and refurbishment.

SPX Flow, established in 1912, is a manufacturer of industrial machinery to solve processing challenges based in Charlotte, North Carolina. The company manufactures various machinery such as mixers, pumps, valves, homogenizers, and heat exchangers. The machinery is used in nutrition, health, mining, construction, and chemical industries. The company provides services such as designing, engineering, and installing turnkey process units or full-scale plants. The SPX Flow brands include Anhydro, Bran+Luebbe, Gerstenberg Schrӧder, Pneumatic Products and Seital Separation.

ProXES GmbH, based in Hameln, Germany, is a manufacturer of process technology solutions and is a combination of three brands, namely FrymaKoruma, Stephan, and Terlet. FrymaKoruma produces vacuum processing equipment, mills, and inline machines used in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries to make products such as ketchup, lipstick masses, and active pharmaceutical ingredients. Stephan produces machines and plants for dairy products, meat, and confectionery. Terlet specializes in developing and producing components and turnkey plants for treating and processing liquid products. Some of its products include scraped surface heat exchangers, process vessels, and moving coil tanks.

Tetra Pak is based in Switzerland since 1952 as a manufacturer and supplier of food processing and packaging solutions. The company collaborates with food and beverage industries to provide suitable food processing solutions based on the type of food. Food processing includes ensuring the wellness of the food and getting it ready for packaging. The type of packaging is also decided such as aseptic packages, chilled packages, and standard food packages that preserve the quality of the food and the beverage as well as make it easier for distribution.

Ciat S.A. (a part of Carrier Global Corporation), founded in 1934 and headquartered in Culoz, Rhone-Alpes, France, is an HVAC equipment developer and manufacturer. The company's products are water-cooled units, air-cooled units, and chillers. It also produces all of the components for commercial-use HVAC systems, including controls for comfort units and heat pumps, air heaters, and air handling units. The company specializes in providing custom HVAC and air treatment solutions for the healthcare, hospitality, and commercial building sectors.

Scheuch GmbH is a manufacturer of air and environmental control products founded in 1963 and based in Aurolzmünster, Austria. The company's product list includes soundproofing and insulation solutions, evaporative cooler systems, heat exchangers, filter control devices, and thermal sensors for fire or explosion prevention. These are used for dust extraction, air purification, noise protection, and industrial ventilation purposes. The company's products have various applications in cement and lime processing, glass or metal foundries, energy generation, and the petrochemical industry.

Cryostar Industrial Cryogenics is based in Hésingue, France, and is a manufacturer of cryogenic systems and equipment established in 1967 as a part of the Equans Group. The company offers reciprocating pumps for high pressure applications, centrifugal pumps for unloading or loading of liquid gasses, and expanders for air separation or gas liquefaction processes. It also offers small-scale companders and heat exchangers for LNG distribution or storage. The company is ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 45001-certified, and chiefly serves clients in the industrial processing sector.

NOV Inc. is an ISO 9001-certified manufacturer specializing in equipment used in the oil and gas industry. It was founded as Oilwell Supply in 1862 before merging with National Supply in 1987. The company produces equipment, consumables, and digital products used in oil drilling operations. These include drilling rigs, coiled tubing units for well intervention, and data analysis software or hardware. The company also provides customers with oilfield services such as equipment inspection, maintenance, and repair. Some of its notable clients include Halliburton, ExxonMobil, and Transocean.

Tranter, founded in 1932 and headquartered in Wichita Falls, Texas, United States, is an American-based global manufacturer of heat exchangers. The company's products include shell and plate heat exchangers, gasketed and welded plate heat exchangers, and heat exchanger accessories, including instruments, gauges, and clean-in-place (CIP) systems. It also specializes in OEM replacement components and custom turnkey heat exchange systems. It serves sectors that include hydrocarbon processing, chemical processing, and engineering procurement.

Thermal Solutions LLC is headquartered in Lancaster, Pennsylvania. The company is a manufacturer of water heating equipment and boiler control systems used across commercial and industrial applications for customers across the United States through an independent sales network. The company’s 3 product lines include both condensing and non-condensing ultra high-efficiency hot water boilers & heaters and packaged systems & accessories. Condensing heaters range in capacity from 400,000 BTU/hour to 1 million BTU/H inputs at 97% efficiency. Non-condensing heaters maintain 87% efficiency at noise levels below 50 decibels.

