All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for round countersunk screws as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 24 round countersunk screw manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked round countersunk screw companies as of July, 2025: 1.Tayal Screw Products, 2.Suraj Metal Corporation, 3.Kroon B.V..
Table of Contents
1985-2014: Worked for Alstom Corporation, ABB Corporation, and Gadelius Corporation, designing Jungstrom air preheaters and mechanical design of diamond soot blowers. (ABB Corporation: https://new.abb.com/jp)
2014-2021: Worked as an engineering and project manager at Alvos Inc.
https://www.linkedin.com/in/yoichi-hiroki-92192394/
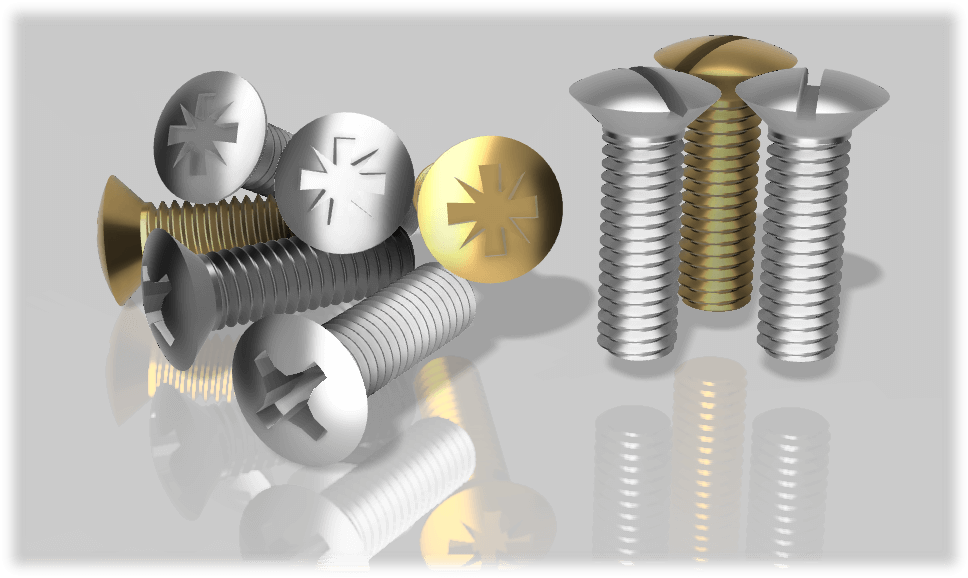
Round countersunk head screws, also known as oval head screws, feature a tapered conical shape that narrows toward the screw side, resembling a dish from the side. Unlike flat head screws, the top of a round countersunk screw head is rounded, offering a sleek appearance. They are screws with a small nominal head diameter and usually have a slotted or cross-holed drive.
