All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for laser diodes as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 49 laser diode manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked laser diode companies as of July, 2025: 1.Frankfurt Laser Company, 2.OSI Laser Diode, Inc., 3.ProPhotonix.
Table of Contents
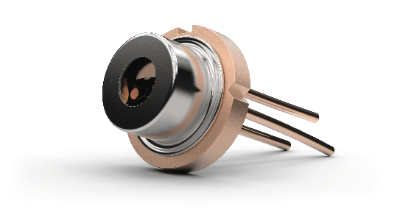 A laser diode is a device that uses a semiconductor mechanism known as recombination emission. The word “laser” is an acronym for "Light Amplification by the Stimulated Emission of Radiation", where radiation is light.
A laser diode is a device that uses a semiconductor mechanism known as recombination emission. The word “laser” is an acronym for "Light Amplification by the Stimulated Emission of Radiation", where radiation is light.
The color of the laser is determined by the elements that make up the semiconductor. Some lasers operate at room temperature, while others require cooling, depending on the resonator structure and output power.
The difference between laser diodes and LEDs is that laser diodes meet the requirements for laser oscillation. Variations in wavelength and amplitude of the light are much smaller in laser diodes as well.
Laser diodes (LDs) are widely used in consumer information equipment because of their small size, low power consumption, and low cost. They’re also lightweight, efficient, and highly reliable.
They are used in barcode readers, in optical pickups for optical drives such as CDs, DVDs, and BDs, copiers, laser printers, and optical fiber-based communication devices. High-power laser beams are also used in laser markers and laser processing machines.
The diffusion-resistant and long-distance reach of laser light makes them suitable for use in surveying instruments and laser pointers for pointing at objects. Because they emit coherent light, they are ideal for leveling and alignment applications.
In laser diodes, coherent light is emitted by the recombination of holes ("holes" here means spaces from which electrons have been released) and electrons when a voltage is applied.
The emitted photon causes another electron to recombine with the hole one after another, emitting photons, so that the generated light has the same phase and wavelength. Since the wavelength of the light is always constant, it is used in barcode readers, laser pointers, fiber-optic communications, and other applications requiring a constant amount of light.
The L/I curve is used to understand laser diodes specifications. This curve allows us to keep track of the drive current supplied by the light intensity output.
This curve is used to determine the operating point (drive current at rated emission output) and threshold current (starting current of laser oscillation) at the laser and is also used to determine the current required to obtain high output power at a particular current.
By reading this curve chart, one can see that optical output depends greatly on temperature, and that as temperature increases, laser parameters decrease. This makes it possible to visualize and estimate the efficiency of laser diodes by incorporating the L/I curve.
While both are classed as electro-electronic components, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have disparate phases, so light rays are diffused radially; in contrast, laser diodes are in phase with each other, resulting in a linear beam of light. The light emitted by a laser is also monochromatic, meaning it’s a bright, single-colored emission. Moreover, laser light is stimulated to emit coherently and efficiently, while light-emitting diodes utilize the electro-luminance effect, which is inferior.
Therefore, light-emitting diodes have an unfavorable characteristic in that their emitted light won’t easily enter a fiber with a small core system due to the wide surface of the light-emitting layer. On the other hand, laser diodes have a narrow emitting layer, making it easy for the light to enter a fiber with a small core system.
And since laser diodes emit photons by colliding every emitted photon with another atom, the light produced is coherent and the light beam is monochromatic. In contrast, the light produced by a light-emitting diode is incoherent and the emitted light consists of various colors.
The average life expectancy of laser diodes varies depending on the operating environment (operating temperature, static electricity, power surges) and is generally between 10,000 and 50,000 hours.
The following section discusses operating temperature as a variable among the environmental factors that affect the average life of LDs.
Operating temperature is said to reduce life expectancy by half when the operating temperature rises by 10°C. If the operating temperature continues to rise above the maximum operating temperature, then laser diodes are more likely to be damaged and their long-term performance degraded. The degradation rate at operating temperatures increases exponentially with the operating temperature.
Therefore, the use of heat sinks (radiating plates) is recommended to reduce the effects of operating temperature and to increase luminous output. Heat sinks dissipate the thermal energies generated by power electro-electronic components. Passive cooling is one solution, but active cooling devices are available. These include air-cooling and water-cooling mechanisms.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Frankfurt Laser Company, founded in 1994 and located in Friedrichsdorf, Germany, is a supplier of FP, DFB, and DBR laser diodes. The company offers a range of products that include laser diodes, superluminescent diodes, laser illuminators, laser modules, and optics. They are used for laser-based applications, optical imaging, lighting, and optical system integration. The products offered by Frankfurt Laser Company cater to a range of industries and applications, including telecommunications, medical, industrial, entertainment, and optical sensing.

OSI Laser Diode is a US-based company that was founded in 1967. The company is a manufacturer and designer of advanced optoelectronic components and solutions. The company's products include laser diodes, fiber optic receivers, and high-speed detectors. These products are used in various applications such as defense, aerospace, medical, telecommunications, and industrial markets. The company also provides technical support, product training, and repair and maintenance services to ensure the optimal performance of its instruments.