Alfa Laval Corporate AB was founded in 1883 and headquartered in Lund, Sweden. Alfa Laval serves energy, utilities, home, personal care, food, dairy, beverage, marine, transportation, pharmaceutical, biotech, water, and wastewater industries. Alfa Laval provides heat transfer, separation, and fluid handling products and solutions worldwide. Alfa Laval operates in three divisions: Energy, Food & Water, and Marine. Alfa Laval offers oil & gas-fired steam and composite steam boilers, exhaust gas economizer, and ballast water treatment systems, and exhaust gas cleaning products. Alfa Laval also provides sensing and control, cleaning validation, condition monitoring, agitators, tank, powder mixers, fittings, and tubes, as well as wall mounted cleaning nozzles, rotary jet and heads; and tank accessories and covers.

PONAR Wadowice S.A., established in 1965 and based in Wadowice, Poland, is a manufacturer and supplier of oil hydraulic elements and systems. The company offers a diverse product catalog, including control cards electronics, directional control valves, hydraulic cylinders, heat exchangers, and accumulators and blocks. It also provides systems such as high-pressure water systems, prediction and monitoring systems, hydraulic systems, and industrial application systems. These products find applications in mining, aerospace, automotive, hydro-engineering, and scientific research.

VELO ACCIAI S.R.L. is based in Ezzelini, Treviso, Italy, and is an OHSAS 18001-certified manufacturer of industrial fittings that was established in 1980 as a sister company to VLS Technologies. The company offers stainless steel fittings for regulating or connecting fluid movement networks, as well as catwalks and stairs for height access or positioning. It also offers related stainless steel components for customizing or optimizing fluid network installations. The company’s products are used mainly by clients in the chemical processing, recreational beverages, and petrol industries.

Keller Lufttechnik GmbH + Co. KG, established in 1903 and based in Kirchheim unter Teck, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of filtration and extraction systems. The company's product portfolio includes room air purifiers, compact wet separators, and oil mist collectors. These products find applications in various industries, including healthcare, metalworking, and the welding and fabrication industry. The company has three subsidiaries in Switzerland, the United States, and China, each holding ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, and ISO 50001:2018 certificates.

Beijing Holtop Air Conditioning Co. Ltd., established in 2002, is a manufacturer headquartered in Beijing, China, producing heat and energy recovery technology. The company, certified with ISO 9001:2015, offers a range of air handling units, energy recovery ventilators, and heat exchangers. With the capacity to produce up to 20 series and 200 specifications, Holtop was a supplier for the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing and the Expo 2010 in Shanghai, China. The company also offers services covering heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) and cleanroom design, construction, and installation.

Cimbria A/S, established in 1947 and based in Thisted, Denmark, is a manufacturer, exporter, and supplier of seed processing machinery. The company produces other products for conveying, drying, storage, and seed processing and supplies to customers worldwide. Apart from this, the company designs agricultural machinery and abides by various quality and environmental standards such as ISO-45001, ISO-9001, ISPM 15, and EN 1090 while manufacturing the products. The company has production facilities in Denmark, Austria, Czech Republic and Italy.

FläktGroup, formed through the merger of FläktWoods and DencoHappel in 2016 and headquartered in Herne, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of indoor air technology solutions. The company's products include heat pumps, precision air conditioners as well as fan coils, and offers services such as air treatment, conditioning, and diffusion. It serves consultants and architects, installers and contractors, and property owners. The company's products find applications in the oil and gas, data center, and pharmaceutical industries.

UNIVERSAL HYDRAULIK GMBH, established in 1983 and headquartered in Neu-Anspach, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of hydraulic systems, cooling systems, and heat exchangers. The company's product portfolio includes tube bundle heat exchangers, air heat exchangers, electrical oil pre-heaters, hydraulic solutions, and hydraulic components. These products find applications in various industries, including textile, gear manufacturing, mining, chemical, and the rubber and tire industry. The company provides services including installation, repair, and testing and inspection. The company is ISO 9001:2015 certified with overseas manufacturing facilities in the Czech Republic and the United States.

