











16 Driveshaft Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for driveshafts as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 16 driveshaft manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked driveshaft companies as of April, 2024: 1.Quigley Motor Company, Inc., 2.Johnson Power, Ltd., 3.Mark Williams Enterprises Inc..
Table of Contents
What Is a Driveshaft?
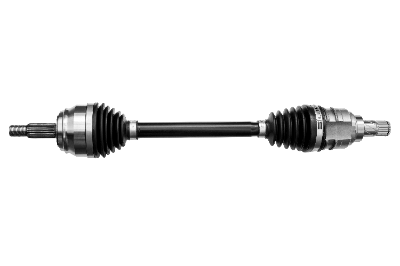 A driveshaft is a rotating shaft used to transmit the power of a prime mover to rotating equipment.
A driveshaft is a rotating shaft used to transmit the power of a prime mover to rotating equipment.
Driveshafts are generally known as automobile driveshafts, but they are also widely used for power transmission in ships, industrial machinery, construction machinery, railcars, and other vehicles.
Driveshafts do not have to be arranged in a straight line from the power section to the transmission section, but can still transmit power by using constant velocity joints.
Driveshafts are especially needed in automobiles to drive wheels that are subject to large vibration displacement.
Uses of Driveshafts
Driveshafts are also most commonly used in automobiles. Driveshafts in automobiles are components that transfer the power of the engine to the wheels.
In front-wheel drive vehicles, power is transmitted from the engine to the wheels via the Driveshaft. In the case of rear-wheel-drive vehicles, power from the engine is transmitted via the propeller shaft to a differential gear in the rear, which drives the wheels using the Driveshaft.
For applications other than automobiles, the propeller shaft is connected to motors for blowers, pumps, compressors, cranes, reduction gears, etc., and to drive shafts for rolling mill rolls and tension reels in steel manufacturing machinery. They are also used as drive shafts for rolls in chemical machinery, hydraulic pump drive shafts in construction machinery, and hydraulic pump drive shafts in truck mixers.
Further applications include work equipment drive shafts for agricultural tractors and drive shafts for machine tools, printing machinery, and paper manufacturing machinery.
Principle of Driveshafts
Driveshafts in automobiles and other equipment usually do not form a straight line from the engine power unit to the wheel power transmission unit. Therefore, constant-velocity joints are installed at both ends of the shaft to smoothly transmit power at a constant velocity even if the shaft is angled.
There are two types of constant velocity joints: fixed type and sliding type.
1. Fixed Type
This type cannot slide in the direction of the drive shaft. The constant velocity joint has parts called the outer race and inner race, and several steel balls are placed inside the outer race and outside the inner race. The steel balls allow the constant velocity joint to be angled.
2. Sliding Type
This type can slide in the direction of the drive shaft. There are two types: One type has grooves on the outer race and inner race that are parallel to the axial direction and can slide in the axial direction. The other type has a three-axis component attached to one of the rotating shafts, each end of which has a roller. When rotated at an operating angle, the rollers roll in grooves inside the housing to enable axial sliding.
Other Information on Driveshafts
1. Life of a Driveshaft
The life of a Driveshaft is generally the time it takes for the constant velocity joint to wear out to the point of noise or breakage. For automobiles, the standard is 200,000 km in terms of mileage.
A symptom of a failing Driveshaft approaching the end of its service life is the production of abnormal noise.
The most common type of vehicles in which abnormal noise can be easily recognized are front-wheel drive (FF) vehicles. When the angle of the constant velocity joint is large due to steering, a rattling noise may occur when accelerating. The cause of the noise is excessive clearance due to wear of the inner race, outer race, and steel balls, which are the key parts of the constant velocity joint.
The main causes of wear are deterioration of lubrication performance due to deterioration or decrease in the amount of grease sealed in the constant velocity joint for lubrication, and accelerated wear due to foreign matter such as sand entering the joint.
Grease deterioration can be caused by aging due to long-term use, early deterioration due to heat generation in the joint caused by continuous high load, and deterioration due to moisture contamination. Most of the causes of low grease level and foreign matter contamination at joints are deterioration or damage to the bellows-like parts called boots that protect the joints.
2. Drive Shaft Boots
Boots protecting joints are mainly manufactured from rubber or flexible resin. The boots are cylindrical bellows-shaped, installed to cover the entire joint and secured with metal bands tightened at both ends.
The main functions of the boot are to retain lubricating grease in the joint and to prevent foreign matter from entering the joint. When inspecting the Driveshaft externally, it is important to check if the boot is torn or if grease is leaking from the fixed part. Reduced lubrication and foreign matter in the joints accelerate wear.
Replacing the boot used to require removal of the Driveshaft from the vehicle body, but now there are split-type boots that can be replaced without removing the boot from the vehicle body.
After the old boot is removed, the new boot, which is split in two, is installed so that it is sandwiched between the joints, and the mating joints are welded together with adhesive and heat to achieve a strength similar to that of conventional products.
When replacing the boot, the grease inside is also replaced with a new one, thus restoring lubrication performance.
List of 16 Driveshaft Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- Italy
-
-

