











36 Ball Screw Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for ball screws as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 36 ball screw manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked ball screw companies as of July, 2024: 1.Joyce/Dayton Corp., 2.Isotech, Inc., 3.Rockford Ball Screw Co..
Table of Contents
What Is a Ball Screw?
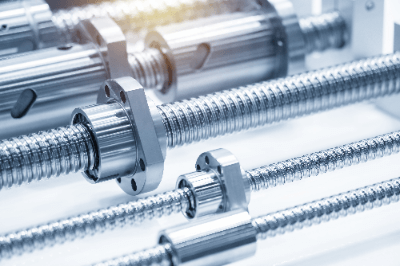 A ball screw is a type of feed screw that converts rotational motion into linear motion to move the position of a component. The screw shaft and nut are actuated by a ball. As the screw shaft and nut rotate relative to each other, the balls roll in an endless cycle. The sliding resistance between the screw and nut is much lower than that of conventional trapezoidal screws.
A ball screw is a type of feed screw that converts rotational motion into linear motion to move the position of a component. The screw shaft and nut are actuated by a ball. As the screw shaft and nut rotate relative to each other, the balls roll in an endless cycle. The sliding resistance between the screw and nut is much lower than that of conventional trapezoidal screws.
The precision grade of the screw and ball allows for precise motion, resulting in high positioning accuracy. They are used in automotive steering devices and precision machine tools.
Uses of Ball Screws
Ball screws are machine elements that convert the rotational motion of a motor, etc., into linear motion. Major applications include transportation and positioning of products and parts, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, industrial robots, and machine tools. Since the amount of travel (lead) per revolution of a ball screw can be precisely reproduced, high positioning accuracy can be achieved by combining it with a stepping motor.
In NC-controlled machine tools, ball screws are used to configure the feed mechanism and obtain precision positioning accuracy. Ball Screws are also used in food machinery, medical equipment, robots, injection molding machines, printing equipment, amusement equipment, automobiles, trains, aircraft, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and inspection equipment.
Principle of Ball Screws
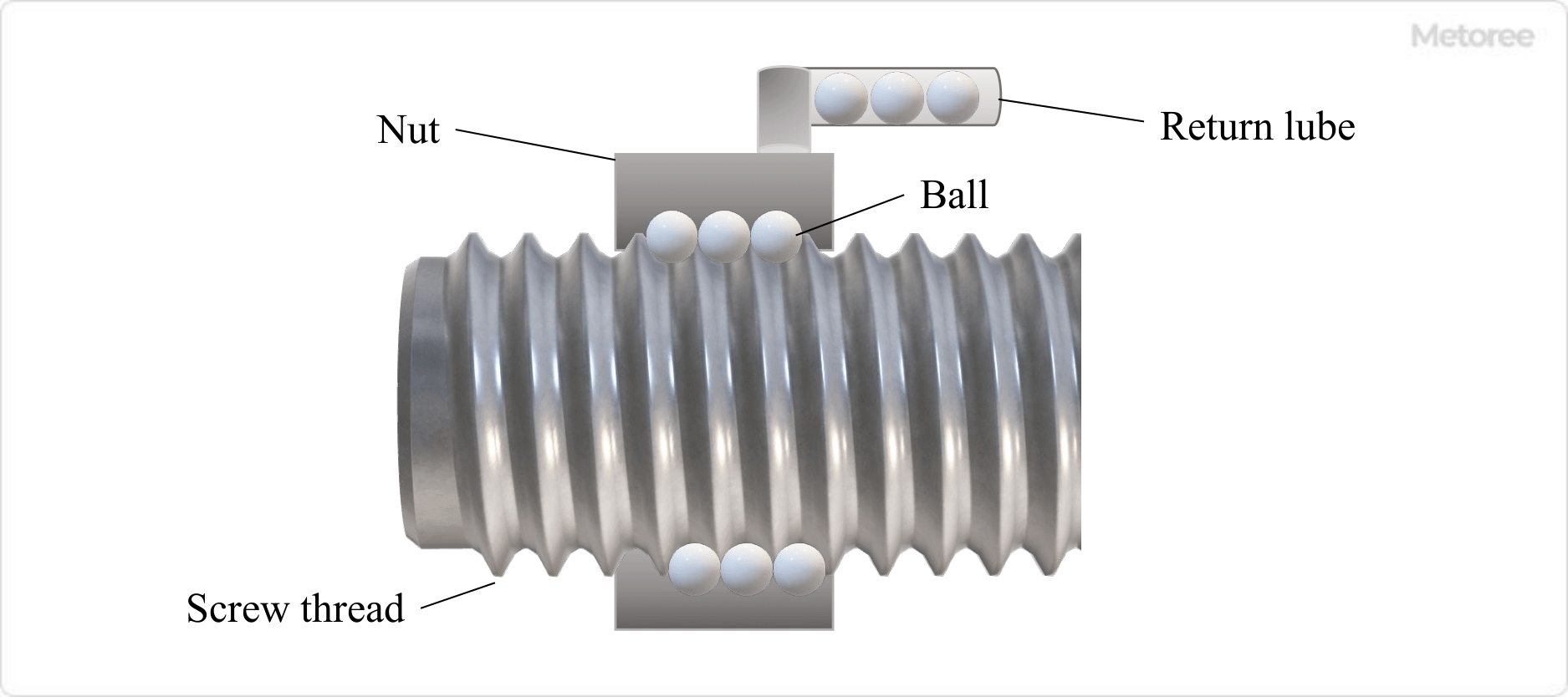
Ball screws are machine element parts consisting of a screw shaft, nut, and ball, which convert rotational motion into linear motion or linear motion into rotational motion. This component uses tribology technology that allows a ball to be placed between the screw shaft and nut and to roll lightly. It converts sliding contact motion on the screw surface into rolling contact motion. Balls need to circulate infinitely, so circulating parts are required.
There are several types of recirculation systems, such as return tube type, end deflector type, end cap type, and piece type, as well as return plate type, and their applications are classified according to size and precision. When using ball screws, a guide rail is required to guide the nut. Guide rails bear vertical loads and moment loads other than the axial load applied to the nut.