Ekin Industrial, also known as MIT Industrial Products, established in 2005 and based in Turkey, is a manufacturer and supplier of thermal energy equipment Its product line includes water heater tanks, plate heat exchangers, and accumulation tanks used with plate heat exchangers to supply utility water in various community settings like hotels, dormitories, and public administration facilities. The company has adapted to ISO quality management system procedures, completed the CE security and quality certification period, and have matched foreign standards like GOST.

FUNKE WÄRMEAUSTAUSCHER APPARATEBAU GMBH, established in 1974 and based in Gronau, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial heat exchangers. The company’s product portfolio includes gasketed plate heat exchangers, air-cooled heat exchangers, and shell-and-tube heat exchangers. These products are used in various industries, including the renewable energy industry, food and beverage sector, and the pulp and paper sector. The company is ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certified and sells its products globally to various countries, including the United States, Brazil, and China.

SGL Carbon is located in Wiesbaden, Germany, and is a manufacturer and supplier of graphite as well as composite materials and products founded in 1992 following the merger between SIGRI GmbH and Great Lakes Carbon. The company primarily produces carbon fibers and composites for the aerospace, energy, and automotive sectors. It also offers specialty graphite products for industrial applications such as for battery production, and application-specific process technology plants, such as for industrial pumping or turbine operations. The company is ISO 13485:2016, UL, and CSA-certified, and serves clients in the industrial processing and energy sectors.

Zhejiang Bofine Power Equipment Co., Ltd, established in 2003 and based in Jiaxing City, China, is a manufacturer and supplier of special equipment serving the power industry. The company's product portfolio includes heat exchangers, hydraulic oil stations, and ultrasonic decontamination equipment. These products find applications in various industries, including power generation, automobile manufacturing, and the clock and watch industry. The company possesses ISO 14001:2015, ISO 45001:2018, and ISO 9001:2015 certifications. It has partnered with various companies, including Hitachi, Siemens, and General Electric.

stk makina, established in 1981 and based in Sakarya, turkey, is a manufacturer and supplier of turnkey facilities for milk and dairy processing plants. The company's product portfolio includes milk cooling tanks, pasteurization units, and drying cooking machines. These products are used by various sectors, including the dairy, general food processing, and pharmaceutical industries. The company is ISO 9001:2008 certified and offers services including technical support, product installation, and the design of products to meet the specific needs of customers.

OHM ELECTRIC CO., LTD, founded in 1961 and headquartered in Hamamatsu, Japan, is a manufacturer specializing in wiring accessories, as well as temperature and environmental control devices. OHM offers various wiring accessories including cable glands, insulation caps, and junction boxes. To meet the requirements for maintaining a clean work environment, especially in manufacturing sites, the company provides a range of coolers, dehumidifiers, and condensate evaporators for indoor temperature and humidity control, as well as oil mist and dust collectors. Moreover, OHM offers system integrations with regard to electrical engineering solutions and automated machinery for various industries, including medical, food, and robotics.

Shineheat Corp, established in 2008 and based in China, is a manufacturer and distributor of heat exchangers. The firm sells around 23 countries in Asia, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe. The company is a member of HESSA (Heat Exchanger Supply and Service Alliance) in China. It creates a comprehensive portfolio that includes heat exchangers with a plate and gasket, a welded frame, a welded bloc, etc. The company is a one-stop shop for the power plant, metallurgy, chemical, food, and environmental industries. The business produces equipment under international codes and standards such as ASME, PED, API, JIs, and DNV.

Munters, established in 1955 and headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, is a manufacturer and supplier of climate solutions. Munters operates across three core business areas: AirTech, specializing in energy-efficient air treatment; Data Center Technologies, providing climate cooling solutions for data centers; and FoodTech, offering climate systems for livestock farming and greenhouses. Its climate control technologies include HVAC, humidification, dehumidification, and pollution control, serving many industries and emphasizing quality, sustainability, and environmental responsibility. Munters delivers efficient, eco-friendly solutions to industries where precise indoor humidity, temperature, and energy efficiency control is paramount.

AEROFIN, established in 1923 and headquartered in Lynchburg, Virginia, is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer and supplier of spiral fin and plate fin heat exchanger coils. The company’s product portfolio includes bare tube coils, combustion preheating steam coils, and nuclear cooling coils. These products find application in various industries, including the HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), fossil fuel power generation, and nuclear power generation. The company also provides services such as technical support, warranty coverage, and custom fabrications.

