











18 Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for printed circuit boards (pcb) as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 18 printed circuit board (pcb) manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked printed circuit board (pcb) companies as of April, 2024: 1.Liberty Intercept, 2.MOOG, 3.Meiko Electronics Co., Ltd..
Table of Contents
What Is a Build-Up Board?
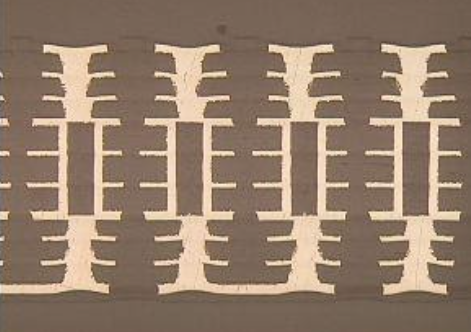
A build-up board is a printed circuit board consisting of multiple layers.
The use of build-up substrates allows the use of high-density substrates in a small area, making it possible to create multifunctional products, even for small devices. Build-up substrates consist of layers of conductors and layers of insulators stacked on top of each other, with laser drilling and wire processing to penetrate the layers, making it possible to obtain complex substrates in a small area.
Emergence of Build-up Substrates
With the increasing density of substrates, it has become increasingly difficult to deal with the current via-hole structure alone. The development of cell phones has led to the demand for lighter, smaller, and more compact substrates, and substrates that can handle these demands have become necessary. Build-up boards began to appear around 2000 and have continued to the present day.
As the name "build-up" implies, it refers to a printed circuit board with many layers stacked on top of each other. Normally, a multilayer board can be built up into a single layer, but since it is built up many times, the number of processes increases, which means that it costs more. However, the use of this method is gaining momentum due to its ability to reduce wasted space and make small holes with a laser.
Reason 1: to reduce wasted space
When using via holes (holes to connect other layers) on a multilayer board, wiring cannot be done outside of the connecting layer because of the vias. Therefore, wiring efficiency will not be improved even if a multilayer board is used.
Reason 2: small holes can be drilled with a laser
Advances in equipment have made it possible to drill smaller holes at higher speeds with lasers than with drills. When drilling with a drill, the hole will penetrate the underlying layer. On the other hand, with lasers, it is possible to drill holes in the resin and stop the process on the copper, depending on the combination of conditions. Therefore, by repeating the process of drilling holes with a laser, plating, and then building up the next layer and processing it with a laser (build-up), the area of the via holes can be effectively used and high-density is possible.
By using build-up substrates, high-density substrates can be used in a small area, making it possible to create multifunctional products, even for small devices. Complex substrates in small areas can be obtained.
Uses of Build-up Substrates
Build-up substrates are widely used in small, lightweight electronic devices. When build-up substrates were first commercialized, they were used in PCs and cell phones. Today, they are used in small measurement devices, and IoT devices such as smart meters, digital camera modules, and PC peripherals.
The accuracy of drilling and other operations in the build-up board manufacturing process has a set standard, and it is necessary to choose exactly what level of accuracy to request when requesting the creation of a build-up board.
Build-up Substrate's Process
This section describes the manufacturing process of build-up boards. The manufacturing process for build-up substrates includes insulator layer formation, via processing, smear removal, and plating on vias. Each of these processes is described below.
Formation of the Build-Up Layer
An insulator layer is built up on top of the printed circuit board. Prepreg, a rigid material, is used in some cases, while film is used in others. Prepreg is often used for digital cameras, smartphones, and semiconductor packages.
Via Processing
This is the process of drilling holes called vias in the insulator layer between substrates. Currently, holes are generally drilled using lasers.
Various types and wavelengths of lasers are used, including carbon dioxide gas and UV-YAG. Carbon dioxide lasers have a long wavelength (infrared) and are commonly used in digital cameras and smartphones, while UV-YAG lasers have a short wavelength (ultraviolet) and are used in high-density areas such as semiconductor package substrates.
Resin Residue Removal (Desmear)
The residue generated by laser processing is called smear. Resin residue cannot be connected, so it must be removed.
This process is called desmear. If the smear remains on the build-up substrate, it will lead to poor connections, etc., so it must be removed without fail. A strong chemical (potassium permanganate) must be used to remove the smear. However, recent high-speed resins may not be able to remove the smear by themselves, so plasma or other methods may be used in combination with the removal process.
Plating On Vias
Via plating is used to connect circuits between substrates with insulators in between. Since plating is done on small holes, it is necessary to prevent air bubbles from entering.
Names of Vias On Build-Up Boards
The names vary depending on the placement and structure of the holes, so a brief explanation is given below.
Staggered Vias
This is a method of shifting the position of vias like a staircase.
Stacked Vias
A via is stacked on top of another via. A via that overlaps on all layers is called a full-stack via.
Build-up Substrate Materials
Currently, two types of materials are mainstream: glass cloth, which is the same material used for ordinary substrates, and film, which is mainly used for packages. Looking at the past, various materials have been used, which are briefly explained below.
Originally, build-up substrates started when IBM developed a technology to support large computer flip-chip mounting for its product line. Various studies were conducted in the process.
As a result, we adopted a method of exposure and development using a UV-curing resin known as photovia. This had the advantage that vias could be formed in a batch. Since interlayer thickness was required, we developed and mass-produced the product based on solder materials resist for curtain coaters, which can earn film thickness. As with solder resist, an insulating layer was formed by applying, exposing, and developing, followed by final curing with heat.
After that, chemical copper is deposited and electrolytic copper plating is performed to form layer after layer. In addition, chemical copper formation is difficult to achieve peel strength because of the resin that causes photo-polymerization, and it is very difficult to control the conditions. In addition, the development process required a solvent and was subject to various regulations, so it could not be said to be a technology that would be widely used.
Subsequently, the micro via formation method was changed from optical formation to laser processing, as the processing speed of vias increased dozens of times due to the significant evolution of laser processing equipment. At that time, RCC (Resin Coated Copper Foil: copper foil with resin) was adopted. This is a thermosetting resin that is coated on top of the copper foil and is in the same semi-cured state as prepreg.
Therefore, it has the advantage that the lamination process, which is the same process used for conventional substrates, can be used. In addition, since peel strength is easy to achieve, via formation by light has been replaced by laser formation of RCC.
As electronic devices have become smaller and more handy, the use of build-up substrates has expanded. In this context, further cost reduction and reliability that can handle high density are required.
In addition, significant improvements in laser processing technology have made it possible to process commonly used materials with glass cloth, which has led to a significant shift to materials with glass cloth. Cell phones, digital cameras, and various types of mobiles are of this type.
On the other hand, in LSI packaging, high-density, multi-stage build-up has been demanded in response to higher-density LSI flip chips. To meet the demand for multiple layers and low thickness, thinner interlayer thickness, smaller vias, and flat surfaces are required. Film-type materials were developed to meet these requirements.
To fill the circuit with resin, a vacuum laminator is required, and a line dedicated to the unique process is needed to deposit chemical copper on the resin surface. This requires a large capital investment. In packaging applications, it is used for MPU large-scale LSI in PC smartphones.
List of 18 Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- China
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- Sweden
- United Kingdom
-
-