The threaded shaft is made to move with high accuracy by combining the length of the lead, which is the amount of movement per nut revolution, with the number of threaded strips. The ball is pressurized to eliminate any nut backlash, and high positioning accuracy can be obtained without uneven rotation of the screw shaft or nut.
Other Information on Ball Screws
1. Characteristics of Ball Screws
Ball screws are capable of converting the rotational motion of a machine into a linear motion. Conversely, it can also convert linear motion into rotational motion. The torque to drive the screw shaft rotation can be reduced to 1/3 or less compared to that of an ordinary screw. Therefore, the motor that drives the Ball Screw can be made smaller and lighter.
The difference between starting frictional torque and kinetic frictional torque is small, and a stick-slip phenomenon can be avoided, enabling high-precision machine control. Nuts can be preloaded by using two nuts or by using balls with a larger diameter in advance. Backlash is eliminated and rigidity is increased, resulting in better controllability.
The wear life and rolling fatigue life of ball screws can be predicted by calculation, thus increasing operational reliability. The coefficient of friction at the contact surface between the screw and nut is about 0.1 to 0.2 for a sliding screw, whereas it is 0.002 to 0.004 for a Ball Screw. Therefore, the transmission efficiency is high and over 90%.
Since dimensions and accuracy are internationally standardized and mass-produced in dedicated factories, they are easy to use and cost-effective. On the other hand, ball screws have the disadvantage of being vulnerable to impact. Since the sliding parts are in point contact, they are prone to leave dents and other marks when subjected to impact. In addition, foreign matter entering the sliding parts may cause malfunctions or failures. When used as a slide shaft of a machine tool, it is necessary to cover it with a cover, etc., to prevent chips from getting into it.
2. Manufacturing Method of Ball Screws
Ball Screws can be classified into "rolling" and "grinding" depending on the method of production.
Rolling Ball Screw
In this method, a round bar is pressed against a tool called a rolling die while rotating to form a threaded groove by plastic deformation. Compared to grinding, the accuracy grade tends to be lower.
Ground Ball Screw
This method uses a machine tool called a thread grinder to form the thread groove by grinding. Since cylindrical grinding is performed after heat treatment, the surface is smoother than that of rolling. This method is used when high-precision machine control is required, such as for slide axes of small machine tools for precision instruments.
List of 36 Ball Screw Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- Germany
- India
- Japan
- Korea
- Taiwan
- United Kingdom
-
-

