All Categories
History





This section provides an overview for phase contrast microscopes as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 6 phase contrast microscope manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked phase contrast microscope companies as of March, 2026: 1.Leica Microsystems Vertrieb GmbH, 2.Labomed, 3.Standard Steel.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Phase Contrast Microscopes
1976~2001: Worked at the Geological Survey of the Industrial Science and Technology Agency of the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (initially). Engaged in research on resource geology at the Hokkaido Branch.
2001~2016: Worked as an industry-academia-government collaboration coordinator at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, and also served as the head of the Manufacturing Fundamental Technology Support Office.
2004~2016: R&B Park Sapporo Odori Satellite is a base to support the development of products and technologies through industry-academia-government collaboration in Hokkaido.
Currently working as a science and technology advisor.
 A phase contrast microscope is a type of optical microscope that converts the phase difference of light into contrast for observation.
A phase contrast microscope is a type of optical microscope that converts the phase difference of light into contrast for observation.
With an ordinary optical microscope, differences in the reflection and absorption spectra of light from different parts of a sample are observed as differences in brightness or color (contrast). However, when observing nearly colorless materials such as living cells, microorganisms, and bacteria, these contrasts are almost nonexistent, and information such as shape cannot be obtained.
Even if a material is colorless and transparent, if its refractive index differs from that of its surroundings, the diffraction of light will occur at the boundary. Phase contrast microscopes use the phase difference between the diffracted light and the light traveling straight through the material to create a contrast between light and dark, making it possible to observe colorless transparent materials.