Ningbo Gongtie Smart Technology Co., Ltd., established in 2008 and based in Ningbo, China, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision CNC lathes and whole machine automation. The company's product portfolio includes the M Series precise CNC centers, back feeding for shaft parts, and big gantry-type structure industrial robots. These products find applications in various sectors, including the automotive industry, valve manufacturing, and bearing production. The company provides services, including technical support and customized solutions tailored to the specific needs of customers. The company is ISO 9001:2015 certified, with its research and development center located in Reggio Emilia, Italy.

Pegasus Glass established in Cambridge, Ontario in 1968 is a distributor and manufacturer of borosilicate glass products that are used in chemical, industrial, lighting, and optics. Their product range includes glass rods, glass tubing, sight glass, lampworking supplies, and processed glass. Their products are also used in industries such as Medical Devices Artistic Glass Chemical Pharmaceutical Biotech. The company has a warehouse with 375 standard sizes of glasses and also produces recycled or re-used galasses to have zero waste.

O.M.F.B. S.p.A. Hydraulic Components is a manufacturer and supplier of hydraulic components established in 1979 and based in Provaglio d'Iseo, Italy. The company offers piston pumps for impelling liquids and compressed gasses, and power take-off (PTO) units for transferring mechanical power from an engine to other equipment. It also offers mini power packs, hand pumps, and accessories for truck installation of its portfolio products. The company’s products are used by clients in the agricultural, transportation, and construction industries.


Buchiglas (Büchi AG), founded in 1946, is a manufacturer headquartered in Uster, Switzerland, specializing in reactor systems. The company provides both standard and custom solutions tailored for the chemical and pharmaceutical industries as well as research institutions. Its product lineup includes glass reactors and process equipment constructed from borosilicate glass, glass-lined steel, and other corrosion-resistant materials. Additionally, Buchiglas offers pressure reactors and stirred autoclaves made from various metals and glass, which are specifically designed for applications such as catalyst screening, corrosion testing, and hydrogenation. The company also provides comprehensive engineering, manufacturing, and installation services that meet regulatory and operational requirements.

MFP Automation Engineering, founded in 1991 and based in Hudsonville, Michigan, is a manufacturer and distributor of fluid power, motion control, and automation products. It stocks products such as fire suppression systems, hydraulics, and connectors and has over 80,000 SKUs in inventory from brands like ACE, SKF, and Parker. It even has an on-site Parker store that stocks thousands of ready-to-go parts like servo motors and hose assemblies. The company is ISO 9001 certified and provides on-site installations, filtration analysis, and systems engineering services. Its CNC vertical machining centers range from five to twenty-five spindle horsepower.

Leonardo DRS, Inc., established in 1925 and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, is a manufacturer and supplier of heating and cooling coils, as well as air handling units (AHUs). The company's range of products includes industrial process coils, Marloair air handling units, and turbine inlet cooling and heating coils. These products are used in various industries, including industrial manufacturing, power and energy generation, and semiconductor manufacturing. The company provides technical support, warranty support, and customized solutions, and it is ISO 9001 certified for its quality management system.


Armstrong International Inc., founded in 1900 and based in Three Rivers, Michigan, is a multi-national manufacturer of thermal utility solutions such as heat transfer coils, heat pumps, and steam products. It provides custom services to companies in various industries, including hospitality, healthcare, and higher education, and a majority of its international facilities have ISO 9001 certification. The products also conform to the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) requirements of 2014. In 1996, it pivoted from manufacturing and added thermal energy engineering services, and in 2005, it received trading approval from the United Nations’ UNFCCC for its steam system methodology.



Alfa Laval, founded in 1883 and headquartered in Toronto, Canada, is a supplier of heat transfer, separation, and fluid handling products like boilers, separators, and heat exchangers. The company’s operations are based on three key technologies, which are heat transfer, separation, and fluid handling, and it helps farmers separate, process, and store milk products. The company has 42 production units, out of which 22 are based in Europe, and it sells its products in over 100 countries. It invests about 2.5% of its total yearly sales in research and development, resulting in around 25-30 new product launches per year.