-
MOOG
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
Moog Inc. was incorporated in 1951 and is headquartered in East Aurora, New York. The company designs manufactures and integrates precision motion and fluid controls and control systems for customers including OEMS in industries such as aerospace, defense, industrial machinery, motorsports, and construction. The company’s product offerings include both systems and components. Examples of systems include actuation systems, naval systems, turreted weapon systems, and space vehicles. Examples of components include manifolds, slip rings, actuators, and servo actuators.
-
-
-
-

-
Wedin International, Inc.
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
Wedin International Inc., established in 1936, is a manufacturer of motion & linear control systems and machine tool drive components headquartered in Cadillac, Michigan. The company’s product portfolio includes power supplies, gears & splines, Acme screws & nuts, ball screws, and reversing screw & housing assemblies. It's also a ball screw repair service provider offering ball screw regrinding, emergency repair and reconditioning services. The ball screw and nut products are used in the mining, machine tool, oceanography, medical, and oil field & gas industries.
-
-
-
-

-
Rockford Ball Screw Co.
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
Rockford Ball Screw, a company founded in 1973, based in Rockford, Illinois, is a manufacturer and supplier of ball screws. The company offers flagship products which include ball screws and guide rail products with various configurations and custom specifications. The products are desigend with the latest advanced technology in ball-screw and linear guide rail technology. These products are used in multiple commercial and industrial machinery applications. The company also offers services and repairs with unique linear motion techniques.
-
-
-
-

-
NOOK INDUSTRIES, INC
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
NOOK INDUSTRIES, INC, established in 1969 in the United States, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in precision linear motion systems and components. The company offers a comprehensive range of products, including ball screws, linear actuators, and linear guides. NOOK INDUSTRIES, INC has been a pioneer in the field of linear motion technology. Their products find applications in industries like automation, robotics, and manufacturing, enabling precise and efficient motion control solutions. NOOK INDUSTRIES, INC's unique worth lies in their devotion to providing customizable linear motion solutions, such as ball screws that enhance CNC equipment and automation systems.
-
-
-
-

-
LinTech
Ball Screw Assemblies
Manufacturer Overview
LinTech was founded in 1971 and is headquartered in Monrovia, California. The company is a manufacturer that also designs and engineers positioning components and systems for use in a wide range of linear motion control applications for customers in aerospace, food processing, machine tool, semiconductor, and other markets. The company offers a range of products from linear ball bushings & shafts to ball screw assemblies, rotary stages, and more. The company offers extensive technical support and customer service including assistance with CAD files.
-
-
-
-

-
Joyce/Dayton Corp.
Ball Screws and Nuts | Joyce
Company Overview
Joyce/Dayton Corp. was established in 1873 and is headquartered in Kettering, Ohio. The ISO 9001:2015 certified company is a manufacturer of screw jacks, actuators, and lifting equipment to customers in aluminum smelting, marine, solar energy, and nuclear industries across North America through external distributors. The company’s product segments include screw jacks, actuators, cylinders, solar products, and others. Solar products include solar tracking jacks and actuators as well as custom solar trackers designed to enhance the efficiency of standard solar panels.
-
-
-
-

-
TPA Motion, LLC
Ball Screws
Company Overview
TPA Motion was started in 2002 and based in Fort Mill, South Carolina. TPA Motion is now part of the Acuvi AB group of companies. Acuvi is a Swedish Technology company focusing on developing compact drive solutions for life science, medical, and industrial applications. TPA Motion is an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer and distributor of motion and precision assemblies. TPA Motion has 2 main product segments, component products and engineered OEM solutions. Component products include rails, actuators, bearings, guides, and assemblies. Engineered OEM solutions include microplate robots, curved rail systems, special telescopic slides, and high temperature systems.
-
-
-
-