Manufacturer Overview
Moog Inc. was incorporated in 1951 and is headquartered in East Aurora, New York. The company designs manufactures and integrates precision motion and fluid controls and control systems for customers including OEMS in industries such as aerospace, defense, industrial machinery, motorsports, and construction. The company’s product offerings include both systems and components. Examples of systems include actuation systems, naval systems, turreted weapon systems, and space vehicles. Examples of components include manifolds, slip rings, actuators, and servo actuators.
-
-
-
-

-
FlexLink Systems, Inc.
GENIUS - PCB HANDLING SYSTEM
Manufacturer Overview
FlexLink Systems, Inc., founded in 1980 in 6580 Snowdrif RDs, Ste 200 Allentown, Pennsylvania, PA, is a manufacturer of automated production and material flow solutions. The company produces handling and track pallet conveyor systems, production lines, palletizers, handling systems, and solutions for tracing, routing, positioning, balancing, and planning in the automotive, transportation, industrial, and power distribution industries. It provides services such as maintenance, line inspection, incident management, troubleshooting, and equipment relocations.
-
-
-
-

-
Midcom
Printed Circuit Boards
Manufacturer Overview
Würth Elektronik Group, established in 1969 in Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of quality electronic and electromechanical components. Their extensive product catalog includes passive components, connectors, inductors, sensors, and more, catering to various industries like automotive, telecommunications, and industrial automation. Würth Elektronik's components are integral to building ideal electronic circuits, enabling seamless data transfer and power management. Courtesy of its creativity and sustainability, it aims to provide cutting-edge solutions and good customer service, meeting the diverse needs of its global clientele.
-
-
-
-