Tonelli Group Ltd., founded in 1948, is an Italian manufacturer based in Collecchio, Parma, producing bakeries and food manufacturing equipment. The company offers a range of food mixing technologies, including vertical and horizontal mixers, centrifugal mixers, and continuous aerating mixers (CAMs). It also develops heat treatment equipment like thermal exchangers and multifunctional mixers for cooking and cooling processes. Its products extend to food processing machinery, including fat plasticization machines and pasteurization systems. With patents for batch and continuous cooling as well as cream cooking and filling equipment, the company also provides customers with laboratory facilities for recipe testing using its machinery.






Thermohran Engineering is a manufacturer of vegetable and fruit processing machinery and equipment established in 1991 and based in Stara Zagora, Bulgaria. The company primarily produces programmable slicing machines with multiple preset operations. These include dividing cabbage into four parts after removing its stump, or coring and slicing apples into five slices. It also offers custom design and engineering services for unique projects. The company’s products are mainly used in the food and beverage, snack foods, and bakery industries.



Pentair is a supplier of sustainable water solutions since 1966 and is based in St. Paul, Minnesota. The company serves the residential community by providing equipment for pools and spas and products for water softening and filtration to run through houses. The business industry benefits from the products that include commercial pool and spa equipment such as chemical controllers, heaters, lightings, and also valves and pumps for water supply as well as for water disposal. The Agricultural products include irrigation equipment and as for the Oil & Gas industry, there is the Biogas upgrading, CO2 Technologies, and much more.