-
Isotech, Inc.
Ball Screws
Company Overview
Isotech was founded in 182 and is headquartered in Hatfield, Pennsylvania. Isotech is a manufacturer’s representative and distributor of proprietary mechanical and electromechanical products to the industrial, medical, and military OEM and in-plant markets. Some of Isotech’s products include linear slide assemblies & rail sets, shock/vibration mounts & pads, linear bushings & shafting, telescoping lifting columns, positioning stages, air bearings, gas springs/air cylinders, motorized positioning tables, laser marking cutting systems, foamed aluminum/metal/composites, stamped metal, noise control products, and belt driven actuators.
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
MORIMOTO SEIMITSU SHAFT Co., Ltd
Ball screw
Manufacturer Overview
MORIMOTO SEIMITSU SHAFT Co., Ltd, established in 1971 and headquartered in Osaka, Japan, is a manufacturer of shafts used for producing mechatronics products. The company's range varies from general-purpose shafts and slide shafts to ball screws, miniature slide screws and support units. These products are used for manufacturing high performance parts such as industrial electronic equipment and semiconductors, industrial-use robots, food machinery and cars. The company has obtained ISO certifications for quality management and environmental management systems.
-
-
-
-

-
NSK Ltd.
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
NSK Ltd., based in Japan, is a manufacturer of precision bearings and motion control solutions which started its journey in 1916. The company has established itself as a major supplier for multiple industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, and aerospace. Their extensive product portfolio encompasses ball bearings, roller bearings, and linear motion components. Their Motion & Control products and technologies support the motion that brings comfort and convenience in cars, planes, wind turbines, satellites, and almost anything with moving parts.
-
-
-
-

-
TSUBAKI NAKASHIMA CO., LTD.
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
TSUBAKI NAKASHIMA CO., LTD., established in 1936 and based in Katsuragi, Nara, Japan, is a manufacturer of precision balls, rollers, and mechanical parts. The company offers precision ceramic balls, ball screws, large-scale blowers, and customizes stampings. It also makes customized products for medical, metrology, general industrial, semiconductor, and electric injection industries. The company also has manufacturing facilities in the United States, Slovakia, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Bosnia. The manufacturing facilities are Class 8 compliant, FDA registered, and ISO 13485:2016 certified.
-
-
-
-

-
KURODA JENATEC
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
KURODA JENATEC, founded in1925, is a manufacturer and supplier of rotary and linear motion products with manufacturing facilities in the USA, Germany, and Japan. The company started out as a gauge manufacturer but has since expanded into manufacturing grinding machines, machining tools, polishing machines, ball screws, and precision measuring systems for customers in the semiconductor, processing machine, electric, electronic, and automobile industries. This ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 50001 certified.company offers both small and large ultra-precise ball screws for automotive, medical, and machining manufacturers, among other product applications.
-
-
-
-

-
Steinmeyer
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
August Steinmeyer GmbH & Co. KG, established in 1920 by August Steinmeyer and headquartered in Albstadt, Germany is a manufacturer of high-precision ball screws. Its production line is segmented into precision lead screws, ultra-thrust ball screws, rotating nuts, cooled ball screws, and differential roller screws. The company also offers ball screws for aerospace applications including flap actuators, braking system actuators, and electromechanical actuators such as door and air-conditioning actuators. The company serves various industry sectors including machine tools, robotics & handling systems, renewable energies, semiconductor fabrication, and heavy machine tools.
-
-
-
-

-
NTN Corporation
BALL SCREWS
Manufacturer Overview
NTN Corporation established in 1918, is a precision machinery manufacturer that researches, develops, and sells bearings and driveshafts (CVJs) based in Japan. Their main products, bearings are essential and precision components that support rotation of machinery. They are used in different types of machinery including automobiles, wind turbines, rolling stocks, and others to support the lives of people around the world. The group has 212 bases in 34 countries around the world (118 sales bases, 72 manufacturing bases, 15 R&D bases, and 7 other bases as of the end of March 2023).
-
-
-
-

-
GMT Global Inc.
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
GMT Global Inc. was founded in Taiwan in 1994. GMT initially started as a manufacturer and seller of precision mold components. In 2008, GMT expanded to optimize manufacturing procedures and improve machining technologies, so they developed automation components. The products offered by GMT are Ball Screws and Supports, Feeding Screws, Couplings, Slide Tables, Cross Roller Bearings, Automation, and Precision/Alignment Stages, Optical and Linear Motion Components, Motors, and Drives. These products are used in semiconductors and in the smartphone industry. GMT Global is CE and ISO 9001-2015 Certified.
-
-
-
-