Phase contrast microscopes are widely used in biology and medicine for observation of cultured cells and clinical examination. Periodontal bacteriological examination in dental clinics is a familiar application for the public. It helps to motivate patients to take better care of their oral health by letting them know how their own oral bacteria are doing.
Phase contrast microscopes allow observation of live cells without the need to stain the specimen. When observing colorless cells with a conventional optical microscope, the sample is stained for observation, but this method has the disadvantage that the staining is time-consuming and kills living cells.
In addition, phase contrast microscopes are also effective in analyzing asbestos, a toxic substance. One method is the dispersion staining method, in which crystals in the immersion solution with a specific refractive index are irradiated with polarized light under a phase contrast microscope, and the color produced is used to determine whether the sample is asbestos or not.
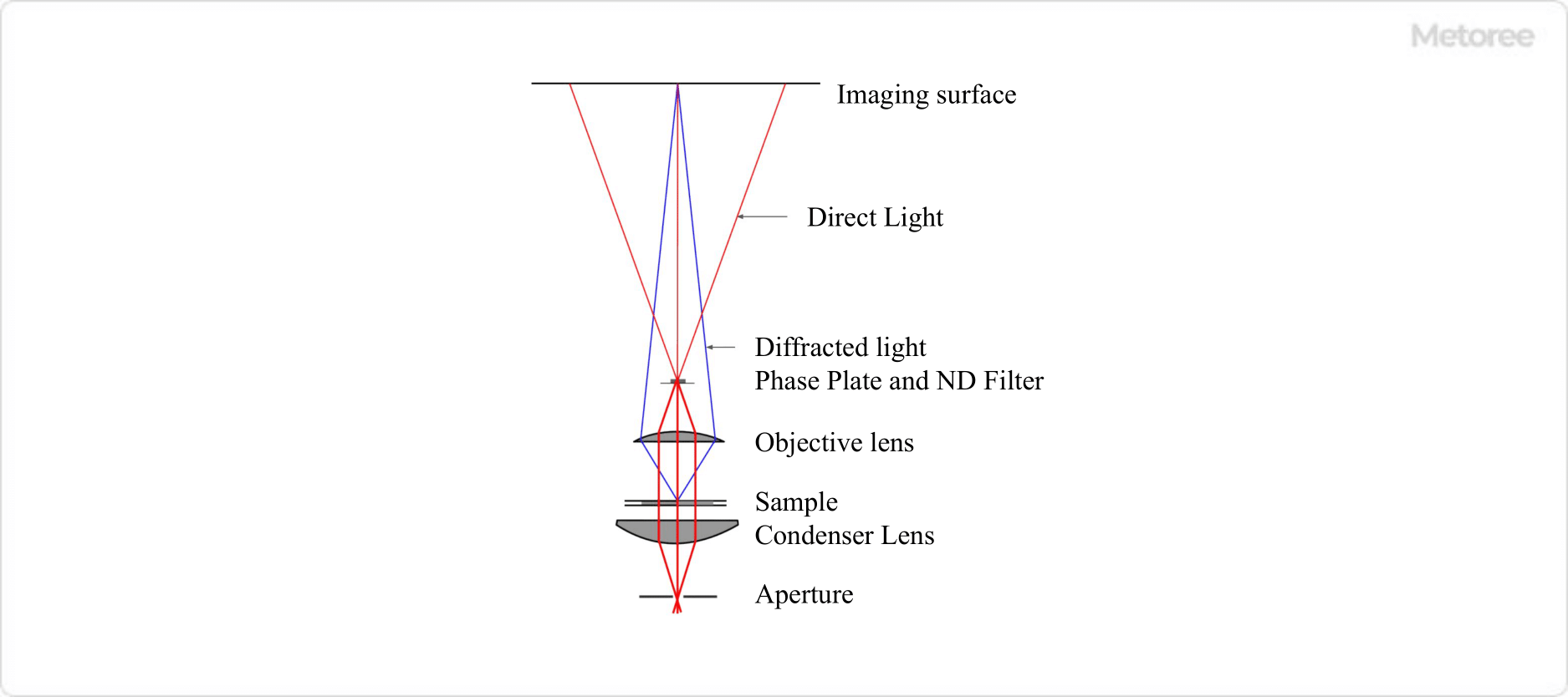
Figure 1. Optical system of a phase contrast microscope
In a phase contrast microscope, a phase plate is inserted only at the position where the direct light passes between the objective lens and the image plane to advance or retard the phase of the direct light by 1/4λ. At the same time, a ring-shaped ND filter is inserted to reduce the intensity of the direct light, but does not change the phase or brightness of the diffracted light.
By these operations, the phase difference between the direct light and diffracted light becomes 1/2λ or 0, and the light and dark contrasts are created by interference.
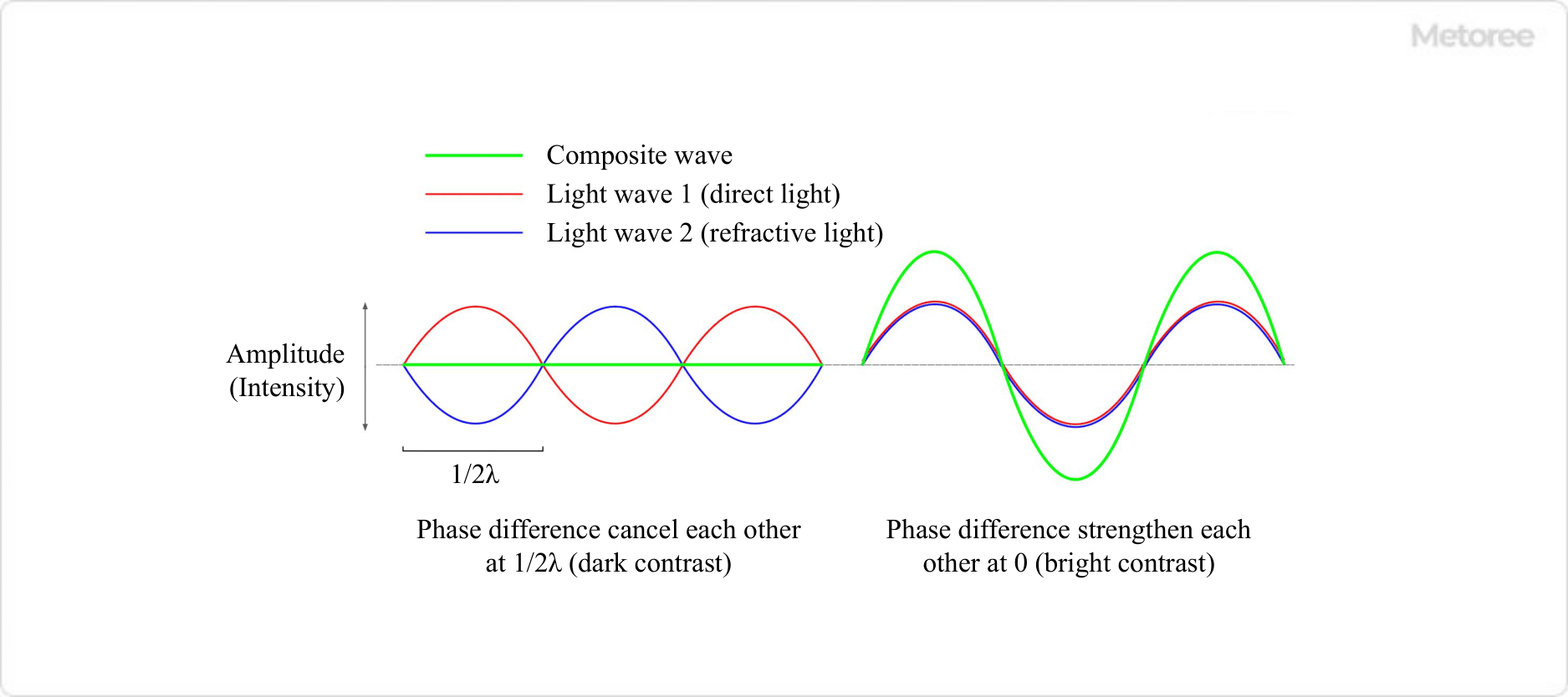
Figure 2. Interference between amplitude-matched direct light and diffracted light
In other words, at the site of a sudden change in refractive index where diffracted light is generated, when the phase difference is 1/2λ, direct light and diffracted light interfere with each other in a weakening manner, resulting in a dark appearance. This is the dark contrast. On the other hand, when the phase difference is 0, direct light and diffracted light interfere with each other in such a way that they strengthen each other, making the site of the abrupt change in refractive index appear bright. This is the bright contrast.
