All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for digital gauges as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 15 digital gauge manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked digital gauge companies as of July, 2025: 1.Waytek, Inc., 2.Intempco Controls, Inc., 3.CARE PROCESS INSTRUMENTS.
Table of Contents
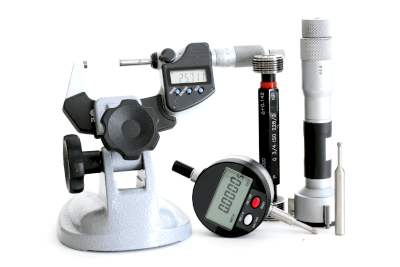
A digital gauge is a type of measuring instrument used to measure minute changes in height, inclination, depth, etc. of a point relative to another point.
Digital gauges, which cannot operate independently, are attached to equipment for specific measurement purposes.
Different sellers may refer to digital gauges as Digimatic Indicators.
There are also dial gauges, which are simple in construction and resistant to shocks, but their accuracy is not as high as that of digital gauges.
Digital gauges are widely used in the production of various products to ensure accuracy and for various tests. Although it is possible to directly read the numbers on gauges, they are mainly used to derive the desired rate of change from the amount of change in the numbers.
Digital gauges can measure displacement in micrometers, so they can be used to measure fine details such as surface steps, hole depths, and thicknesses of parts, and they can also be used to measure large, visible changes such as distortion when pressure is applied to building materials, automobile parts, etc.
Digital gauges are available in several types, the most common of which are the spindle type and the photoelectric type.
In the spindle type, a spindle is brought into contact with the surface of the object to be measured, and the ups and downs of the tip of the spindle in accordance with changes in the object's shape are output as measurement results. This method is also often used for dial gauges, and is suitable for objects with a large amount of change.
The photoelectric type has a contact part similar to the spindle type, but instead of directly outputting the motion as a measurement result, it measures the phase displacement of the light generated from the light source when it reaches the light receiving element through two slits (a moving slit linked to the spindle and a fixed slit) and converts it into a measurement result. This method, offering detailed displacement checks, is more suitable for measuring minute changes than the spindle type.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Meriam Process Technologies, established in 1911 and based in Cleveland, Ohio, USA, is a manufacturer of process measurement and control instruments. The product portfolio includes pressure gauges, digital manometers, flow meters, and calibrators. These instruments are used for precision, stability, and accuracy, making them essential tools for industries such as oil and gas, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing for process control solutions. With an abundance of ranges and accuracies, the digital manometers are made to accommodate all needs, whether pressure or vacuum, wet or dry. Several portable, simple-to-use measurement devices also allow mobile data logging.

S.A.M.A. Italia S.r.l., established in 1974 and headquartered in Viareggio, Italy, is a manufacturer of precision measuring and control instruments and calibration solutions. The product line includes an extensive range of options, such as flow meters, temperature sensors, pressure gauges, and calibration tools. These optimal-precision devices make it possible to precisely measure and regulate vital characteristics across an array of sectors, including petrochemical, manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace. The products' stability, accuracy, and longevity are essential to quality control and industry compliance in measuring and control solutions for organizations all over the world.
Adarsh Industries is a manufacturer of industrial components and equipment that was established in 1992 and is headquartered in India. Specializing in the production of components, the company's portfolio includes items such as precision turned parts, industrial fasteners, and custom machined components. It caters to diverse industries including automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing, among others. Its products are utilized for assembly and manufacturing processes facilitating to the seamless functioning of various manufacturing operations.

Charun Instruments, established in 1997 in Ahmadabad, Gujarat, India, are manufacturers, wholesalers, and exporters of various instruments such as Electromagnetic Flow Meters and Data Loggers. Their range extends to Automation Solutions, Control Panels, and solutions for Flow, Humidity, Level, Temperature, and Pressure. They also provide Maintenance, Repair, and Calibration of Process Control Instruments. Known for low power consumption and operational efficiency, their products are rigorously quality-tested. Led by Mr. Neeal Shah for over a decade, the company's transparent practices and expertise ensure customer satisfaction.

Precision Mass Products Pvt. Ltd., founded in 1967, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision weighing instruments. They offer a diverse range of products, including precision balances for laboratories, industrial scales for manufacturing applications, laboratory weights for calibration, analytical balances for research and pharmaceutical use, and weighing indicators for integrated weighing systems. The company has obtained ISO 9001:2015 certification, ISO 14001:2014, and OHSAS 18001:2007 certifications for its facility, complete with production, projects, design & development, customer service, and sales & marketing resource management.

eddylab GmbH, established in 2014 and headquartered in Bayern, Germany, is a manufacturer of measuring technology for distance and position detection. The company's products include draw-wire sensors, signal converters, and laser distance sensors. It also offers software for the analysis and configuration of its products. These products have applications in flight simulator positioning, cylinder stroke control for mold oscillation, and minimizing shrinkage during injection molding with UV curing. It serves sectors that include chemical processing, power generation, and material testing.

