











59 Torque Sensor Manufacturers in 2024
This section provides an overview for torque sensors as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 59 torque sensor manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked torque sensor companies as of July, 2024: 1.Transducer Techniques, LLC, 2.Micro Quality Calibration, Inc., 3.Ono Sokki.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Torque Sensors
What Is a Torque Sensor?
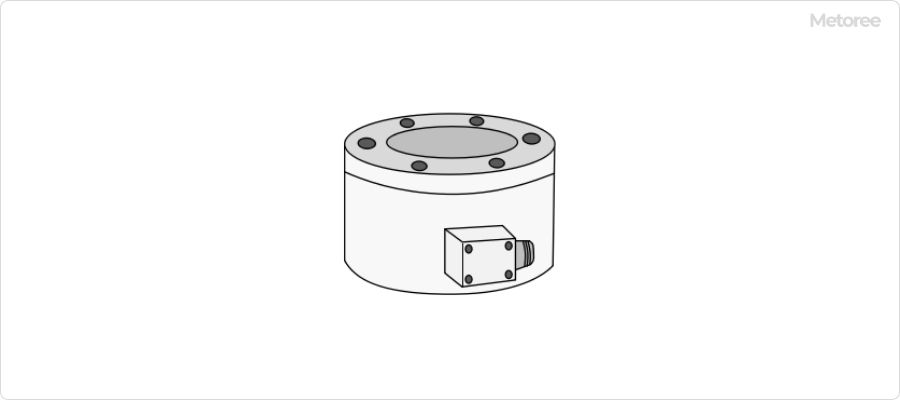
Figure 1. Appearance of a Torque Sensor
A torque sensor is a device that measures torque, the force that causes a shaft to rotate, as illustrated in Figure 1.
It converts the slight twist of a shaft under torque into a measurable output, displaying the torque value. Torque sensors are crucial in various scenarios requiring torque measurement, including torque management in production lines and evaluating the performance of industrial machinery.
While it may also be referred to as a torque gauge or torque meter, there are no strict naming conventions. This article will use "torque sensor" consistently regardless of application.
- Torque Sensor
A device used in electric bicycles and robots to control motors or robots based on detected torque. - Torque Gauge
A device for measuring the tightening torque with tools like screwdrivers and instantly checking the torque value on a display. - Torque Meter
A device for assessing motor torque in motor testing setups.
Uses of Torque Sensors
Torque sensors are commonly used in electrically powered bicycles, where they detect the pedal force (torque) applied by a cyclist. The motor then provides the necessary assistance based on this torque, easing the pedaling effort.
In industrial settings, torque sensors are vital in quality control and research testing.
1. Quality Control
Torque sensors are utilized mainly in:
- Spot Checks
Examining how tightly container caps are sealed during production. - Periodic Inspections
Ensuring electric screwdrivers on the production line operate within expected parameters before work commences.
2. Test and Research
In testing and research, torque sensors are mainly employed in:
- Strength Measurement
Assessing test materials and components for torsional strength. - Motor Performance Evaluation
Determining motor performance under various loads. - Rotational Torque Measurement of Machinery
Measuring the torque in machinery, such as rotary printing press rollers, to find optimal operating conditions.
Principle of Torque Sensors
The operation of torque sensors involves the following steps:
- A torque is applied to the shaft.
- This torque induces torsion/strain on the shaft.