-
Mark Williams Enterprises Inc.
DRIVESHAFTS
Manufacturer Overview
Mark Williams Enterprises Inc. is an American manufacturer based in Louisville, Colorado, specializing in automotive and industrial driveline components. The company's extensive product offerings include axles, brakes, chassis components, and modular rear ends. Moreover, the company provides components tailored for specific applications, such as classic or drag racing purposes, off-road driving, as well as the National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing (NASCAR). The company provides industrial services such as broaching, induction hardening, and torsional testing. Its expertise also extends to the manufacturing of custom parts, specifically addressing components like shafts and spines that might be challenging to source through conventional means.
-
-
-
-

-
Precision Shaft Technologies
CUSTOM DRIVESHAFTS
Manufacturer Overview
Precision Shaft Technologies, founded in 2002 and located in Clearwater, Florida, is a manufacturer of driveshafts. The company offers a diverse range of products, including drag shafts, circle track shafts, and custom driveshafts. These driveshafts are used for enhanced performance, durability, and customization in racing and specialized automotive applications. The company’s products are designed for specific applications, including drag racing, circle track racing, and custom vehicle setups. Precision Shaft Technologies caters primarily to the automotive performance, racing, and customization sectors.
-
-
-
-

-
The Driveshaft Shop
DRIVESHAFT
Manufacturer Overview
The Driveshaft Shop, founded in 1995 and located in Salisbury, North Carolina, is a manufacturer of drivetrain solutions for street and racing use. Its broad range of products includes CV axles, driveshafts, conversions, and custom applications. These products have specific uses, such as upgrading street and racing vehicles, handling engine swaps, and catering to unique vehicle builds. The company's offerings are used to improve performance, durability, and customization in the automotive industry. The Driveshaft Shop caters to sectors such as automotive performance, racing, customization, and restoration.
-
-
-
-

-
Johnson Power, Ltd.
Driveshafts
Manufacturer Overview
Johnson Power Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial universal joint drive shafts, composite drive shafts, gear couples, repairs and custom components. The company was founded in 1866 and established at Mba USA. The company specializes in shafts, gear, pumps used in steel and paper mills, water treatment plants, and other industrial power hauling machines. The Markets Johnson Power Ltd serve includes steel and paper mills, pump, and other industrial applications.
-
-
-
-

-
Quigley Motor Company, Inc.
Driveshafts
Manufacturer Overview
Quigley Motor Co., Inc. (QMC) is an American manufacturer specializing in four-wheel drive (4x4) conversion solutions that was established in 1974. Based in Manchester, Pennsylvania, the company primarily produces 4x4 conversions for full-sized vans and cut-aways, as well as specialty upfits and driveshafts. They offer customized 4x4 systems to optimize for different specifications, such as stability, clearance, or traction. QMC products and services are used by client companies and businesses in the construction, tourism, emergency services, and recreational vehicles markets.
-
-
-
-
-
Orlandi Gear Co.
Driveshafts
Manufacturer Overview
Orlandi Gear Co. (OGC) is an American ISO 9001 certified manufacturer of mechanical power transmission components that was established in 1944 in Fraser, Michigan. The company's products include splined and keyed shaft models, spur and bevel gears, and various couplings as well as connectors for joining components together. These are used in hydraulic pumps, construction equipment, power take-off systems, and mining operations. OGC also offers various customization and finishing services including hobbing, broaching, honing, and coating for protective or decorative purposes.
-
-
-
-