The terms "round countersunk small screws" are commonly used to refer to this type of screw.
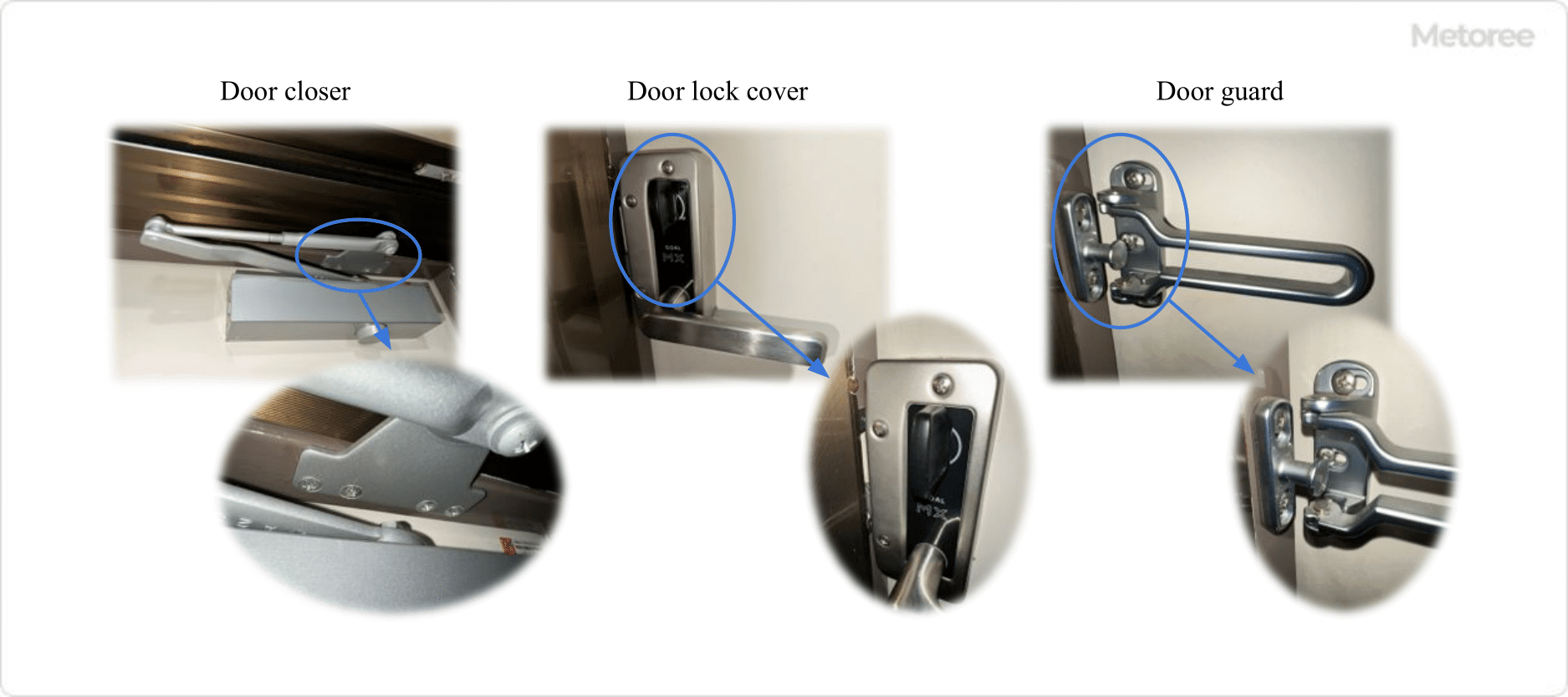
Figure 1. Example of Using a Small Round Countersunk Screw
Round countersunk screws are primarily used in applications requiring female threads, where a tapered counterbore is drilled into the workpiece slightly larger than the screw's tapered head. This allows the rounded part of the screw head to protrude slightly above the surface, providing a more aesthetic finish than flat head screws, especially in visible areas such as door closers, lock covers, and guards.
Similar to other countersunk screws, round countersunk screws are designed for direct insertion into tapped female threads without the need for a nut. They are tightened using a Phillips or flat-blade screwdriver inserted into the screw head's cross or slot. The length of these screws includes the head, differing from bolts where the length is measured excluding the head.