- The shaft's torsion/strain is measured.
- The torque on the shaft is calculated from this measurement.
The measured torsion/strain is converted into an electrical signal, often amplified by an amplifier for easy interpretation and displayed by an A/D converter. Some sensors come with a display for immediate torque reading.
Types of Torque Sensors
Various methods exist for measuring shaft torsion and strain, with the following four being prevalent in current torque sensors:
1. Strain Gauge Type Torque Sensor
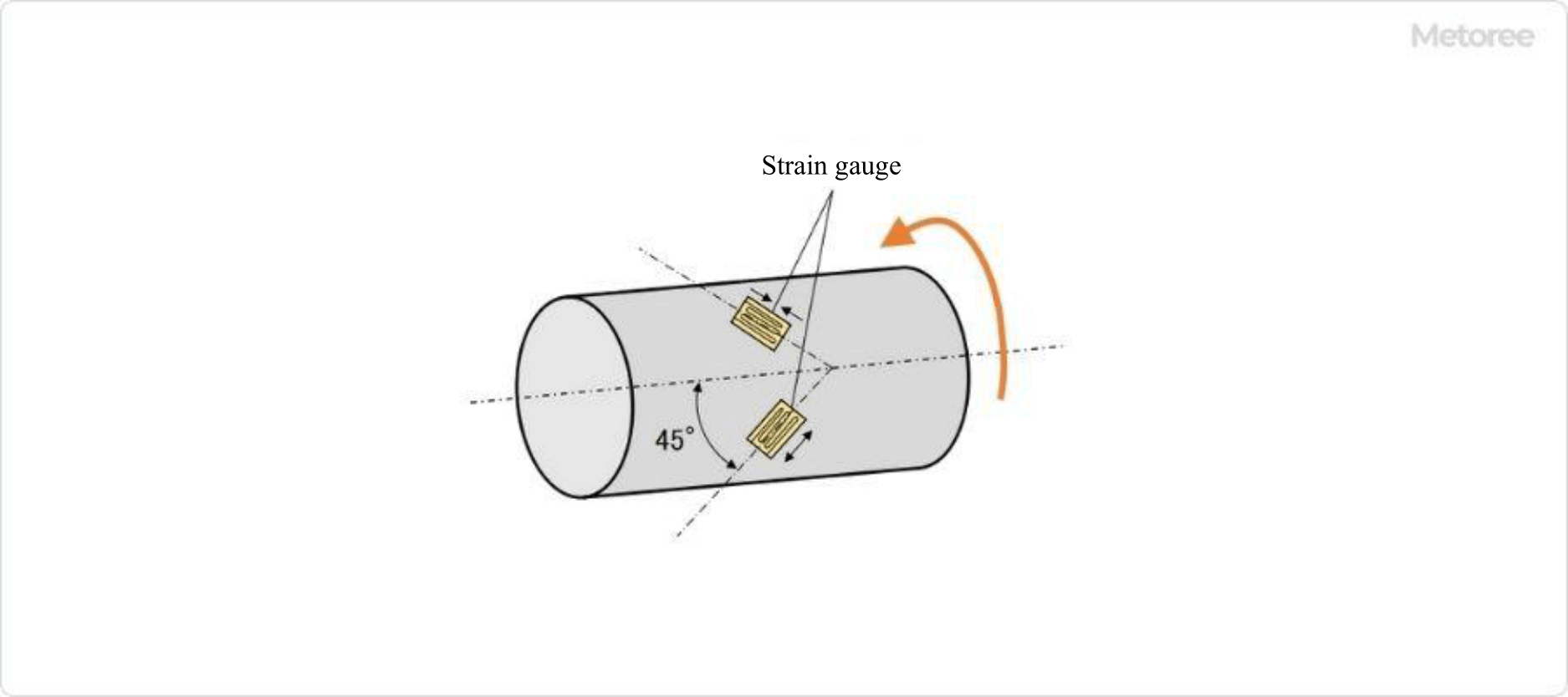
Figure 2. Axis of Strain Gauge Type Torque Sensor
This method employs strain gauges to measure shaft strain due to electrical resistance changes during expansion and contraction. As depicted in Figure 2, tensile and compressive stresses occur at ±45° angles when torque is applied, which is measured by strain gauges.
2. Capacitive Torque Sensor
This method gauges shaft strain through capacitance changes between two electrodes on the shaft, affected by its warping.
Due to its simpler structure and shorter shaft requirement, it's widely used in robotic torque sensors.
3. Magnetostrictive Torque Sensor
Here, shaft strain is measured by detecting inductance changes in a coil due to the inverse magnetostrictive effect when torque is applied, altering the magnetic permeability.
Advantages include non-contact measurement capabilities, making it suitable for rotating shafts without compromising shaft integrity.
4. Optical Torque Sensor
An optical sensor measures shaft strain by detecting changes in light amount due to emitter and receiver displacement under torsion or distortion.
Other Information on Torque Sensors
Products With Built-in Torque Sensor
Advancements in technology have led to the miniaturization of torque sensors, integrating them into industrial products. Here are examples:
1. Motor With Built-in Torque Sensor
Integrates a motor, reduction gear, and torque sensor for compactness and accurate torque measurement for smoother operation and safety enhancement through human contact detection.
2. Torque Sensor for Robots
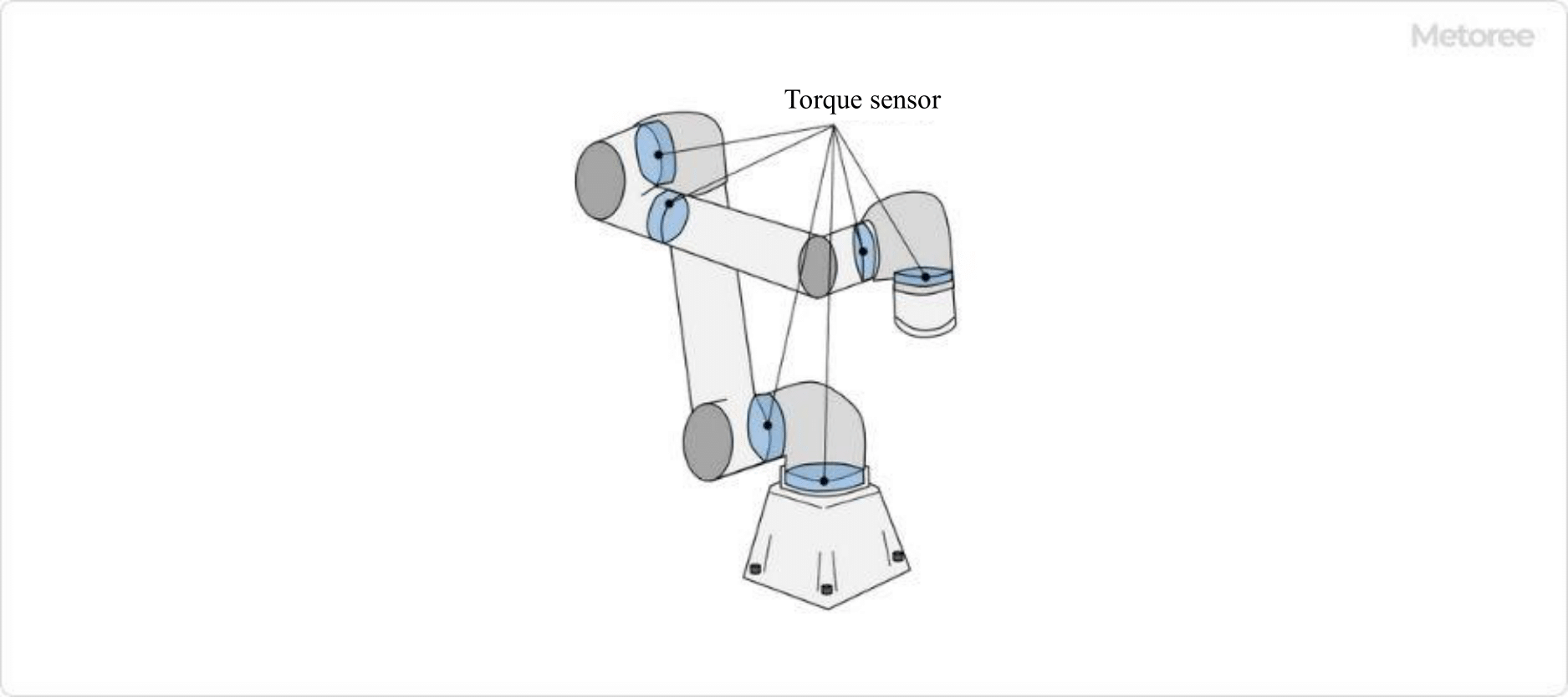
Figure 3. Torque Sensor Built Into the Cooperative Robot
Articulated robots with integrated torque sensors, especially in cooperative robots, enable precise control of force and detection of human or obstacle contact.
List of 59 Torque Sensor Manufacturers
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
- Default
- Company Size: largest first
- Year Founded: oldest first
- Year Founded: earliest first
Sort by Area
- United States of America
- Belgium
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom
-
-