Saint Clair Systems, established in 1990 and based in Washington, Michigan, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in industrial temperature and viscosity control solutions. The company's product portfolio includes water-based temperature control systems, falling-piston viscosity sensors, and heat exchangers. These products are used in various industries, including the automotive industry, aerospace, and robotics and automation. The company also provides services including technical support, training programs to ensure that customers understand how to use its products, and custom solutions tailored to specific industries and applications.
Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | THERMAL FLUID SYSTEMS, INC. |
3.5%
|
| 2 | Barksdale |
2.8%
|
| 3 | Gaumer Process INC. |
2.7%
|
| 4 | Caterpillar Inc. |
2.6%
|
| 5 | ProSonix, LLC |
2.1%
|
| 6 | Pick Heaters, Inc. |
2.1%
|
| 7 | Inproheat Industries Ltd. |
2.0%
|
| 8 | Dry Coolers, Inc. |
2.0%
|
| 9 | Taco Comfort Solutions |
1.9%
|
| 10 | CoorsTek, Inc. |
1.7%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the heat exchanger page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
52 | 49.5% |
 Germany
Germany
|
15 | 14.3% |
 China
China
|
7 | 6.7% |
 Italy
Italy
|
6 | 5.7% |
 Japan
Japan
|
5 | 4.8% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
5 | 4.8% |
 Canada
Canada
|
2 | 1.9% |
 Switzerland
Switzerland
|
2 | 1.9% |
 Denmark
Denmark
|
2 | 1.9% |
 Portugal
Portugal
|
2 | 1.9% |
 Turkey
Turkey
|
2 | 1.9% |
 Australia
Australia
|
1 | 1.0% |
 France
France
|
1 | 1.0% |
 Netherlands
Netherlands
|
1 | 1.0% |
 Spain
Spain
|
1 | 1.0% |
 Poland
Poland
|
1 | 1.0% |
546 products found
546 products
Matsuzawa Works Co., Ltd.
1100+ people viewing
Last viewed: 21 hours ago
You can design the optimal cooling equipment according to your purpose and use.
4 models listed
Matsuzawa Works Co., Ltd.
780+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
You can design the optimal cooling equipment according to your purpose and use.
4 models listed
Masaie Co., Ltd.
1470+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
■ Features The K series is a standard product and is the most model of Kaori's products. It can be used for various systems. ■ Main use Freezing a...
10 models listed
Poec Co., Ltd.
1060+ people viewing
Last viewed: 42 minutes ago
■ Plate & shell heat exchangers that achieve high efficiency and compact performance with a unique structure As a high -performance and compact nex...
7 models listed
HISAKA WORKS, LTD.
510+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
Structure of plate heat exchanger ■Basic structure Heat transfer plates are made by press-forming thin plates of corrosion-resistant metals such as...
ES Japan Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
About total heat exchanger ■Features and good points - Approximately 70% of indoor exhaust heat is recovered, resulting in significant savings in e...
Edifice Energy Saving Tech Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 18 hours ago
■Mechanism of heat exchange Switches between air supply and exhaust in a 70 second cycle. One set consists of two ventilation units, and the air su...
Yoshiro Kiko Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 42 minutes ago
Due to the high-precision helical structure heat exchange tube position accuracy, baffle, the fluid flow through the heat exchanger can create a tu...
SGL Carbon Technique Japan Co., Ltd.
1090+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
■Summary We use Tokabait, a structural material for chemical equipment that is made by impregnating graphite material with excellent corrosion resi...
10 models listed
Ikeda Shokai Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Just as high-efficiency water heaters are called Eco-Jozu, ultra-high-efficiency GHPs are called Exare in the industry. The new Exare II was launch...
Inoue Heater Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Summary Both have a large heat transfer area and are economical. For this reason, it is used for a wide range of purposes. The P-5 type uses boile...
TIG Co., Ltd.
310+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
For the first time in the world, we successfully developed a titanium flexible tube in cooperation with Nippon Steel Corporation and used it in an ...
MDI Co., Ltd.
300+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
This is a "plate type" developed for the purpose of heat exchange between fluids containing fibers and coarse particles, and fluids with high visco...
Edifice Energy Saving Tech Co., Ltd.
290+ people viewing
■Mechanism of heat exchange Switches between air supply and exhaust in a 70 second cycle. One set consists of two ventilation units, and the air su...
Yoshiro Kiko Co., Ltd.
210+ people viewing
■Silicon carbide tube Silicon carbide (SIC) Silicon carbide tubes, which are the core components of heat exchangers, are manufactured from high-pur...
Tokyo Forming Co., Ltd.
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
■Using in-house developed equipment, we can also handle special processing We manufacture thin-walled stainless steel pipes from coiled materials f...
Ikeda Shokai Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
Excel Plus not only generates its own power and operates in the event of a power outage, but also outputs 3.5kW of external power per unit, making ...
Inoue Heater Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
■Summary Both have a large heat transfer area and are economical. For this reason, it is used for a wide range of purposes. The P-5 type uses boile...
TIG Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
Compact with free bending process. Make the most of your flexible tubes. Applying the characteristics of flexible tubes to titanium tubes, the ther...
MDI Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
It is used in processes where dangerous reactions are expected when two fluids that exchange heat are mixed, and in applications where a mixing acc...
Degree Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Dedicated plating plate heat exchanger manufacturer Finally, we are the first in the world to create a special structure for gas/liquid design usi...
Edifice Energy Saving Tech Co., Ltd.
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
■Mechanism of heat exchange Switches between air supply and exhaust in a 70 second cycle. One set consists of two ventilation units, and the air su...
Tokyo Forming Co., Ltd.
180+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Used in a wide variety of industries This is a heat exchanger made by assembling pipes and sheet metal parts using TIG, seam welding, caulking, et...
Inoue Heater Co., Ltd.
170+ people viewing
■Summary It has the largest heat transfer area and can withstand harsh use. Especially suitable for large heaters. We also manufacture products mad...
TIG Co., Ltd.
310+ people viewing
The turbulent flow effect of corrugated pipes increases the heat exchange rate, making it suitable for a wide range of uses, even in large-scale fa...
MDI Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 minutes ago
This is a "plate type" developed to handle fluids that soak rubber gaskets and highly permeable fluids. The seals of the two plates are laser welde...
TIG Co., Ltd.
250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
Precision-machined titanium coils exhibit excellent properties even under harsh conditions. We have a rich lineup to suit the purpose of use and se...
Edifice Energy Saving Tech Co., Ltd.
250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Mechanism of heat exchange Switches between air supply and exhaust in a 70 second cycle. One set consists of two ventilation units, and the air su...
Inoue Heater Co., Ltd.
170+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Summary Both have a large heat transfer area and are economical. For this reason, it is used for a wide range of purposes. The P-5 type uses boile...
Frontier technology Co., Ltd.
560+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■ Characteristics ・ Lightweight and compact. Installation costs and installation spaces are more advantageous than shell & tube heat exchangers. ...