-
Sunnen Products Company
Driveshafts

Manufacturer Overview
Sunnen Products Company, founded in 1924, is an American manufacturer and supplier headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri, specializing in of high-precision and bore sizing machines, tools, and abrasives. Joe Sunnen, founder of the company, invented the first manual cylinder hone in 1928. Over the years, Sunnen has developed industrial honing machines, tools, and abrasives with bore sizing and finishing systems, lapping machines, deep hole drilling machines and tools, bore gaging and roller burnishing systems. These products find applications in various industries, such as honing solutions in the automotive sector, as well as a line of machines, tools, and abrasives for energy drilling.
-
-
-
-

-
USA Standard Gear
Driveshafts
Distributor Overview
USA Standard Gear, founded in 2006 and headquartered in Everett, Washington State, is a supplier of differential and traction, driveshafts, transfer cases, and manual transmission. The company offers a diverse range of products, including bearing kits, front driveshafts, dropout housings, front OE replacements, and spider gears. The company’s products find specific applications in automotive repair, off-road upgrades, customization, and drivetrain overhauls. These products are used to ensure smooth operation, performance enhancement, and customization options for differentials, driveshafts, and transmissions in vehicles.
-
-
-
-

-
Modern DriveLine
Drive Shafts, Yokes & Flanges
Distributor Overview
Modern DriveLine, founded in 1998 and located in Caldwell, Idaho, is a supplier and distributor of flywheels and driveshafts. The company’s diverse range of products includes bellhousings, MDL flywheels, MDL clutches, Tremec crossmembers, and supporting parts. These products are utilized for automotive conversions, performance upgrades, custom builds, and proper mounting. The company’s offerings cater to automotive performance enhancement, customization, and conversions. Modern DriveLine's products are used to improve drivetrain compatibility, enhance vehicle performance, and provide customization options within the automotive industry.
-
-
-
-

-
American Powertrain
Custom Order Driveshafts
Distributor Overview
American Powertrain, founded in 2003 and located in Cookeville, Tennessee, is a distributor of drivetrain technology. Its broad range of product lines includes Pfitzner sequential, hydraulic clutch systems, clutches, fluids, and electric power steering. The company’s product line is used for different purposes, such as automotive performance enhancement, racing applications, custom builds, clutch optimization, and power steering enhancement. These products cater to vehicle enthusiasts, racers, and customization needs and are used to improve performance and control in the automotive industry.
-
-
-
-

-
The Rowland Company
Driveshafts
Distributor Overview
The Rowland Company was founded in 1732 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania when Benjamin Franklin was just 25 years old. Today the Rowland Company specializes in the distribution, fabrication, and assembly of industrial power transmission products, including application engineering, and modification of products to customer needs. Industries served include commercial laundry, amusement parks, marine, metalworking, power generation, pulp & paper, transit, water treatment and wastewater treatment Rowland Company’s product categories include air starters, brakes, clutches, crane controls & electrification, flexible couplings, friction and wear materials, gearboxes, industrial lighting & signals, mobile crane brake parts, universal joints, and driveshafts.
-
-
-
-

-
Comer Industries Spa
DRIVESHAFTS
Manufacturer Overview
Comer Industries S.p.A., established in 1970 and headquartered in Reggiolo, Italy, is an industrial and agricultural mechatronic components and solutions manufacturer. The company's agricultural products include planetary drives, gear boxes, and hydrostatic traction drives. Its industrial products include tractor attachments, electric motors, and single-drum compactors. These products are used in road construction vehicles, mining machines, and construction equipment. The company also owns a number of brands, including Walterscheid, Walterscheid Services, and Mechanics Drive Shafts.
-
-
-
-