-
S. Himmelstein and Company
TORQUE TRANSMITTERS
Manufacturer Overview
S. Himmelstein and Company (SHC) is an American manufacturer of torque sensors and signal conditioners that was established in 1960 in Hoffman Estates, Illinois. The company produces various torque measurement and calibration products including reaction and rotating torque sensors, as well as transfer standards for traceable calibration of torque sensors or instruments, and signal conditioners for amplifying, filtering, or converting signals from portfolio products. SHC products are used by their clients in the aerospace, energy production, automotive, and industrial manufacturing sectors.
-
-
-
-

-
Honeywell International Inc
torque sensors
Manufacturer Overview
Honeywell International Inc. was founded in 1885 and headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. Honeywell is a diversified technology and manufacturing company to global customers in many industries such as aerospace, building technologies, performance materials, manufacturing, and safety. Honeywell produces hardware and software solutions for each industry it serves. In building technologies, Honeywell designs access controls, electrical and wiring, fire life safety, and employee training services. In aerospace, Honeywell designs cockpit systems and displays, engines, cabin management and cleaning, and health and usage monitoring.
-
-
-
-

-
Mountz Torque
Torque Sensor
Manufacturer Overview
Mountz Torque, founded in San Jose, CA, in 1965 is a manufacturer of torque products such as Robotic Screwdrivers, Torque Calibration, and Measuring Torque. The company's product portfolio includes Preset Torque Limiters, Torque Sensors, Run Down Adapters, Calibration Equipment and Torque analyzers and Sensor Accessories. Their products are used in the energy sector for wind turbine assembly and maintenance, critical aerospace components and systems and automotive assembly lines and maintenance applications. The company serves industries such as Oil and Gas, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Construction, and Power Generation.
-
-
-
-

-
Omega Engineering, Inc.
Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
OMEGA Engineering Inc., founded in Norwalk, CT, in 1962 is a manufacturer of products used to measure temperature and humidity, flow and level, and pressure. The company's product portfolio includes thermocouple probes and assemblies, pressure gauges and switches, and air velocity measurement systems, wireless systems and portable optic sensors. The company serves markets including Automotive and Electric Vehicles, Renewable Energy and Energy Storage and Electronics and IT Infrastructure. The company also offers customer services that include support, custom research projects and customized services.
-
-
-
-

-
PCB Piezotronics
REACTION TORQUE SENSOR
Manufacturer Overview
PCB Piezotronics, founded in 1967 and headquartered in North Carolina, is a manufacturer of sensors for design engineers and predictive maintenance. They design and manufacture various sensors such as microphones, vibration, pressure, force, and torque sensors. Their products are used for testing, measurement, monitoring, and control requirements in automotive, aerospace, military, and other industries in order to gather accurate data, ensure safety, enable predictive maintenance, and facilitate advancements across multiple industries. PCB Piezotronics is a subsidiary of Amphenol Corporation.
-
-
-
-

-
Interface, Inc.
TORQUE TRANSDUCERS
Manufacturer Overview
Interface, Inc., based in Arizona, and established in 1968, is a manufacturer of load cells and a provider of force measurement solutions. Beside load cells, the company also produces torque transducers, multi-axis sensors, and other instrumentation. These products are great solutions for aerospace, automotive, factory automation, energy, medical, and other industries. Besides offering products, It offers repair services and calibration on load cells and other force measurement devices. The company received the 2019 Manufacturer of the Year and 20 Promising Energy Tech Solutions Providers 2020. It becomes the supplier for Fortune 100 companies such as Boeing, Airbus, NASA, Ford, and others.
-
-
-
-

-
AMTI (Advanced Mechanical Technology, Inc.)
Force Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
AMTI (Advanced Mechanical Technology, Inc.), established in 1976 and based in Watertown, Massachusetts, USA, is a manufacturer and supplier of biomechanics instrumentation. The company's product range includes force plates, instrumented treadmills, force torque sensors, joint simulators, and related accessories. These products are essential in fields such as biomechanics, gait analysis, ergonomics, and orthopedic implant testing. Serving industries like medical equipment manufacturing, orthopedic research, and biomechanics, these products enhance scientific research and advanced engineering. The company's services comprise calibration services, installation assistance, and the development of custom designs.
-
-
-
-
Manufacturer Overview
AIMCO, founded in the United States in 1970, is a manufacturer of pneumatic power tools. The company's product portfolio includes an extensive range of pneumatic hand tools, including impact wrenches, air drills, grinders, sanders, and riveters. It serves industries such as aerospace, agriculture, general industry, manufacturing, and medical devices. The company also provides services including tool selection, troubleshooting, and maintenance to ensure maximum tool longevity and exports to over 33 countries.
-
-
-
-