-
Shenzhen Kinwong Electronic Co.,Ltd.
Conventional PCBs
Manufacturer Overview
Shenzhen Kinwong Electronic Co., Ltd., established in 1993 and headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is a manufacturer that specializes in the development and production of printed circuit boards. The company offers a range of products, including conventional PCBs, flexible PCBs, RF PCBs, rigid-flex PCBs, and metal-base PCBs. It also offers engineering and design services to support customers in the development of its electronic products. Its products are used in applications where space is limited and high reliability is required. The company has achieved ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016 certifications. It serves industries such as automotive, medical devices, aerospace, IoT, energy, and more.
-
-
-
-

-
Alphasense Ltd
Support Circuits
Manufacturer Overview
Alphasense, established in 1996, is a manufacturer of gas sensors based in Braintree, UK. The company's catalog includes electrochemical, catalytic, infrared, particle counters and photo-ionization detector sensors classified under A, B, C and D series depending on the size. The products are used in industries and residential places to detect gas leaks. Alphasense uses kaban and cellular technologies to manufacture products that meet specific customer requirements. The sensors have barcodes or serial numbers on labels, which customers can use to trace the test results of the sensors in the company's data sheets on the website.
-
-
-
-

-
STM S.p.A.
ESV Slim series
Manufacturer Overview
STM S.p.A., established in 1976 and headquartered in Via del Macci Breccia, Italy, is a manufacturer that specializes in producing gearboxes and geared motors. The company designs and manufactures gear reducers, gear motors, and variators. It also offers high-tech gearboxes, worm gearboxes, and torque limiters. Its product is designed to increase resistance to torsional and structural flexibility. Furthermore, the company has achieved the Directive ATEX 2014/34/UE certifications. It serves various industries, including the chemical, conveyor, and lifting industries.
-
-
-
-

-
OKI Circuit Technology Co.,Ltd.
PRODUCTS
Manufacturer Overview
OKI Circuit Technology Co., Ltd. is a Japanese manufacturer of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electronic components established in 2012 and based in Tsuruoka, Yamagata. The company produces various PCBs that are able to manage high frequencies, radiation levels, currents, and speeds. These are used in automotive components, consumer electronics, medical equipment, and communication devices. Aside from its products, the company also offers custom design and testing services for customers with unique project requirements.
-
-
-
-

-
PCBCart
HDI PCB
Manufacturer Overview
PCBCart, established in 1986 with headquarters in China and numerous facilities across China, is a manufacturer of printed circuit boards and a provider of PCB assembly services. The company's product line includes the custom PCB manufacture of rigid PCBs, flex PCBs, MCPCBs, and Rogers PCBs. PCBCart's products are used across industries for the production of consumer products, home appliances, automotive electronics, and telecommunications infrastructure. The company also offers turnkey PCB assembly services to meet custom THT, SMT, PoP, and other assembly requirements.
-
-
-
-

-
Meiko Electronics Co., Ltd.
High layer count PCB
Manufacturer Overview
Meiko Corporation is a Japanese company headquartered in Ayase, Kanagawa Prefecture. The company designs and manufactures printed circuit boards primarily for the automotive and telecommunications industries, as well as for home appliances, medical equipment, and robotics. Meiko designs advanced PCBs and related parts and offers comprehensive electronic manufacturing services (EMS) for electronics. EMS services cover each step from pattern design (CAD) through tool inspection, assembly, and quality inspection. Meiko is the largest manufacturer of circuit boards specializing in cellular phone and automative markets.
-
-
-
-
-
Hongkong Koon Technology Limited
GSM PCB board KN520
Manufacturer Overview
HongKong Koon Technology Limited, established in 1998 and based in Shenzhen, China, is a manufacturer of emergency communication systems and industrial phones. The company excels in crafting products such as VoIP intercoms, emergency outstation telephones, and extensive network management command systems tailored for various sectors such as metro, airports, and petrochemicals. Its range includes weatherproof outdoor telephones, explosion-proof communication devices, and business phone systems. The company also collaborates with major brands like Huawei and Siemens.
-
-
-
-