-
HIWIN GmbH
Ballscrew
Manufacturer Overview
HIWIN GmbH, established in 1974, is based in Offenburg, Germany, and is a manufacturer and supplier of motion control products and systems. The company's main product portfolio includes linear guideways, ball screws, linear motors, and linear actuators. These precision components and systems are used in various industries, including machine tools, automation, and semiconductor manufacturing. HIWIN's performance motion control solutions enable smooth and accurate linear motion, enhancing the efficiency and productivity of industrial processes. With a great ability on research and development, HIWIN,s aims to provide cutting-edge solutions to meet the dynamic needs of the global market.
-
-
-
-

-
Kuroda Precision Industries Ltd.
Ball screw
Manufacturer Overview
KURODA PRECISION INDUSTRIES LTD., founded in 1925, is a Japanese manufacturer headquartered in Saiwai-ku, Kawasaki, specializing in three business domains, namely motion control system, press tool and die system, as well as machine tool and measurement system. Within the motion control system domain, the company offers ball screws, ball screw actuators, precision ground ball screws, and lubrication units. In the press tools and die system domain, it provides laminated precision press tools and precision metal press products. Additionally, in the machine tool and measurement system domain, the company offers grinding, polishing, special grinding, and surface grinding machines, alongside surface configuration systems.
-
-
-
-

-
Dr. Erich TRETTER GmbH + Co.
Kugelgewindetriebe
Manufacturer Overview
Dr. TRETTER was started in 1970 by Dr. Tretter in Rechberghausen, Germany as a manufacturer and supplier of linear technology products using materials such as stainless steel and Hastelloy. These products include tolerance sleeves, ball casters, and linear guides including wave guides, ball bushings, lead screws, and rail guides used in pumps, electric motors, and as construction elements for conveyor systems, feeds, presses or assembly stations. The company also has a facility in Schaffhausen, Switzerland.
-
-
-
-

-
Takeuchi Precision Works Co.,Ltd.
Ball Screw
Manufacturer Overview
Takeuchi Precision Works Co., Ltd, established in 1964, is a manufacturer of machine element components, including ball bushings, feed screws, linear guides, ball screws, and linear shafts, headquartered in Fukushima, Japan. The company offers standard, round, and square-shaped ball splines in long, flange, flange double, standard double, and flange long types. Its ball bushings are available in housing, self-aligning flange, flange, and straight shape standard types with a single-length bearing or high-load capacity double-length bearing. TSK has achieved ISO 9001 & ISO 14001 certifications allowing its products to be used in control equipment, including CNC machine tools, medical equipment, and industrial robots.
-
-
-
-

-
THK U.K.
Ball screw
Manufacturer Overview
THK Co., Ltd. was incorporated in 1946 and is headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. THK is a manufacturer and supplier of machine components such as linear motion components for customers globally. THK’s products are used in many industries including electronics, aerospace, industrial robots, and precision instruments. THK’s primary product categories are Linear Motion, Feed Screw, Rotation, Custom Assemblies, and Seismic Isolation. Linear Motion products assist in linear motion and transportation. They include linear motion actuators, guides, and rollers. Feed screws include ball screws, screw nuts, and change nuts. Seismic Isolation includes both large systems and small guides.
-
-
-
-

-
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Ball screw
Manufacturer Overview
DAI-ICHI Sokuhan Works Co, founded in 1944 is based in Ojiya, Japan, and is a manufacturer and supplier of machinery tool accessories. Their product portfolio includes measuring instruments, air micrometers, electronic micrometers, gauges, precision machine parts, spindle units, and kneading dispersibility measurement. The products are manufactured under superior technology and precision with quality control. The products are used in multiple industries which include aircraft, trains, automobiles, and other modes of transportation.
-
-
-
-

-
NIPPON BEARING CO., LTD.
Slide screw
Manufacturer Overview
Nippon Bearing was established in 1939 and is headquartered in Ojiya-City, Niigata, Japan as a manufacturer of linear motion products. The company is known for producing linear bearings, and some of its other products include Linear and Slide Guides, Ball Splines, Cross Roller Guides, and Linear Bushings. These items have extensive use in industries that work with optical equipment and high-precision measurements as the products have motion accuracy as well as rigidity. The company also provides parts and tools for general machinery as well.
-
-
-
-