-
Magtrol Inc
Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
Magtrol Inc, a company founded in 1957 and based in Buffalo, New York, is a manufacturer and supplier of measurement and control products. The company specializes in providing dynamometers, hysteresis brakes, torque transducers, and load cells. These instruments are used in a wide range of industries including automotive, aerospace, energy, and manufacturing. The company’s products are designed to measure torque, force, speed, and power, enabling customers to optimize their processes and ensuring performance. The company also provides a knowledgeable and responsive customer service team, assisting with product inquiries, technical support, and order processing.
-
-
-
-

-
Mark-10 Corporation
Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
Mark-10 Corporation is a designer and manufacturer of force and torque measurement products established in 1979 and based in Copiague, New York, USA. The company offers torque gauges for measuring rotational force, force gauges for tension or compression testing, and compatible software for data collection and analysis. It also offers related accessories for its portfolio products, such as grips and fixtures, motorized test stands, and wire pull testers. The company’s products are mainly used in industrial manufacturing and automation operations.
-
-
-
-

-
SCHUNK
FTD-Nano-17-T SI-16-0.1

Manufacturer Overview
SCHUNK, founded in 1945 and based in Morrisville, USA, is a manufacturer of automation technology. The company provides technologies like gripping, tool holding and automation technology for modern manufacturing and robot systems. It also supplies complete solutions for robot systems as well as for a wide variety of production and automation processes. The company has received several awards for its technologies, which includes Engelberger Robotics Award in 2010 and Red Dot Award for Product Design in 2021.
-
-
-
-

-
Transducer Techniques, LLC
Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
Transducer Techniques was established in 1979 and is headquartered in Temecula, California. Transducer Techniques designs and manufactures a complete line of load cells, torque sensors, special purpose transducers and related instrumentation that are often used in industries such as process control and factory automation as well as other fields of science and industry. Transducer Techniques product segments include load cells such as button and beam load cells, torque sensors such as reaction and rotary torque sensors, instrumentation with load cell displays and signal condition, accessories, and software.
-
-
-
-

-
ATI Industrial Automation
Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
ATI Industrial Automation is a global engineering-based developer specialising in robotic accessories, robot arm tooling, torque sensing systems, robotic collision chargers, etc. that improve robotic productivity. It was founded in 1989. Many mechanical, electrical, and software engineers work at ATI. All of their products meet the requirement of ISO9001 certifications. Products manufactured at their company are subjected to strict quality assurance and inspection guidelines before they are sent to clients. Their products are widely employed in different markets, including electronics, nuclear, applied research, and aerospace.
-
-
-
-

-
Micro Quality Calibration, Inc.
When Quality & Precision Matter
Manufacturer Overview
Micro Quality Calibration Inc MQC) was founded in 1978 as a technology-oriented calibration, repair, testing, and first article inspection facility for precision measurement test equipment. MCQ follows in strict compliance of ISO-9000 (series 1, 2, 3, and 4) specifications. MCQ offers services in calibration, inspection testing, repair, database management, and analytics. Calibration services are often provided for automotive, electrical components, aerospace, and secure communications, for which MCQ is ISO 17025 accredited.
-
-
-
-

-
OMEGA Engineering inc.
Torque transducer
Manufacturer Overview
OMEGA Engineering was originally begun in 1962 as a manufacturer of thermocouples and has grown to over 100,000 products for measurement and control of temperature, humidity, pressure, strain force, flow, level pH, and conductivity as well as customer service including data acquisition, electric heating, and custom-engineered products. Additionally, OMEGA offers tools to serve as reference for engineers around the world. OMEGA Engineering serves the aerospace, automotive, wireless, sanitary, test & measurement, process control, power monitoring, environmental, and laboratory markets.
-
-
-
-

-
HITEC Sensor Developments
Steering effort sensor
Manufacturer Overview
HITEC Sensor Developments is a manufacturer and supplier of precision measurement and control solutions, established in 1971 and headquartered in Littleton, Massachusetts. The company offers a diverse range of products tailored for precision measurement and control, such as custom load cells designed to measure forces in unique applications, force sensors for accurate force measurement, torque sensors for measuring rotational forces, pressure transducers for monitoring fluid pressures, and specialized instrumentation for data acquisition and analysis. These products find wide application in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and industrial automation.
-
-
-
-

-
Advanced Torque Products LLC
Digital Torque Multiplier
Distributor Overview
Advanced Torque Products LLC, founded in Newington, CT, is a supplier of digital torque multipliers. The company's product portfolio includes Digital Torque Multipliers, Lifting Devices, Angle Verification, Click Wrenches and Ultrasonic boxes. The company also provides services such as calibration, machining, engineering services, repair services and customer and technical support. The company's products are used in markets such as automotive and transportation, telecommunications, industrial automation, healthcare and medical devices, and aerospace and defense.
-
-
-
-

-
DEPRAG SCHULZ GMBH u. CO.
Torque Transducer
Manufacturer Overview
DEPRAG SCHULZ GMBH u. CO. is a German manufacturer of industrial tools that was established in Amberg, Bavaria in 1931. The company’s product portfolio includes air motors and tools such as vane motors, turbine motors, and impact wrenches, as well as handheld and stationary screwdrivers. It also offers automation solutions for industrial facilities, including robotic systems, tool changers, and assembly machines. The company’s products are used primarily by its clients in the automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and energy industries.
-
-
-
-

-
Mecmesin
torque testing
Manufacturer Overview
Mecmesin, established in 1977, is a UK-based manufacturer and supplier specializing in designing force, materials and torque testing solutions for quality control. The company designs and manufactures force and torque testing equipment such as hand-held gauges, software-controlled testers, and torque systems. Their product portfolio also includes custom materials and torque test solutions for specialized applications, from grips and fixtures to fully automated test systems. Operating under ISO 9001 quality standards, Mecmesin serves clients in different industries globally with group headquarters in the United Kingdom and North America, and offices in France, Germany, China and Thailand.
-
-
-
-