-
Dongguan Wahhing Electrical Appliance Co., Ltd
PCBA R&D Design
Manufacturer Overview
Wah Hing, founded in 1980 and headquartered in Dongguan, Guangdong, is a manufacturer of transformers and power switching supplies. The company offers a diverse product range, including a solar photovoltaic power generation system, PV three-phase isolation transformer, three-phase filter reactor, golf cart lead-acid battery charger, and portable EV charger. These products have applications in railway auxiliary power systems, UPS uninterruptible power systems, EPS emergency power systems, power distribution systems, and medical test equipment.
-
-
-
-

-
Liberty Intercept
Printed Circuit Boards (PCB)
Manufacturer Overview
Liberty Intercept, established in Braintree, US in 1996, is a manufacturer of packaging materials such as Intercept Shrink Film, Intercept Woven and Intercept Fabric. Their product portfolio includes protective packaging materials like bubble wrap, foam inserts, and void fillers, AT Film that is used for shipping of delicate electronics, and AT Flame Retardant film. The company serves markets such as Electronics and Technology, Cosmetics and Personal Care, Retail and Consumer Goods, Automotive and Transportation and Industrial and Manufacturing.
-
-
-
-

-
Sihui Fuji Electronics Technology Co., Ltd.
Printed Circuit Board
Company Overview
Sihui Fuji Electronics Technology Co., Ltd., established in 2009 and based in Zhaoqing City, Guangdong, China, is a manufacturer and supplier of electric printed circuit boards(pcb). The company’s products include server motherboard pcb, printed communication power amplifier pcb, depth controlled routing process pcb, camera sensing module pcb, and inductive rotatory sensor pcb. The products are used in telecommunication, network, robotics, power, and medical industries. The company has obtained international system certifications such as ISO 9001:2015, IATF 16949:2016, ISO 13485:2016, and IECQ QC 080000:2017.
-
-
-
-

-
Rowsum Electronics co., LTD
PCB Manufacturing
Company Overview
Rowsum Electronics co., LTD, established in 2004 and based in Shenzhen, China, is a manufacturer and supplier for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Printed Circuit Board Assemblies (PCBAs). The company's product portfolio includes single-sided PCBs, double-sided PCBs, multi-layer PCBs, and printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs). These products are used in various industries including automotive, aerospace, telecommunications, consumer electronics, and industrial controls. The company is ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and IATF 16949 certified, with clients in various countries, including the USA, Europe, Southeast Asia, and Africa.
-
-
-
-

-
Rubröder GmbH Factory Automation
PCB-Magazines for Transport and Storage
-
-
-
-

-
ABIS CIRCUITS CO., LTD.
Printed Circuit Board
-
-
-
-

-
Shenzhen Fast PCB Technology Co., Ltd.
Rigid PCB
-
-
-
-

-
Tianjin Printronics Circuit Corp.
Circuit board
-
-
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of April 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liberty Intercept |
24.4%
|
| 2 | MOOG |
13.3%
|
| 3 | Meiko Electronics Co., Ltd. |
11.1%
|
| 4 | Alphasense Ltd |
8.9%
|
| 5 | OKI Circuit Technology Co.,Ltd. |
8.9%
|
| 6 | ABIS CIRCUITS CO., LTD. |
6.7%
|
| 7 | Rowsum Electronics co., LTD |
6.7%
|
| 8 | PCBCart |
6.7%
|
| 9 | STM S.p.A. |
4.4%
|
| 10 | FlexLink Systems, Inc. |
4.4%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the printed circuit board (pcb) page as of April 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
- Meiko Electronics Co., Ltd.: 12,337
- Midcom: 8,000
- OKI Circuit Technology Co.,Ltd.: 754
Newly Established Company
- PCBCart: 2005 (19 years ago)
- Liberty Intercept: 1996 (28 years ago)
- Alphasense Ltd: 1996 (28 years ago)
Company with a History
- Meiko Electronics Co., Ltd.: 1975 (49 years ago)
- STM S.p.A.: 1976 (48 years ago)
- FlexLink Systems, Inc.: 1980 (44 years ago)
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
Global Distribution of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 China
China
|
2 | 22.2% |
 Japan
Japan
|
2 | 22.2% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
1 | 11.1% |
 Sweden
Sweden
|
1 | 11.1% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 11.1% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 11.1% |
 Italy
Italy
|
1 | 11.1% |