-
igus GmbH
Lead screw technology
Manufacturer Overview
igus GmbH, established in 1964 and based in Cologne, Germany, is a manufacturer and distributor of technical products made using polymers for movement. Its products include injection molding frames, motor control systems, and plain bearings, and it has over 240,000 products in over 1,000,000 variations. It serves 188,000 companies from over 80 countries worldwide in 50 different industries, including packaging, automotive, and renewable energy. The company is ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 50001 certified, and in 2023, it recorded €1.115 billion in sales. Since 2021, the company has purchased 380 new injection-molding machines and has replaced 275 old ones.
-
-
-
-

-
NSK Americas, Inc.
Ball Screws
Manufacturer Overview
NSK Americas, Inc., founded in 1973 with headquarters in the USA and facilities worldwide, is a global manufacturer of bearings, automotive components, and precision machinery. The company's product line includes numerous bearings, direct-drive motors, cartesian robots, automotive wheel hub units, and steering systems. NSK's products are used in various manufacturing industries for optimized production and automation, including automotive, chemical processing, construction, steel, and consumer product manufacturing markets. An example is the company's Monocarriers MCH Series, which features high-rigidity rails used for cantilever beams and other factory automation applications.
-
-
-
-

-
Thomson
Ball screw
Manufacturer Overview
Thomson Industries, headquartered in the United States, is a global manufacturer of motion control solutions since 1936. They have been one of the forerunners in the motion technology industry with products supplying optimized motion solutions to a broad range of industries and application areas including factory automation, medical, aerospace and defense, and more. The company merged with Regal Rexnord in 2023 as a key business in the automation and specialty platform. As part of Regal Rexnord, they are even more equipped to provide complete system solutions through their control, drive, power transmission and precision linear motion technologies.
-
-
-
-

-
SBC Linear Co., Ltd
BALL SCREW
Company Overview
SBC Linear, established in 1982 in South Korea, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision linear motion systems and components. The company’s product range includes linear guides, ball screws, linear tables, and linear motors, catering to industries such as automation, robotics, semiconductor, and medical equipment. SBC Linear's passion for quality and creativity is demonstrated through its advanced solutions that enable precise and smooth linear motion in various applications. With decades of experience and an emphasis on customer satisfaction, SBC Linear continues to provide cutting-edge solutions for the evolving needs of industries worldwide.
-
-
-
-

-
NIPPON THOMPSON CO., LTD.
Ball Screw
Company Overview
Nippon Thompson Co., Ltd. - IKO is based in Japan and was established in 1950 as a manufacturer of bearings. The company designs Linear Motion Rolling guides and Mechatronics series and they were the first to produce Needle Roller Bearings. These products have vast applications in various industries as they are used in Electronics-related Devices and Equipment like semiconductors and for precision devices that are used in laboratory measuring instruments and medical equipment. Textile, printing, construction, transportation, and robotics are also on the list of industries that benefit from IKO products.
-
-
-
-

-
VV Mujumdar & Associates
Ball Screws
Company Overview
VV Mujumdar & Associates, established in 2000 and headquartered in Pune, India, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in machine-tool accessories like flexible couplings, precision locknuts, clamping sleeves, etc. The company's product line includes essential components such as lock nuts, ball screws, lead screws, rolled ball screws, and more. These products cater to various industries, including automobiles, aerospace, motors, energy, and medical equipment. It has served clients such as Mahindra, LMW, Bajaj, and Eicher, among others.
-
-
-
-

-
NSK Europe Ltd.
Ball Screws
Company Overview
NSK Europe Ltd., situated in Maidenhead, Berkshire, England, is a manufacturer and distributor of a range of mechanical components. Its offered components include motion control products, and automotive components such as wheel bearings, engine belt drive parts, and mounting components. These products are used in various applications such as wind turbines, machine tools, production lines, and vehicles. The company holds several certifications, including ISO 9001:2015 across all its European sites and IATF 16949:2016 for its automotive operations.
-
-
-
-

-
KSS Co., Ltd.
Ball screw / Lead screw
Company Overview
KSS Co., Ltd., founded in 1978 in South Korea, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision ball screws and linear motion components. The company’s product range includes a wide range of ball screws, linear guides, and actuators, catering to industries such as automation, machine tools, and electronics manufacturing. KSS aims to deliver quality and efficient motion solutions that enhance precision and effectiveness in various applications. Courtesy of its continuous creativity and customer satisfaction, KSS enhances the advancement of industries by providing advanced ball screws and linear motion technology.
-
-
-
-