-
Aikoh Engineering Co., Ltd.
Torque meter
Manufacturer Overview
Aikoh Engineering Co., Ltd., established in 1976 and based in Osaka, Japan, is a manufacturer and supplier of force testers, interfaces, and system equipment. The company's product portfolio includes the digital force gauge RZE series, force measuring amplifiers, and torque testing machines. These products find applications in various industries, including manufacturing, electronics, and construction. The company is ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certified, with local distributors in various countries including South Korea, India, and the Philippines.
-
-
-
-

-
ETH-messtechnik
Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
ETH Messtechnik, established in 1987 in Gschwend, Germany, is a manufacturer of static or rotating transducers and individual sensors for measurement solutions. The company specializes in providing adaptive measurement technology solutions for various industries. The company's product range includes data loggers, temperature sensors, and pressure transducers. These solutions find diverse applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and research, offering accurate and seamless data acquisition. The main advantages of these products include improved process optimization, enhanced product quality, and streamlined data analysis.
-
-
-
-

-
GTM Testing and Metrology GmbH
Torque Transducers
Manufacturer Overview
GTM Testing and Metrology GmbH, established in 1988 and headquartered in Bickenbach, Germany, is a measurement technology developer and manufacturer. The company's precision components include force transducers, non-rotating torque transducers, and precision multi-axis transducers. It also provides strain-gauge measuring amplifiers for precision measurement data acquisition. The company's machines include mechanical, force, and multi-axis standard machines providing solutions used in material, component, and structure testing, as well as calibration labs for inter-lab tests. It also offers custom design, engineering, production of custom equipment and complex systems, and calibration services for its clients.
-
-
-
-

-
Lorenz Messtechnik GmbH
Reactive Torque Sensors, non-rotating
Manufacturer Overview
Lorenz Messtechnik GmbH, established in 1985 and headquartered in Alfdorf, Germany, is a precise sensor for torque and force measurement manufacturer and supplier. The company's products include non-rotating reaction sensors, tension and compression sensors, and electric motor test rigs. It also supplies sensor interfaces, built-in portable measuring devices, and systems. These products are used in laboratory and industrial testing scenarios. The company also provides customized system solutions and test benches for the acquisition of speed, torque, and force characteristics, and offers proprietary calibrations for all sensors and devices.
-
-
-
-

-
CLA Clinical Laboratory Automation SA
SENSORS
Manufacturer Overview
Clinical Laboratory Automation (CLA) S.A., founded in 1997, is a manufacturer based in Delémont, Switzerland, developing automation solutions for medical laboratories, micro technology and watchmaking applications. As the center of expertise for Mitsubishi robots in Switzerland, the company offers various robotic solutions designed to enhance automated operations. It also develops sample management systems (SMSs) for component handling. The company also offers precision measurement devices for torque and force, height clearance, and precision metrology. It further produces specialized machinery for the watchmaking industry, including automatic rating control stations, manual and automatic winding stations, and demagnetization stations for watch movements.
-
-
-
-

-
Auxitrol Weston
Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
Auxitrol Weston is a manufacturer of sensors for aerospace applications that was established in Bourges, France, in 1888 before its acquisition by TransDigm Group Incorporated in 2019. The company primarily offers speed sensors for testing and simulation scenarios, high-accuracy temperature sensors for performance testing, and pressure sensors for a range of industrial applications. The company is ISO 14001, CAA Part 21, and NADCAP certified. It primarily serves clients in the commercial aerospace, military aerospace, and gas turbine industries.
-
-
-
-

-
BL Autotec,LTD.
BL FORCE TORQUE SENSOR
Manufacturer Overview
BL AUTOTEC, founded in 1987 as a member of the Bando Chemical Co., Ltd. group with headquarters in Japan, is a manufacturer of robotics and automated equipment and components. The company's products include automatic tool changing components for robotics, rotary joints developed for positioners and turntables, couple joints used to connect and disconnect pneumatics and electric signals, and lock-up RCC devices commonly used for mounting tools to robotic arms. BL AUTOTEC also supplies a range of tools that include torque sensors, deburring tools, and finishing tools.
-
-
-
-

-
BCM SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES bv
Torque transducer
Manufacturer Overview
BCM SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES bv, established in 2006 and headquartered in Belgium, is a manufacturer of industrial sensors primarily designed for factory automation and process control. The company has a comprehensive product catalog, including those for differential pressure measurement, pressure measurement, torque measurement, force measurement, and strain measurement. These sensors serve vital functions in diverse applications, including stress analysis, signal strength measurement, monitoring machine and product vibrations, and measuring engine emissions, particularly within the automotive sector.
-
-
-
-

-
burster präzisionsmesstechnik gmbh & co kg
Torque sensor
Manufacturer Overview
Burster Präzisionsmesstechnik GmbH & Co KG is a manufacturer of sensors & precision measurement products established in 1961 and based in Gernsbach, Germany. The company produces a wide range of sensors, calibration equipment, and testing devices. Its products include force and displacement monitoring systems, universal calibrators for in-field QA operations, and potentiometric angle of rotation sensors. The company also offers contract manufacturing, OEM, and product modification services. It chiefly serves clients in the automation, chemical processing, and industrial facility engineering sectors.
-
-
-
-