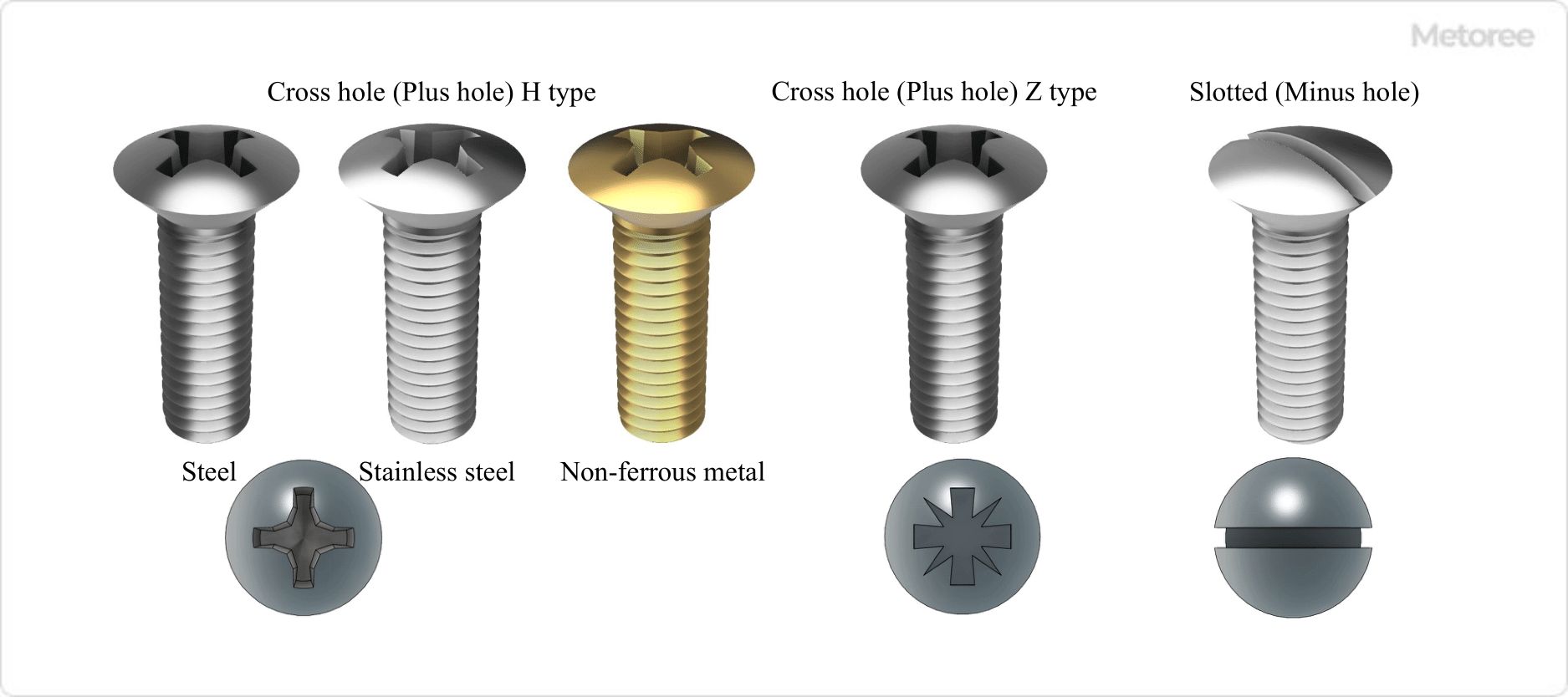
Figure 2. Types, Materials, and Shapes of Small Round Countersunk Screws
Classification of round countersunk screws includes variations in head hole shapes and materials.
Head hole shapes include Cross (Phillips) and Suriwari (Minus), each requiring specific tools for tightening. The H (Phillips) and Z (Pozidriv) shapes differ, with Z types being less prone to cam out. The Suriwari shape, a single straight groove, uses a flat-blade screwdriver for tightening.
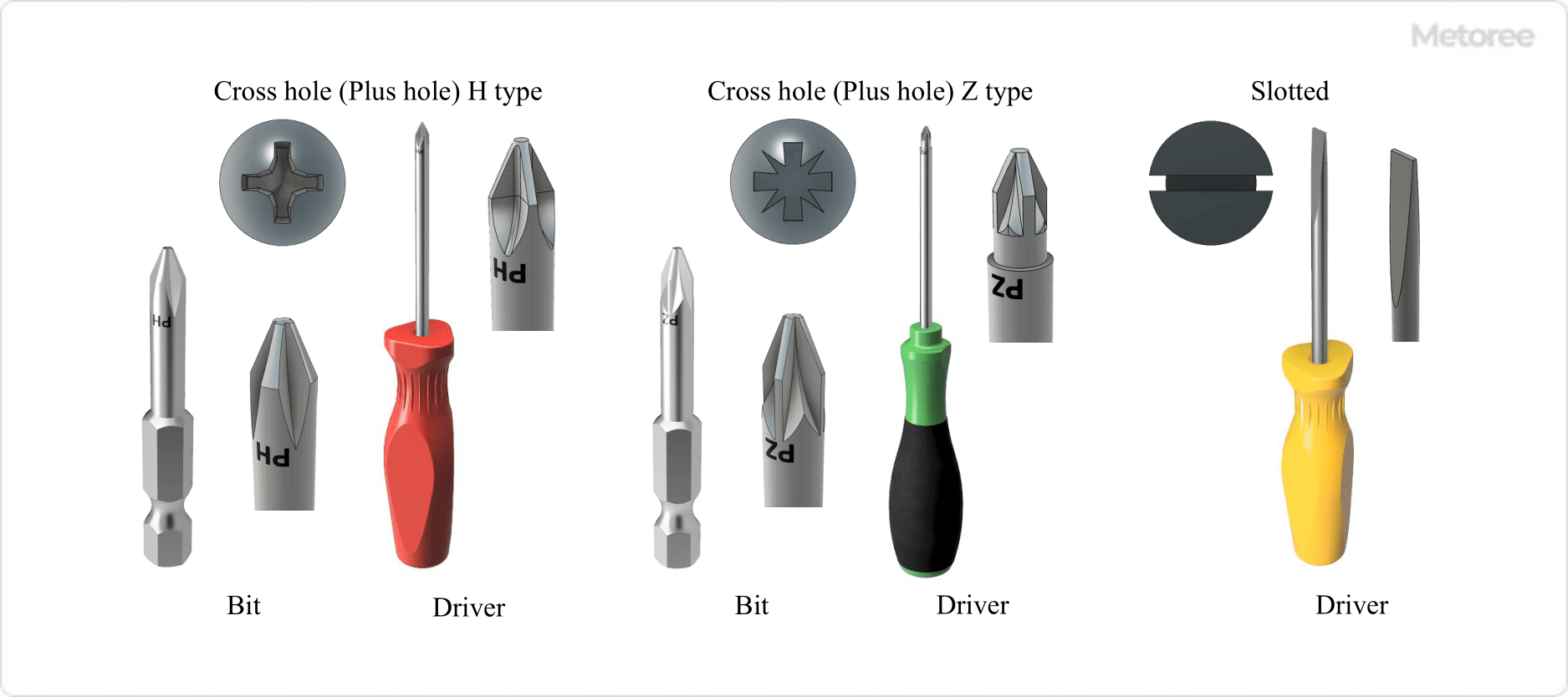
Figure 3. Hole and Tool Geometry of the Head of a Small Round Countersunk Screw
Materials for round countersunk screws include steel, stainless steel, and nonferrous metals, classified by strength and governed by various standards.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