-
Dynatect Manufacturing, Inc.
Ball Screws
Company Overview
Dynatect Manufacturing, Inc. was founded in 1945 and is headquartered in New Berlin, Wisconsin. As a provider of custom motion and protection solutions, they cater to diverse industries, including manufacturing, automation, and medical. Its cutting-edge product range encompasses bellows, protective covers, and ball screw assemblies, vital for ensuring equipment longevity and operator safety. Dynatect's engineering expertise influenced sector advancements, finding applications from manufacturing facilities to medical equipment, ensuring smooth operations and enhanced safety.
-
-
-
-

-
MTAR Technologies Limited
Ball Screws
-
-
-
-

-
Item Industrietechnik GmbH
Ball screw drives
Distributor Overview
Item Industrietechnik GmbH, founded in Germany in 1976, is a supplier of construction solutions and building kit systems for machinery, fixtures, and plants. The company's item product portfolio comprises more than 4,000 high-quality components designed for use in machine bases, work benches, automation solutions, and lean production applications. It has 10 subsidiaries and support centers throughout Germany and also has wholly owned subsidiaries in the USA, China, Italy, Poland, and Switzerland.
-
-
-
-

-
Nadella Inc
Ball Screws
Distributor Overview
Nadella Inc. established in 1930 and based in Milano, Italy, is a supplier of linear guide components and anti-friction bearings. The company also procures and distributes various products, such as telescopic rails, rod ends, spherical plain bearings, ball joints, and precision ball screws. These components are used in agricultural technology, automotive industry, construction machines, and special-purpose packaging machines. It has 8 production facilities and operates in 14 different locations. The company holds ISO 9001-2000 and ISO 14001-2005 and was acquired by ICG in 2018.
-
-
-
-