-
Ono Sokki
Torque detector
Manufacturer Overview
Ono Sokki Co. Ltd., founded in 1954 and based in Yokohama, Japan, is a manufacturer, distributor, and supplier of electronic measuring instruments and control systems. Its products include sound level meters, vibration meters, and FFT analyzers, utilized in research and development, quality control, and by production line engineers, particularly in the automotive industry. The company was the first to be designated by the government as a producer of sound level meters in Japan and also obtained ISO 14001 certification in 1997.
-
-
-
-

Manufacturer Overview
Marposs S.p.A. is headquartered in Bentivoglio, Italy. The company serves industries such asa aerospace, semiconductors, machine tooling, and biomedical as a manufacturer and as a service provider. The company’s products vary by industry but include tools for gauging, profiling, and monitoring, as well as data management systems and machines for testing and automation. The company’s services include after sales service, customer training, original spare parts, retrofit and upgrade of existing machinery, and project management consulting services.
-
-
-
-

-
Hypersen Technologies Co., Ltd.
Torque Sensor
Manufacturer Overview
Hypersen Technologies Co. Ltd. is a manufacturer of precision sensors established in 2015 and based in Shenzhen, China. The company produces standard and custom mechanical or optical sensing devices. These include 6-axis force torque sensors, laser cross beam sensors for edge detection or alignment, and 3D solid-state LiDAR for 3D environment scanning or mapping. The company primarily serves clients in the medical device production, industrial automation, and security sectors. Some of its notable clients include Bosch, Foxconn, and Apple.
-
-
-
-

-
Norbar Torque Tools Limited
Torque Tools
Manufacturer Overview
Norbar Torque Tools Limited, established in 1943 and headquartered in Willoughby, Ohio, United States, is a manufacturer and supplier of torque tools and related accessories and equipment. The company's solutions include torque screwdrivers, electronic torque wrenches, and handheld battery tool multipliers. It also offers ultrasonic bolt measurement devices and calibration equipment. These products are used in various applications where nuts and bolts need to be tightened to specific requirements, such as in traditional engine construction. It offers after-sales service and support that includes the supply of spare parts and repairs.
-
-
-
-

-
Ingersoll Rand Power Tools and Lifting
Transducers
Manufacturer Overview
Ingersoll Rand Power Tools and Lifting, founded in 1859 and based in Davidson, North Carolina, USA, is a manufacturer of power tools and lifting equipment. Its product range encompasses bolting, assembly solutions, surface preparation, applied power, and construction tools. Some of its products are nutrunners, torque multipliers, riveting tools, and wrenches. It also offers air starters, air motors, barring motors, and air starters. The company maintains ISO 9001 certifications for its manufacturing facilities and adheres to global standards.
-
-
-
-

-
Sensor Technology Ltd
TORQUE TRANSDUCERS & TORQUE SENSORS
Manufacturer Overview
Sensor Technology Ltd., established in 1976 and headquartered in Oxfordshire, United Kingdom, is a designer, manufacturer, and supplier of torque and load measurement devices and components. The company's products include rotary torque transducers, wireless load cells, and low-capacity torque sensors. Its products are used in end-of-line tests on transmissions and engines or in function tests on rotary switches. Its standard range of products is warranted against manufacturing defects and component failure for two years. The company also provides services such as equipment rentals, calibration, and repair, serving the fire protection and industrial process control sectors.
-
-
-
-

-
SCS Concept
Torque Transducers
Manufacturer Overview
SCS Concept is a manufacturer of quality control and production equipment founded in 2005 and headquartered in Milan, Italy. The company's product list includes various test benches for power tools and wrench testing, digital torque wrenches, torque analyzers, ultrasonic positioning systems, and joint simulators. It also offers software for production management and accessories, such as torque multipliers and reversible ratchets. The company's in-house laboratory is ISO 17025 certified for its additional torque and angle calibration services. Its products chiefly serve clients in the industrial manufacturing, railway, automotive, and aerospace sectors.
-
-
-
-

-
BONGSHIN LOADCELL CO., LTD.
Torque Sensors
Manufacturer Overview
Bongshin Loadcell CO. Ltd, established in 1985 and headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, is a manufacturer of strain gauge-based Load cells, digital indicators, and crane scales. The company's main offerings encompass tension meters, digital indicators, and weighing systems. It offers timely responses to inquiries, aiding clients in making informed business decisions. Exported to 38 countries, including the USA, EU, and Japan, its products bear approvals such as "OIML," "NTEP," and "CE," signifying adherence to international standards. The company emphasizes improving product quality and ensuring competitive pricing through cost-efficient practices.
-
-
-
-

-
Datum Electronics Ltd
Torque Sensors, Meters and Transducers
Manufacturer Overview
Datum Electronics Ltd., established in 1989 and headquartered in Oxfordshire, United Kingdom, is a designer, manufacturer, and supplier of torque and shaft power measurement solutions. The company's products include bolt-on static and rotary torque sensors, torque transducers, and torque meters. These products are used in various applications, including monitoring ship propeller shafts, fuel flow, and measuring and verifying heavy-duty torque for the insertion of helical screw piles. It also produces custom sensors that provide customized and modular solutions. It serves industries that include maritime, oil and gas, and automotive. Its notable clients include General Electric, Caterpillar, and Rolls Royce.
-
-
-
-

-
Applied Measurements Ltd
Torque Sensors & Torque Transducers
Manufacturer Overview
Applied Measurements, a company established in 1991 and based in Aldermaston, West Berkshire, United Kingdom, is a manufacturer and supplier of measuring systems, transducers, and sensors. The product portfolio has pressure sensors, depth sensors, position sensors, LVDTs, and load cells used in industries involved in the production and supply chains making precise measurements and calculations. The ISO 9001-certified company offers various services including calibration, designing, repair, bonding, and custom control of specific products with a 3-annuals warranty.
-
-
-
-