NBK America LLC, founded in 2015 and based in King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, is an American manufacturer and a subsidiary of Japan's Nabeya Bi-tech Kaisha, specializing in mechanical components. Their product range includes couplings, like miniature shaft couplings for precision machine tools and semiconductor manufacturing equipment, special screws, such as vacuum application screws and other machine components. NBK offers finite automaton (FA) solutions, including wireless positioning units for production lines and setup operations. NBK provides machine component servicing, such as vibration resistance treatment and laser engraving. Services for couplings and special screws include coupling stainless steel screw alteration and screw length adjustment.

Portland Bolt & Mfg. Co. is a manufacturer founded in 1912 in Portland, Oregon. The company produces large, nonstandard anchor bolts and construction fasteners. Its products are used all over the United States, Canada and more tha. 30 countries all over the world. It has carried out successful projects related to mining, power and energy, stadiums, rail and military. Its long lasting experience has allowed the firm to hold a high production capacity, making and exporting 6.8 billion pounds (3.08Kg) of anchor bolts and construction fasteners only in 2018.

British Tools & Fasteners, located in Lyons, NY, United States, is a supplier of nuts, bolts, screws, taps, and tools. The company supplies tools including drill bits, grease nipples, hose clips, license plates, and motorcycle cables. The products are used in the automotive, aerospace, construction, manufacturing, and energy industries. The company is operated by Caswell Inc and all its orders are shipped prepaid from the headquarters. It only accepts returns within 30 days with a 10% restocking fee.

Ramesh Steel Corporation, founded in 1983 and headquartered in Mumbai, India, is a supplier and manufacturer of stainless steel, alloy steel, and carbon steel products. The company specializes in producing various industrial and construction materials, including pipes, flanges, buttweld fittings, screwed fittings, and socket weld fittings. Its products cater to industries such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, oil and gas, and construction. The company holds ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 certifications, ensuring industrial quality and environmental management systems.

Harikrishna Enterprise, formed in 2012 and located in Ankleshwar, India, is a manufacturer of active pharmaceutical ingredients and related products. The company produces 4-amino-6 chlorobenzene-1,3-disulfonamide, N iodosuccinimide, and methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate. It also fabricates N-Boc-piperazine, boron tribromide, and 5 bromo 2 chloropyrimidine. Its 4-amino-6 chlorobenzene-1,3-disulfonamide is available in white crystalline powder with a density of 1.768g / cm3 and is used in animal pharmaceuticals or in laboratories. It serves the agriculture, chemical, food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries.

Micro Metals, established in 2008 and located in Khetwadi Lane, Mumbai, is a manufacturer of stainless steel forgings, fasteners, and round bars. The company's products include stud bolts, threaded rods, countersunk screws, anchor bolts, and self-tapping screws. The products are used in the manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. The company has certifications such as EEPC INDIA, ISO 9001:2015, PED 2014, ISO 14001:2015, and ISO 18001:2007 occupational health management system.