-
Drive Shafts Incorporated
Drive Shaft
Manufacturer Overview
Drive Shafts Incorporated, founded in 1977 and located in Tulsa, Oklahoma, is a designer and custom manufacturer of driveshafts. Its broad range of product lines includes the series transmission yoke, series U-joint, series chromoly transmission yoke, series quick disconnect yoke, and center supporting bearing. The company’s specific product applications include easy maintenance and driveshaft stability. These products are used in connecting and transmitting power within drivetrain systems, enhancing vehicle performance, flexibility, and durability. Drive Shafts Incorporated caters to automotive repair, performance enhancement, customization, and specialized vehicles.
-
-
-
-

-
Stromag
DRIVESHAFT
Company Overview
Stromag, founded in 1932 and based in Unna, NRW, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of power transmission components. The company's product range includes Brakes, Clutches, Couplings, Limit Switches, and SIOT Monitoring and control. These components are used in various machinery ensuring smooth operation and efficiency. It serves industries such as Amusement Rides and ski Lifts, Cranes and hoists, Elevators and escalators, and Farms and agriculture. Additionally, the company provides services such as customized solutions, technical support, and product maintenance.
-
-
-
-

-
Cyner Industrial Co., Ltd.
Drive shaft
Company Overview
Cyner Industrial Co. Ltd. was founded in 1978 in Taichung, Taiwan, and is a manufacturer, developer, and designer of various OEM parts. The company manufactures gears, shafts, and transmission parts for automobiles, motorcycles, electric cart parts, tractors, and machinery. It is a supplier for several major OEM factories in the global market, including in the USA, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia. The company also designs high-precision products, including 250cc to 8,000cc gasoline and diesel engine parts, and is ISO-9001 certified.
-
-
-
-

-
Summit Racing Equipment
Driveshafts
Distributor Overview
Summit Racing Equipment, founded in 1968 and located in Tallmadge, Ohio, is a distributor of automotive parts. The company’s diverse range of products includes cooling and heating, engines and components, exhaust, exteriors and accessories, and fasteners and hardware. These products have specific applications, including engine temperature regulation, performance enhancement, exhaust flow improvement, exterior and interior customization, and secure assembly through fasteners and hardware. These applications are used in the automotive industry to address the diverse needs of vehicle owners. The company's offerings cater to sectors within the automotive industry, including maintenance, restoration, and the aftermarket.
-
-
Driveshaft Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of April 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quigley Motor Company, Inc. |
14.4%
|
| 2 | Johnson Power, Ltd. |
10.4%
|
| 3 | Mark Williams Enterprises Inc. |
9.1%
|
| 4 | USA Standard Gear |
8.4%
|
| 5 | The Driveshaft Shop |
8.0%
|
| 6 | Precision Shaft Technologies |
7.3%
|
| 7 | Modern DriveLine |
5.8%
|
| 8 | Sunnen Products Company |
5.8%
|
| 9 | Drive Shafts Incorporated |
5.5%
|
| 10 | Summit Racing Equipment |
5.4%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the driveshaft page as of April 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
- Modern DriveLine: 1998 (26 years ago)
- Drive Shafts Incorporated: 1977 (47 years ago)
- Comer Industries Spa: 1970 (54 years ago)
Company with a History
- The Rowland Company: 1732 (292 years ago)
- Summit Racing Equipment: 1968 (56 years ago)
- Comer Industries Spa: 1970 (54 years ago)
Driveshaft Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
- Mark Williams Enterprises Inc.
- Precision Shaft Technologies
- The Driveshaft Shop
- Johnson Power, Ltd.
- Quigley Motor Company, Inc.
- Orlandi Gear Co.
- Sunnen Products Company
- USA Standard Gear
- Modern DriveLine
- American Powertrain
- The Rowland Company
Global Distribution of Driveshaft Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
11 | 91.7% |
 Italy
Italy
|
1 | 8.3% |