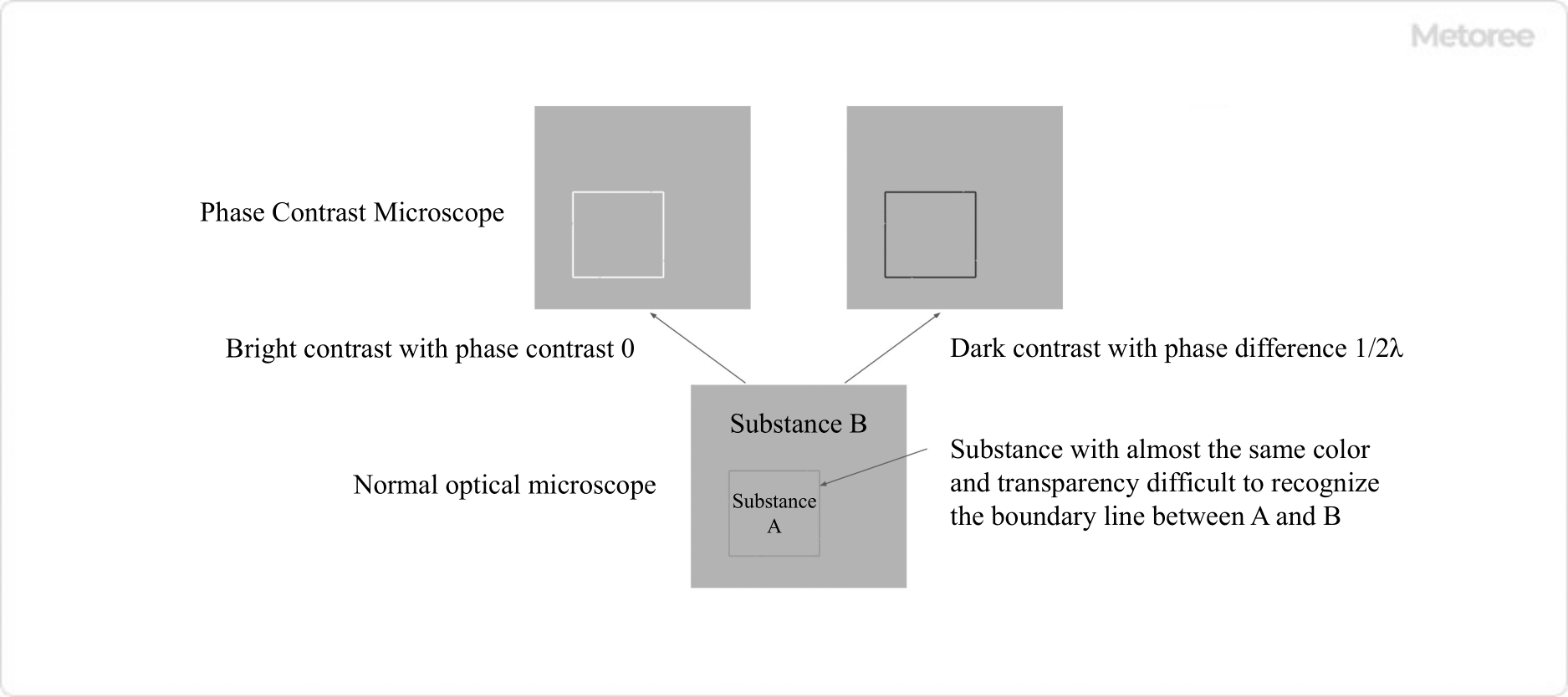
Figure 3. Bright contrast and dark contrast
In ordinary optical microscopy, a substance can be identified by differences in either the intensity (amplitude) or the color (wavelength) or both of the light transmitted through the substance under observation. Therefore, for example, it is not easy to recognize the difference or boundary between a colorless transparent substance A and a colorless transparent substance B that is in contact with another colorless transparent substance A, even if they are observed with an ordinary optical microscope.