-
Gather Technology Co., Ltd.
Torque sensor
Manufacturer Overview
Gather Technology Co. Ltd, established in 2014 and headquartered in Shaanxi, China, is a manufacturer of load cells, force sensors, and measuring solutions. The company’s products include steel and aluminum load cells, transmitters, and electronic weighing equipment. It provides facilities for strain gauge application, temperature compensation, and testing across various environmental conditions. Its solutions find applications in heavy industries, petrochemicals, and scientific research. The company manufactures products with corrosion resistance, waterproofing, and lightning protection, utilizing laser welding and balancing equipment for precise measurements.
-
-
-
-

-
ME systeme
Torque sensors
Manufacturer Overview
ME systeme was founded in 1995 and is a manufacturer of sensors and measurements electronics based in Hennigsdorf, Brandenburg, Germany. The company manufactures various products such as force sensors, strain gauge, and measuring amplifiers. These products are used in various industries including mechanical engineering, agricultural machinery, and medical technology. Various companies such as Bombardier, Daimler, and Invenio have been part of the company's customer base. The company has obtained certificates of standards such as ISO 9001:2015, CE, and RoHS.
-
-
-
-

-
TE Connectivity
Torque Sensors & Torque Meters
Manufacturer Overview
TE Connectivity Ltd., started in 2007 and headquartered in Schaffhausen, Switzerland, is a designer and manufacturer of sensor and connectivity solutions for harsh conditions. It operates three primary segments, namely transport, industrial, and communication solutions, and its product portfolio includes automotive connectors, fiber optic connectors, analog power meters, RTD sensors, and circuit breakers. It serves customers in approximately 140 countries and several industries, including aerospace, automotive, rail, IoT connectivity, and E-mobility. The company manufactures 192 billion products annually and has invested over 610 million USD in research development and engineering.
-
-
-
-

-
ALTHEN
Torque sensor / transducer
Manufacturer Overview
ALTHEN, established in 1978, headquartered in Kelkheim, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier that specializes in providing precision sensors and measurement solutions. Their product range includes strain gauges, load cells, pressure transducers, and displacement sensors, catering to industries such as aerospace, automotive, renewable energy, and robotics. ALTHEN's sensors enable accurate data collection, testing, and monitoring of various parameters critical to the performance and safety of industrial processes and structures. They maintain ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certifications, ensuring the quality of their products for precise measurements across diverse industrial applications.
-
-
-
-

-
Kistler Instrument Corp.
Torque sensor
Manufacturer Overview
Founded in Switzerland, Kistler serves both public and private customers in the automotive, aerospace, maritime, transportation, medical, semiconductor, energy and life sciences industries. Products include sensors as well as connectivity, signal, and data acquisition devices as well as software solutions. Applications of these solutions include R&D to safety testing, and condition monitoring. Key technologies include dynamic pressure, force, torque and acceleration measurement technologies.
-
-
-
-

-
Hottinger Brüel & Kjær
Torque transducers & torque sensor
Manufacturer Overview
HBK, formerly named HBM, is a global ISO9001 and ISO14001-certified company founded in 1950. It is known for providing the best technology and expertise in test and measurement. With branches in 30 countries, it provides clients with different solutions ranging from sound and vibration to propulsion efficiency and weighing. Examples of product offerings include transducers, amplifiers, sensors, strain gauges, data acquisition systems, etc. Such products are used in different markets, including aerospace, automobiles, telecom audio, and more. Besides supplying products, they also entertain their customers with after-sales services.
-
-
-
-

-
TEST GMBH
STATIC TORQUE TRANSDUCER 411
Company Overview
Test gmbh, founded in 1994 and headquartered in Erkrath, Germany, is a manufacturer and distributor of calibration machines. The company provides electronic handheld dynamometers, friction coefficient testing machines for M3 to M80 fasteners, and ampoule testing machines for the pharmaceutical industry. These products are used in the food, automotive, and electrical industries. The company maintains ISO 9001, 13485, and 17025 certifications. Additionally, it operates a DAkkS calibration laboratory specifically for quantities force and materials testing machines.
-
-
-
-

-
Unipulus
Torque meter
Company Overview
Unipulus is a manufacturer of sensors and measuring instruments that was established in 1977 in Tokyo, Japan. The company specializes in precision equipment for measuring a wide range of factors such as durability, tension, and rotational force. Its products include force gauges that test material quality, load cells that measure compression, and torque meters. The company also offers customization, repair, and calibration services for customers needing additional support. Some of its notable clients include Komatsu, Olympus, and Kyoto University.
-
-
-
-

-
NBC Elettronica Group S.r.l.
Torque transmitter
Company Overview
N.B.C Electronica Srl, established in 1980 in Italy, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial automation and control systems. The company's product portfolio includes programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), remote I/O systems, and field bus communication devices. These advanced technologies find application in sectors like manufacturing, energy, automotive, and beyond. The company's team of seasoned engineers and professionals collaborates closely with clients to provide unique operational needs, and maintains long-term customer relatioships.
-
-
-
-

-
Novatech Measurements Limited
Torque transducer
Company Overview
Novatech Measurements Limited, established in 1972 in the United Kingdom, is a manufacturer and supplier of precision load cells and weighing systems. The company’s product range includes a wide range of load cells, force transducers, and weighing instrumentation, catering to sectors like industrial manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and research. Novatech's ambition to provide quality services is evident in its collaborative approach with clients, offering personalized solutions that address specific measurement challenges. The company also enhances the advancement of precision measurement and weighing systems within various industries.
-
-
-
-