-
Accelerated Parts
Ball Screws
Distributor Overview
Accelerated Parts is a supplier of fasteners, motion control components, robotics, and tools, established in 2003. They offer a wide selection of fasteners, including bolts, nuts, and screws. In addition, they provide motion control components such as actuators, ball screws, ball splines, and bearings. Furthermore, Accelerated Parts offers a comprehensive range of robotic parts, including end-effector kits, sensors, gearboxes, tool changers, and wheels. Their products support the performance, functionality, and efficiency of various applications in industries ranging from manufacturing and automation to robotics.
-
-
Ball Screw Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of July 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Joyce/Dayton Corp. |
9.3%
|
| 2 | Isotech, Inc. |
5.7%
|
| 3 | GMT Global Inc. |
5.3%
|
| 4 | Rockford Ball Screw Co. |
5.0%
|
| 5 | HIWIN GmbH |
4.5%
|
| 6 | LinTech |
4.4%
|
| 7 | MOOG |
4.2%
|
| 8 | DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO. |
3.9%
|
| 9 | Takeuchi Precision Works Co.,Ltd. |
3.8%
|
| 10 | Wedin International, Inc. |
3.7%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the ball screw page as of July 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
- NSK Ltd.: 30,577
- NSK Americas, Inc.: 30,577
- NTN Corporation: 23,027
Newly Established Company
- VV Mujumdar & Associates: 2000 (24 years ago)
- MTAR Technologies Limited: 1999 (25 years ago)
- HIWIN GmbH: 1993 (31 years ago)
Company with a History
- Joyce/Dayton Corp.: 1873 (151 years ago)
- NSK Ltd.: 1916 (108 years ago)
- NSK Europe Ltd.: 1916 (108 years ago)
Ball Screw Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
- MOOG
- Wedin International, Inc.
- Rockford Ball Screw Co.
- NOOK INDUSTRIES, INC
- LinTech
- Joyce/Dayton Corp.
- TPA Motion, LLC
- Isotech, Inc.
Global Distribution of Ball Screw Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 Japan
Japan
|
13 | 46.4% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
8 | 28.6% |
 Germany
Germany
|
3 | 10.7% |
 Taiwan
Taiwan
|
1 | 3.6% |
| Korea | 1 | 3.6% |
 India
India
|
1 | 3.6% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 3.6% |
List of Ball Screw Products
401 products are listed.
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Ball screw (axis end finished product)
70+ people viewing
Since it has already been processed into a common and easy -to -use axial terminal shape, it can be used as a device as it is, and the design man -...
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Ball screw (not processed axis)
20+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 hours ago
Various size of C3 class unprocessed products are in stock, so the axial end shape of the customer specification can be used in a short time. ・ Ac...
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Ball screw (standard axis terminal processed) C5 series
20+ people viewing
We achieve short delivery time and cost performance to special axial end processing, and we have a wide variety of inventory size. Even if the accu...
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Ball screw (unprocessed in the axis) C7 series
10+ people viewing
We achieve short delivery time and cost performance to special axial end processing, and we have a wide variety of inventory size. Even if the accu...
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Ball screw (axis terminal unprocessed product) C3 stainless steel series
20+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
Because it is made of stainless steel, it can be used in a wide range of fields such as clean room, vacuum environment, food machine, and medical i...
Ozak Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abundant lineup lead screw ball screw KBSC series
20+ people viewing
New system. Ordering items necessary for motor drive at once ■ Characteristics ・ Accuracy grade: C7 ・ Axial diameter: φ8 ~ φ32 ・ Reed: 1.5 to 2...
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Lubricating unit OS unit built -in ball screw smart series
80+ people viewing
Contribute to the long -term maintenance free of the device The industry's first (patent registration already) Incorporated a lubrication unit in t...
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Lubricating oil supply device OS with a unit with a unit
20+ people viewing
Reduction of environmental impact due to significant reduction in lubricating oil supply. Realized long -term maintenance -free. ■ Characteristics...
Ozak Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abundant lineup lead screw ball screw RBSDA (large lead) series
20+ people viewing
New system. Ordering items necessary for motor drive at once ■ Characteristics ・ Accuracy grade: C10 ・ Axial diameter: φ10 ~ φ40 ・ Reed: 10 ~ 4...
Ozak Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abundant lineup lead screw ball screw BSD-A (large lead) series
20+ people viewing
New system. Ordering items necessary for motor drive at once ■ Characteristics ・ Accuracy grade: C10 ・ Axial diameter: φ16 ~ φ40 ・ Reed: 16-40 ...
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Super miniature ball screw
50+ people viewing
■ Characteristics ・ Precision ball screws are the world's smallest axial diameter of φ2mm. ・ According to the accuracy grade C3 class, high -precis...
DAI-ICHI SOKUHAN WORKS CO.
Inside return type ball screw bsir compact type
20+ people viewing
High -speed power inside return type ball screw overflowing from inside ROHS Directive products ■ Characteristics ・ Realizes further faster and qu...
Ozak Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abundant lineup lead screw ball screw RBSMA (medium lead) series
20+ people viewing
New system. Ordering items necessary for motor drive at once ■ Characteristics ・ Accuracy grade: C10 ・ Axial diameter: φ8 ~ φ40 ・ Reed: 2-10 ・...
Ozak Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abundant lineup lead screw ball screw BSM (medium lead) series
20+ people viewing
New system. Ordering items necessary for motor drive at once ■ Characteristics ・ Accuracy grade: C10 ・ Axial diameter: φ10 ~ φ40 ・ Reed: 4, 5, ...
Ozak Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abundant lineup lead screw ball screw KBS series
30+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
New system. Ordering items necessary for motor drive at once ■ Characteristics ・ Accuracy grade: C5 ・ Axial diameter: φ8 ~ φ32.8 ・ Reed: 1.5 ~ ...
Ozak Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abundant lineup lead screw ball screws BSW-A (super large lead) series
30+ people viewing
Last viewed: 7 hours ago
New system. Ordering items necessary for motor drive at once ■ Characteristics ・ Accuracy grade: C10 ・ Axial diameter: φ16 ~ φ32 ・ Reed: 32 ~ 6...
Ozak Seiko Co., Ltd.
Abundant lineup lead screw ball screws BSS (small lead) series
20+ people viewing
New system. Ordering items necessary for motor drive at once ■ Characteristics ・ Accuracy grade: C7, C10 ・ Axial diameter: φ4 ~ φ16 ・ Reed: 1, ...