This is because there is no difference in the intensity and color of the transmitted light and no contrast between A and B. However, if the refractive indices of substances A and B are different, at the boundary between them, light is divided into direct light that travels straight through the sample and diffracted light whose path is altered. Since diffracted light is generated at the point where the refractive index changes abruptly, it contains information about the boundary shape and internal structure of each material in the sample.
It is important to note that diffracted light is delayed by a quarter of a wavelength (λ) (1/4λ) relative to the direct light traveling straight through the sample. Such a delay of a fraction of a wavelength is called a phase difference. Even if diffracted light is generated, the phase difference is minute because it is very weak compared to direct light.
Therefore, the image formed by adding the direct light and diffracted light together has a wave shape similar to that of the direct light, and no contrast between bright and dark is produced with an ordinary optical microscope.
In addition to phase contrast microscope, differential interference microscope is another type of microscope that uses light interference to obtain contrast. In differential interference microscopy, the light incident on a sample is separated into two polarizations with slightly different paths, and the two lights interfere with each other after passing through the object of observation to obtain contrast.
It is similar to the phase contrast microscope in that it can observe colorless and transparent materials, which is impossible with the phase contrast microscope. However, phase contrast microscope provides contrast in areas where the refractive index of the sample changes abruptly, whereas differential interference microscope provides contrast in areas where there is a gradient in the thickness or refractive index of the sample.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Labomed, Inc. serves as a manufacturer and provider of Labomed LB Microscopes and Microscope parts. The company's microscopes deliver superior image quality and optical performance across industrial, medical, and scientific research applications. The company extends its expertise to UV-Visible Spectrophotometers, ensuring accurate measurements for both conventional and research laboratories. Labomed's unwavering focus on excellence is evident in their range of medical diagnostic equipment, microscope cameras, and cuvettes. ISO 9001, CE Conformity, and FDA Licensing validate their adherence to quality standards.

Standard Steel, founded in 1998 with headquarters in India, is a manufacturer of hospital furniture and equipment. The company's product line includes hospital beds, examination couches, autopsy tables, operating tables, and laboratory tables, among many others. Its products are used in hospitals, healthcare centers, doctors offices, and research laboratories. The company also provides custom design and production of white-label and OEM products to meet client-specific requirements. It exports primarily to countries across Africa, Latin America, Australia, and Oceania.
Pulse Life Science, founded in 2009 and headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India, is a projecting manufacturer and supplier specializing in advanced biotechnology solutions. Their extensive product range encompasses laboratory equipment, cell culture technologies, bioreactors, and specialized consumables. Pulse Life Science plays a pivotal role in scientific research, offering essential tools for diverse applications, from pharmaceutical development to regenerative medicine. For its quality and modernization, the company is an integral partner in driving progress across the life sciences sector, aiding discoveries and breakthroughs globally.

Leica Microsystems is a developer and manufacturer of microscopes and scientific instruments for the analysis of microstructures and nanostructures. The company is a provider in compound and stereo microscopy, digital microscopy, confocal user scanning, and super-resolution microscopy with related imaging systems, electron microscopy, sample preparation, and surgical microscopy used in medical, life science, and industrial applications. The company’s services include service plans, preventative maintenance, remote care, and qualification services for ensuring compliance of Leica equipment to governmental regulations.

Radical Company is an enterprise engaged in the manufacturer and distributor of modern audiovisual technologies and was founded in 2011 based in Pennsylvania, United States. The primary emphasis of their work centers around the development of state-of-the-art projection systems, interactive displays, and immersive audio technologies. The company is in the forefront of pioneering breakthroughs in the audiovisual (AV) sector. Their diverse range of solutions encompasses both large-scale event installations and tailored home entertainment setups, consistently pushing the frontiers of sensory experiences on a global scale.

Meiji Techno Co., Ltd. (MTC) is a Japanese manufacturer and distributor of optical microscopes originally established in 1964 as Azuma Optics Company before rebranding in 1975. Based in Saitama, the company produces various microscopes for applications in education and life sciences, including inverted, compound, stereo, and polarizing models. These are utilized by clients in laboratory operations and quality control, analysis, and testing within the industrial sector. MTC has manufacturing facilities in Japan and China, with distribution operations in Shanghai, California, and New Jersey. Its North American subsidiary Meiji Techno America was incorporated in 1986, and is located in San Jose.