-
SCAIME S.A.S.
Torque sensor
Company Overview
SCAIME S.A.S., founded in 1983 and headquartered in Juvigny, France, is a manufacturer of process weighing, measurement, and control solutions. The company offers comprehensive weighing components and solutions designed for manufacturing scales and the supervision of production processes. Its product line includes solutions for measuring strain, force, torque, and displacement, meeting the demands within the manufacturing sector. Its fiber-optic measurement systems are specifically engineered for monitoring structural integrity in critical environments. Servicing in more than 70 countries, the company collaborates with specialist partners and distributors, and its quality management system is evidenced by ISO 9001:2015 certification.
-
-
-
-

-
KYOWA ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS CO., LTD
Torque transducers
Company Overview
KYOWA ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS CO., LTD., founded in 1949 as Kyowa Radio Laboratory Co., Ltd., is a Japanese manufacturer and distributor based in Chofu, Tokyo, specializing in stress measuring equipment with strain gages. Their product offerings include strain gages, bridge boxes or input adapters, transducers, and related accessories. Additionally, KYOWA operates TAMAYA TECHNICS INC., a subsidiary that manufactures navigation, surveying, and meteorological instruments. KYOWA's stress measuring products find applications in various industries. For example, their measurement instruments are used in riding quality evaluation and safety tests of automobiles and railway roads. These devices are also utilized in construction, civil engineering, and healthcare sectors.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
PMC-STS, Inc.
Torque Transducers
Company Overview
PMC-STS Inc., founded in 1963 and based in Danbury, Connecticut, is a manufacturer of pressure, vacuum, and level sensor instruments for aerospace, motorsports, and water applications, among others. The company also provides customized solutions and products to meet challenging customer requirements. It is the first manufacturer offering flush-mounted transmitters for measuring in-process pulp in wastewater, paper, and other difficult fluid level and pressure measurements. In 2022, the company was acquired by Sensor Technik Sirnach AG to help penetrate the North American market further and benefit from both application and product expertise.
-
-
-
-

-
Desoutter Industrial Tools
TORQUE MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS
-
-
-
-

-
n-gineric gmbh
orque Intelligence
-
-
-
-

-
HS-Technik GmbH
Torque measuring technology
-
-
-
-

-
ASA-RT srl
Contactless measuring of torque
-
-
-
-

-
Montronix, Inc.
Torque sensors
-
-
-
-

-
ANDILOG TECHNOLOGIES
Torque
Company Overview
Andilog Technologies, founded in 1986, is a manufacturer based in Vitrolles, France, producing measuring instruments for force and torque applications. The company’s measuring devices include manual test stands and material testing devices. Other products include test benches, force and torque gauges, and portable force and torque sensor displays. Complementing these products, the company develops data acquisition and analysis software. Various fixtures and accessories are also available, such as peeling fixtures and sliding tables, wire crimp terminals, and self-closing clamps. The company serves multiple industries, including automotive, electricity, and medical.
-
-
Torque Sensor Manufacturer Ranking
*Including some distributors, etc.Ranking as of July 2024
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transducer Techniques, LLC |
6.9%
|
| 2 | Micro Quality Calibration, Inc. |
5.3%
|
| 3 | Ono Sokki |
5.3%
|
| 4 | ATI Industrial Automation |
4.2%
|
| 5 | Hottinger Brüel & Kjær |
4.2%
|
| 6 | Novatech Measurements Limited |
3.8%
|
| 7 | ALTHEN |
3.8%
|
| 8 | Marposs |
3.8%
|
| 9 | Kistler Instrument Corp. |
3.8%
|
| 10 | BCM SENSOR TECHNOLOGIES bv |
3.4%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the torque sensor page as of July 2024. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
- Ono Sokki: 613
- KYOWA ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS CO., LTD: 548
- SCAIME S.A.S.: 95
Newly Established Company
- CLA Clinical Laboratory Automation SA: 1997 (27 years ago)
- GTM Testing and Metrology GmbH: 1988 (36 years ago)
- ANDILOG TECHNOLOGIES: 1986 (38 years ago)
Company with a History
- KERN & SOHN GmbH: 1844 (180 years ago)
- Auxitrol Weston: 1888 (136 years ago)
- ALTHEN: 1947 (77 years ago)
Torque Sensor Manufacturers in United States
*Including some distributors, etc.
- S. Himmelstein and Company
- Honeywell International Inc
- Mountz Torque
- Omega Engineering, Inc.
- PCB Piezotronics
- Interface, Inc.
- AMTI (Advanced Mechanical Technology, Inc.)
- AIMCO
- Magtrol Inc
- Mark-10 Corporation
- SCHUNK
- Transducer Techniques, LLC
- ATI Industrial Automation
- Micro Quality Calibration, Inc.
- OMEGA Engineering inc.
- HITEC Sensor Developments
- Advanced Torque Products LLC
Global Distribution of Torque Sensor Manufacturers by Country
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
17 | 44.7% |
 Germany
Germany
|
7 | 18.4% |
 Japan
Japan
|
5 | 13.2% |
 France
France
|
3 | 7.9% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
2 | 5.3% |
 Italy
Italy
|
2 | 5.3% |
 Switzerland
Switzerland
|
1 | 2.6% |
 Belgium
Belgium
|
1 | 2.6% |
List of Torque Sensor Products
20 products are listed.
Sunk Japan Co., Ltd.
High-precision measurement rigid type 6-axis force/torque sensor FT-AXIA with a freedom of 6 ° axis
80+ people viewing
Power/torque sensor High -precision measurement rigid type 6 -axis force / torque sensor with a degree of freedom of 6 ° axis Advantages and benef...
Sunk Japan Co., Ltd.
High -precision measurement rigid type 6 -axis force/torque sensor FT with a degree of freedom of 6 ° axis
20+ people viewing
Power/torque sensor High -precision measurement rigid type 6 -axis force / torque sensor with a degree of freedom of 6 ° axis Advantages and benef...