Fong Prean Industrial Co., Ltd, founded in Taiwan in 1968, is a manufacturer of screws and related tool accessories. The company's product portfolio includes self-tapping screws, tek screws, stainless steel screws, collated screws, and custom screws. Its products find application in outdoor walls, roofs and fences and indoor frames and ceilings. The company holds various international standard certifications, including CE, ISO, ETA, and TORXTTAP. It also offers expert guidance, product consultation, and customer support.
Pioneer Industrial Corporation, founded in 1972 and headquartered in Mumbai, India, is a manufacturer of metal accessories for industrial application. The company produces an array of metal screws and nuts, fasteners, industrial bolts, SS washers, self tapping screws and nylon nuts. It also provides precision traub component and metal turned parts, machined and turned components and SS customised bending products. The company operates a dedicated design unit and provides customization services. Its products are exported worldwide, with the top five export destinations being the UK, Kuwait, Italy, Mauritius, and Korea.

Fabory USA Ltd., established in 1947 and based in Tilburg, Netherlands, is a manufacturer of standard fasteners. The company produces products such as threaded rods, bolts, screws, sockets and fasteners. All its products are supplied to different industries, including truck, trailer, and coach building, the petrochemical industry, building and construction, medical and food, and dairy. The company has operations in 10 European countries and holds ISO/QS 9000 certification. The products are produced by abiding by the international quality standards in the testing facility that is A2LA Accredited.

Suraj Metal Corporation started its operations in 1973 in Mumbai, India, as a prime manufacturer and supplier of alloy stainless and nickel products. The company is devoted to provide customers with global steel procurement services. They produce industrial goods that are durable, and have the necessary proportions. Round Bars, Forging, and Fasteners are just a few of this organization's Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloys products. They are always faithful to their ideals, which are congruent with ethical business methods.

Sparex is a global supplier of replacement tractor and machinery parts and accessories established in 1965 and based in Durban, South Africa. The company offers engine filters essential for the performance and maintenance of agricultural machinery, and tractor parts from brands such as Massey Ferguson and Valmet & Valtra. It also offers related accessories, including lighting solutions, mounts, and grill guards. The company chiefly supplies clients in the agricultural sector, as well as manufacturers of heavy machinery.

Citizen Valves, founded in 1981 in Mumbai, India, is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial valves like ball, gate, and globe valves. With over 35 years in the valve industry, the company exports to 60 countries and adheres to ANSI, API, and DIN standards. Their valves serve in Gas, Oil, and Chemical sectors, meeting rigorous industry requirements. Committed to quality, Citizen Valves holds multiple certifications, including ISO 9001 and API 6D, offering both standard and custom valve solutions.










Accu Limited, founded in the UK in 2012, is a supplier of engineering components. The company offers a wide selection of bearings and bushings, including plain bearings, roller bearings, ball bearings, a comprehensive range of fasteners, such as screws, bolts, nuts, and washers, available in various materials and sizes and high-quality seals and gaskets for sealing applications in industries like automotive, manufacturing, and more. It serves industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and construction.

Fisher Scientific UK Ltd is a supplier of laboratory chemicals, equipment, and services based in Loughborough, United Kingdom, operating as a subsidiary of Thermo Fisher Scientific, a merger of Fisher Scientific International, Inc. and Thermo Electron in 2006. With a portfolio of over 2 million products, Fisher Scientific offers chemicals, reagents, equipment and instruments, consumables, and safety products. These products cater to various sectors, including clinical diagnostic and research laboratories, pharmaceutical and biotech industries, healthcare, and government agencies. Fisher Scientific also provides business solutions like the New-Lab Start-Up program, as well as SureTRACE and SureTRACE+ for product knowledge and supply chain management.