Ranking as of March 2026
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Leica Microsystems Vertrieb GmbH |
45.0%
|
| 2 | Labomed |
15.0%
|
| 3 | Meiji Techno |
15.0%
|
| 4 | Standard Steel |
10.0%
|
| 5 | Pulse Life Science |
10.0%
|
| 6 | ACOX |
5.0%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the phase contrast microscope page as of March 2026. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 India
India
|
3 | 50.0% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
1 | 16.7% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 16.7% |
 Japan
Japan
|
1 | 16.7% |
34 products found
34 products
Ptech Co., Ltd.
2250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Summary The chairside phase contrast microscope "P-Scope" is a high-performance microscope, but it is also popular because it is affordable, porta...
Advanced Technology Research Institute Ltd.
680+ people viewing
■Summary The newly developed laser phase contrast microscope differs from the conventional Zernike phase contrast microscope in that it can not onl...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
540+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Summary ・Turret type phase difference condenser (dark field filter included). Phase contrast, dark field, and bright field observations are possi...
Nihon Kohki Seisakusho Co., Ltd.
820+ people viewing
This is a portable, field-ready, ultra-compact microscope that can be used separately from the stationary microscope (for indoor use). By installin...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
520+ people viewing
■Summary ・This is a high-performance microscope recommended as a research biological microscope. - Equipped as standard with a Plan achromatic obj...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
650+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Summary ・Turret type phase difference condenser (dark field filter included). Phase contrast, dark field, and bright field observations are possi...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
590+ people viewing
■Summary ・Turret type phase difference condenser (dark field filter included). Phase contrast, dark field, and bright field observations are possi...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
530+ people viewing
■Summary ・High performance dark field microscope. - Equipped as standard with a Plan achromatic objective lens that provides high performance for ...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
570+ people viewing
■Summary -High-grade dark field microscope. ・Dry type (Dry objective lens compatible type) Comes with dark field condenser and dark field filter. ...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
610+ people viewing
■Summary ・This is a high-grade, high-performance microscope recommended as a research biological microscope. - Equipped as standard with a Plan ac...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
610+ people viewing
■Features -By utilizing the difference in the refractive index of light between the specimen and the background, the contrast between light and dar...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
650+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features Colorless and transparent specimens can be viewed alive without staining. - Because it is an inverted type, it can be observed as it is i...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
640+ people viewing
■Summary ・Objective lenses capable of phase contrast observation: 10x, 40x, 100x (oil) ・Objective lens capable of dark field observation: 4x, 10x...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
680+ people viewing
Last viewed: 15 hours ago
■Features The inverted microscope is equipped with a UVC compatible microscope digital system. - Phase contrast observation is possible by combinin...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
690+ people viewing
Last viewed: 20 hours ago
■Summary ・Objective lenses capable of phase contrast observation: 10x, 40x, 100x (oil) ・Objective lens capable of dark field observation: 4x, 10x...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
690+ people viewing
Last viewed: 50 minutes ago
■Sliding phase difference plate type - Observation of blood tests (red blood cells, white blood cells, somatids, etc.) ・Observation of dental and ...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
620+ people viewing
Last viewed: 21 hours ago
■Summary ・Objective lenses capable of phase contrast observation: 10x, 40x, 100x (oil) ・Objective lens capable of dark field observation: 4x, 10x...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
600+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Sliding phase difference plate type - Observation of blood tests (red blood cells, white blood cells, somatids, etc.) ・Observation of dental and ...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
850+ people viewing
■Features ・Uses light diffraction and interference to visualize colorless and transparent specimens by contrasting light and dark. - Suitable for ...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
630+ people viewing
■Summary ・Objective lenses capable of phase contrast observation: 10x, 40x, 100x (oil) ・Objective lens capable of dark field observation: 4x, 10x...
Seihodo Co., Ltd.
730+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Summary ・This is a high-performance microscope recommended as a research biological microscope. - Equipped as standard with a Plan achromatic obj...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
740+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features ・Most techniques required for research in geology, petrology, and mineralogy can be performed more precisely and more easily. ■ Specifi...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
720+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Specifications ・Eyepiece: PL10× (Number of fields of view 22) ・Light source: 6V 30W halogen bulb ・Condenser numerical aperture: 0.3 (WD72mm) ・...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
700+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features Suitable for geology, petrology, mineralogy, toxicology, pharmacy and forensics. ■Specifications ・Eyepiece: WF10× (18mm) with reticle ...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
830+ people viewing
■Features This microscope is suitable for educational and industrial use in geology and mineralogy. ■Specifications ・Lens barrel type: Monocular/...