Tinsley Instrumentation Ltd., established in 1904 and based in Essex, England, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision measurement and portable test and measurement equipment. The company's product portfolio includes transformer test equipment, insulation testers, and decade resistance boxes. These products find application in various industries, including industrial manufacturing, telecommunications, and power generation and distribution. The company offers services including technical support, customization, and ordering and logistics. The company exports its products to various countries, including the United States, China, and South Africa.

Magnescale Co., Ltd., established in 1969 as Sony Magnescale Co., Ltd. and headquartered in Tokyo, is a manufacturer specializing in encoder scales used extensively in the Computer Numeric Control (CNC) machine tool industries. The company offers a range of products, including the Magnescale lineup of magnetic scales for rotational and linear position measurement. Additionally, they develop the Laserscale lineup, utilizing hologram technology and semiconductor lasers as light sources to achieve measurement resolutions at the picometer scale. These scales exhibit position and angle control, as well as environmental resistance to severe conditions such as temperature changes and air pressure fluctuations.

WINTERS INSTRUMENTS is a manufacturer and supplier of pressure and temperature instrumentation, established in 1953 in Canada. The company specializes in producing a wide range of gauges, thermometers, and other measurement devices for industries like oil and gas, food and beverage, and HVAC. With a rich history of innovation, WINTERS INSTRUMENTS is devoted to providing accurate measurement solutions. Their products are designed to withstand demanding environments and ensure the safety and efficiency of industrial processes.

Ralston Instruments, founded in 1969, is an American manufacturer based in Novelty, Ohio, specializing in pressure calibration solutions. The company's product lineup of pressure calibration products encompasses the Ralston Quick-test System, comprising adapter and hose kits, valves, straight adapters, and test point fittings. Alongside these, it offers other calibration products such as compressed gas control, digital pressure calibrations, accompanying software, as well as calibration test pumps. These products find application in various sectors, including maritime, manufacturing, and the oil and natural gas industries. Notably, the company holds accreditation from the American Association for Laboratory Accreditation (A2LA) for performing calibrations on metrological instruments.

Omicron, established in 1953 and headquartered in Mumbai, India, is a manufacturer and supplier of process control instrumentation such as flow switches and pressure gauges. The company's products include pressure and temperature instruments, level instruments, air quality and water quality sensors, psychrometric and portable instruments, and many more. These products find applications in diverse industries, including petrochemical, wastewater treatment, biotech and pharmaceutical, medical, semiconductor, and chemical manufacturing. It serves various clients, including EasyIO, Honeywell, ITC Limited, Sun Pharma, Hitachi, and others.

Waytek Inc., founded in 1970 and headquartered in Chanhassen, Minnesota, is a distributor of automotive wire and DC electrical components across North America. The company offers a broad line of products, including circuit breakers, cable ties, and connectors, serving wire harness manufacturers, OEMs, and upfitters. It sources the products from manufacturers such as GEP Power Products, Lovato Electric Inc., and East Penn Manufacturing. In 1980, the company stopped producing wire harnesses and started concentrating on distribution. In 2021, CIT Relay and Switch awarded it the Blast-Off Growth Award for being among the growing distributors of Picker Components products.

MEOKON SENSOR TECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO. LTD, established in 2008, based in Shanghai, China, is a service provider based on smart sensors. The company’s products include digital pressure gauge, digital pressure switch, intelligent pressure controller, pressure sensor, and pressure transmitter. The products' sensors, display control appliances and measuring control systems can be customized by customer's request. These products are used in for air compressor, automobile professions, spurt & hydraulic pressure, water supply system, and transmitting instrument, among others. The company’s products and testing instruments are imported from the US and Germany.

Intempco Controls Inc. is a trusted temperature measurement and instrumentation leader, offering high-quality sensors and controls for over 30 years. Based in Quebec, Canada, Intempco manufactures instrumentation devices for temperature, level, pressure, humidity, and flow. With global clients & distributors, their products can be configured to your exact application needs and are trusted for high accuracy, innovative design and ease of use. Intempco ensures enhanced quality control with their in-house production, calibration, and engineering capabilities. Their team of experts are ready to assist customers in various industries with their temperature sensing needs.