Tayal Screw Products, founded in 1984 and based in Delhi, India, is a wholesaler, importer and supplier of machine tools and fastener expansion tubes etc. The company supplies products such as metal screws, nuts and bolts, metal washers, fastener expansion tubes, machine tools, pipe clamps, general fixing anchors and more to local and global clients. Its primary market is in China. Many tasks are performed by quality inspectors, packaging experts, and procuring agents.
Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tayal Screw Products |
16.7%
|
| 2 | Suraj Metal Corporation |
16.7%
|
| 3 | Kroon B.V. |
8.3%
|
| 4 | Keller & Kalmbach GmbH |
8.3%
|
| 5 | Canco Fasteners |
8.3%
|
| 6 | Micro Metals |
8.3%
|
| 7 | HARIKRISHNA ENTERPRISE |
8.3%
|
| 8 | Citizen Metals Pvt. Ltd. |
8.3%
|
| 9 | Portland Bolt & Mfg. Co. |
8.3%
|
| 10 | NBK America LLC |
8.3%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the round countersunk screw page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 India
India
|
10 | 47.6% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
4 | 19.0% |
 United States of America
United States of America
|
3 | 14.3% |
 China
China
|
1 | 4.8% |
| Nederland | 1 | 4.8% |
 Netherlands
Netherlands
|
1 | 4.8% |
 Germany
Germany
|
1 | 4.8% |
133 products found
133 products
Bossard Co., Ltd.
790+ people viewing
Last viewed: 17 hours ago
This is the most common general term for screws used to fasten small parts. Tighten by screwing into the female thread cut into the nut or mating m...
20 models listed
Wilco Co., Ltd.
690+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features - A ceramic machine screw with a head shaped like an overturned pot. -Uses alumina, which is a typical ceramic material. ・Excellent mech...
2 models listed
Wilco Co., Ltd.
1140+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
■Features ・The screw itself has a female thread formed on the mating material by plastic molding, so it can be tightened directly into a pilot hol...
14 models listed
Wilco Co., Ltd.
180+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
A screw with a slightly rounded head and a conical seat. It is necessary to countersink (countersunk) the mating material to be tightened. Counters...
Bossard Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
A bind machine screw is a machine screw with a trapezoidal head and a rounded top. It is characterized by a lower head than a pot head and a smalle...
Bossard Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features It is characterized by a round convex head with a part of the sphere cut out. The English name is truss head screw. It is called a truss ...
Essentra Components Japan Inc.
200+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Please contact us for details Contact information: TEL 045-321-2752 FAX 045-410-0383 mail: sales@essentracomponents.jp
Essentra Components Japan Inc.
180+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Please contact us for details Contact information: TEL 045-321-2752 FAX 045-410-0383 mail: sales@essentracomponents.jp
Fukui Metal Crafts Co., Ltd.
430+ people viewing
Last viewed: 17 hours ago
4 models listed
Fukui Metal Crafts Co., Ltd.
810+ people viewing
* There are other part numbers.
10 models listed
Fukui Metal Crafts Co., Ltd.
510+ people viewing
Last viewed: 14 hours ago
2 models listed
Takachi Electric Industry Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
A round countersunk head screw with a hexagonal star-shaped hole on the screw head. Compared to standard Phillips-head screws, they can make the ap...
Liebe Co., Ltd.
140+ people viewing
Last viewed: 17 hours ago
■Summary Deck One+ is a screw that can be installed in hard wood in one shot without the need for pilot holes. Significantly reduces the burden of ...
Hios Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Main features ・Totsupura is a revolutionary screw that ensures compatibility with conventional cross screws and improves the bit lifting (cam-out...
Hios Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
High-Off Clover Screws, featuring a wide fan-shaped three-blade design with excellent stability, have excellent fitability, prevent cam-out, and pr...
Hios Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Main features ・Intertorque, designed for functionality and workability, has a conical inclined guide at the tip of the bit, which automatically g...
Hios Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
■Main features ・DELTA PT is a registered trademark of EJOT, Germany. ・DELTA PT®, which was developed as a self-tapping screw for resin, has a spe...
Sanohatsu Co., Ltd.
180+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Compatible with the era of “lighter weight” and “thinner plates” In an era when many industries are aiming for weight reduction, steel sheets are ...
Liebe Co., Ltd.
150+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
■Summary It is a screw that is difficult to thread because it inserts into hard wood while cutting it. There are two colors: silver and bronze. ■F...
Yamazaki Co., Ltd.
100+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
Yamazaki Co., Ltd.
120+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
Yamazaki Co., Ltd.
100+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Yamazaki Co., Ltd.
130+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
Yamazaki Co., Ltd.
100+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Yamazaki Co., Ltd.
100+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
Yamazaki Co., Ltd.
70+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
■Surface treatment (iron (or standard)) Fabric (or standard), UNIQLO, chromate, trivalent white, trivalent black, nickel, chrome, GB (brown bronze)...