Care Process Instruments is a supplier of process measurement and control instruments that was established in 2004 and is headquartered in the United Kingdom. The company specializes in providing instruments for monitoring and controlling various industrial processes. Certified in ISO 9001:2015, it offers a range of products, including temperature controllers, pressure transmitters, flow meters, level sensors, and analytical instruments. Catering to industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and chemical manufacturing, its instruments find application in ensuring precision and reliability in critical process parameters, facilitating the overall efficiency of industrial operations.
Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CARE PROCESS INSTRUMENTS |
12.0%
|
| 2 | MEOKON SENSOR TECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO. LTD |
12.0%
|
| 3 | Precision Mass Products Pvt. Ltd. |
12.0%
|
| 4 | Waytek, Inc. |
12.0%
|
| 5 | Intempco Controls, Inc. |
8.0%
|
| 6 | WINTERS INSTRUMENTS |
8.0%
|
| 7 | Charun Instruments |
8.0%
|
| 8 | Ralston Instruments |
8.0%
|
| 9 | Tinsley Instrumentation Ltd. |
4.0%
|
| 10 | Adarsh Industries |
4.0%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the digital gauge page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 India
India
|
5 | 62.5% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
1 | 12.5% |
 Italy
Italy
|
1 | 12.5% |
 Canada
Canada
|
1 | 12.5% |
93 products found
93 products
Mahr Inc.
1100+ people viewing
Last viewed: 10 hours ago
■Digital outer micrometer The future is wireless - by Mahr A clear digital display, modern design, and the usual Mahr precision characterize this d...
10 models listed
Watanabe Precision Industry Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
We design and manufacture gauges using dial gauges that can output digital data. Our company has an in-house system development department. We can ...
Mahr Inc.
1220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 minutes ago
■3-point inner micrometer bore measurement - fast and flexible Available as a quick measuring device with scale plate or digital display, or pistol...
10 models listed
Mahr Inc.
1030+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
■Digital dial indicator The future is wireless - by Mahr A digital dial gauge featuring a clear digital display, robust construction, and high Mahr...
10 models listed
Maximator Fluid Technologies Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
The ADT601Ex intrinsically safe digital pressure gauge is designed to improve upon traditional mechanical pressure gauges by providing a reliable a...
Drapas Co., Ltd.
290+ people viewing
Last viewed: 19 hours ago
■Summary The world's lightest design that can be easily operated with one hand. Minimum display 0.001mm: Instrumental error of ±1μm achieved. It al...
Mahr Inc.
1210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
■Digital dial comparator The future is wireless - by Mahr High precision inductive Millimess dial comparators are capable of digital increments dow...
10 models listed
Mahr Inc.
510+ people viewing
Last viewed: 22 hours ago
■Digital test indicator measuring instrument The future is wireless - by Mahr A digital dial test indicator featuring an easy-to-read digital displ...
2 models listed
Marui Co., Ltd.
180+ people viewing
■Concrete: hardened concrete ・Length change test ・Drying shrinkage test ・Freeze-thaw test (Method A/Method B) Introducing hardened concrete rela...
Marui Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
Last viewed: 18 hours ago
■Concrete: hardened concrete ・Length change test ・Drying shrinkage test ・Freeze-thaw test (Method A/Method B) Introducing hardened concrete rela...
Nakajima Koki Co., Ltd.
310+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Easily and easily measure workpieces that require accuracy of 1 μm or less. "MDH-25MB" is a digital micrometer that achieves high-precision measure...
Ushiyama Denki Co., Ltd.
450+ people viewing
Last viewed: 14 hours ago
■Features Ideal for crimp height measurement of crimp terminals. All have constant pressure devices.
4 models listed
Asahi Sangyo Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
From passenger cars to medium-sized and large-sized cars. Measurement history for 4 times (4 tires). High precision with an error of ±3kPa achieved...
Fluke Calibration
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
The Model 2465 Gas Piston Gauge has a long history of use as a gas piston gauge standard in national standards laboratories, industry, and governme...
Fluke Calibration
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
■Gas pressure with vacuum standards from 7 kPa to 7 MPa (0.7 to 1 000 psi) PG7601 covers gauge and absolute pressures, including near-atmospheric a...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 22 hours ago
Danchi Caliper is Zensei's original measuring device that doubles as a small height gauge and depth gauge. By adjusting the position of the probe o...
Fluke Calibration
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 17 hours ago
It is important to consider environmental factors when calibrating piston gauges, but this is a tedious process. You can automate this process usin...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
Danchi Caliper is Zensei's original measuring device that doubles as a small height gauge and depth gauge. By adjusting the position of the probe o...
Fluke Calibration
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 hours ago
■100 kPa to 110 MPa (15 to 16,000 psi) gas pressure The PG7202 is a member of the PG7000 product family of reference level piston gauges, covering ...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 14 hours ago
Danchi Caliper is Zensei's original measuring device that doubles as a small height gauge and depth gauge. By adjusting the position of the probe o...
Fluke Calibration
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
■Automatic primary pressure reference for absolute and gauge pressures up to 500 kPa The PG9607 is Fluke Calibration's next generation absolute pre...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
Danchi Caliper is Zensei's original measuring device that doubles as a small height gauge and depth gauge. By adjusting the position of the probe o...
Fluke Calibration
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
■Hydraulic pressure from 100 kPa to 500 MPa (14.5 to 75 000 psi) PG7302 uses oil as the pressurizing medium to cover gauge and absolute pressures. ...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
Danchi Caliper is Zensei's original measuring device that doubles as a small height gauge and depth gauge. By adjusting the position of the probe o...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Danchi Caliper is Zensei's original measuring device that doubles as a small height gauge and depth gauge. By adjusting the position of the probe o...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 hours ago
A lightweight (550g) and compact height gauge for measuring 0 to 150mm. It has digital caliper specifications and is easy to use and has excellent ...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
150+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
Since the reference surface is small, depth measurements can be made in narrow areas.
Zensei Co., Ltd.
140+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
OGARU" is a measuring device that measures the sole thickness of track and field shoes (such as running shoes). You can measure by placing the meas...
Zensei Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
A tooth thickness caliper is a caliper that has a tooth thickness scale and a tooth height scale that are perpendicular to each other and are integ...
2 models listed