Excelitas Technologies Corp., headquartered in Waltham, USA, is a manufacturer of photonic solutions. The company provides photonic solutions for the illumination, optical and imaging needs of the OEM and end-user customers. The products like cameras, sensors and light sources serve an array of applications across many sectors. These range of applications include clinical diagnostics, autonomous vehicles and X-ray security screening. The company also offers bespoke photonic solutions such as discrete components, sub-assemblies, or complete turnkey solutions tailored to the customers' specific requirements.

ProPhotonix, established in 1951, and headquartered in Massachusetts, USA, is a manufacturer of LED illumination products and laser diode modules. The company’s products are used in various applications, including industrial, medical, and scientific sectors. The LED solutions provide benefits such as energy efficiency, a long lifespan, and precise control of light output. Laser diode modules offer optimal-performance, stability, and precision for applications like machine vision, alignment, and medical equipment. These products find application in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and research. The products’ uniqueness and optimal quality ensures enhanced productivity and precision in various industries.

IPG Photonics Corp. is a manufacturer of industrial fiber lasers, amplifiers and laser systems established in 1990 and headquartered in Massachusetts, USA. The company’s product lineup includes direct diode laser systems, ultrafast fiber lasers along with their respective, and continuous wave (CW) pulsed fiber lasers. It also offers contract manufacturing capabilities, including laser cutting, laser welding, and laser marking services, tailored to meet the specific requirements of client projects. The company is ISO 9001 certified and operates internationally, with subsidiaries in Japan, Russia,and South Korea.

Thorlabs, Inc, established in Newton, NJ in 1989, is a manufacturer of photonics equipment for research, manufacturing, and biomedical applications. Their product portfolio includes optical components, for use in imaging, sensing, and spectroscopy applications, spectrometers and analyzers used for research and industrial applications, fiber optic components and photomultiplier tubes, and imaging devices that capture and measure light signals for diverse applications in scientific research. The company has sales offices in the United States, United Kingdom, Sweden, China, and Brazil.

RPMC Lasers, Inc. is an OEM laser supplier founded in 1996 and based in Missouri, USA. The company offers various laser technology products for the photonics industry. These products include fiber or solid-state optical laser amplifiers, wide wavelength laser diodes, and pulsed lasers. It also offers related accessories such as thin disc mount modules and heatsinks, as well as product customization for customers with unique project specifications. The company's products support client manufacturers in the medical, defense and research sectors.

Blue Sky Research was founded in 1989 and is based in Milpitas, California, is a manufacturer of fiber-coupled laser diode modules and fiber optic-based laser components for various industries. The company provides fiber-coupled lasers & systems, laser diode modules & components, engineered products & prototyping devices that have applications in laser technology, confocal microscopy, life sciences, and, microelectronics sectors. They offer integrated laser drivers, monitor electronics, temperature stability & controls, semiconductor laser products & solutions for microlens technology-based processes and applications.

Optilab, LLC was established in 2002 with its headquarters in Phoenix, Arizona is a manufacturer of laser and photonics systems and instruments for the fiber optics and optoelectronics industries. The company produces laser diodes, pulse lasers, optical modulators, lightwave transmitters, photodiodes, and, amplifiers, that have applications in the aerospace, communications, national research laboratories, and defense sectors. They have also developed MTS-16 Modulator Test Station for automated measurement of bias stability, optical transmission, and, insertion loss of optical modulators as well as firmware for each channel's wavelength and output power control through the touchscreen.

Advanced Photonic Sciences (APS), established in 2003 as Snake Creek Lasers, LLC., with offices and facilities located in Friendsville, Pennsylvania, is a manufacturer of microlaser and laser module products for industrial and government organizations. APS's products are used for biomedical, illumination, and aiming applications in both laboratory and demanding industrial conditions. The company has a history of collaboration with Clemson University, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory, the Naval Research Laboratory, Binghamton University, and Montana State University.

Sheaumann Laser, Inc. is a privately-owned manufacturer and distributor of laser diodes established in 2005 by Jim Hsieh and based in St. Billerica, Massachusetts. The company manufactures single-mode and multimode continuous wave (CW) Diode lasers ranging from 780 to 1070 and with an output power of up to 30W used in medical, industrial, defense, space, and environmental applications. They also manufacture various laser packages, including butterfly, high heat load, TO-Cans, and 2-pin modules. Sheaumann also has in-house capabilities, including wafer growth, processing, and packaging, allowing the company to provide customized solutions for demanding projects of various sizes.

Global Communication Semiconductors, LLC, was founded in 1997 as a California corporation and in addition to its patented optical wafers and chips ("GCS Known Good Die" TM), GCS also provides foundry services for RF/Wireless, Optoelectronics, and Power Electronics. GCS establishes investments in personal development and enhanced manufacturing procedures as it produces III-V compound semiconductors for its water foundry service such as GaAs, InP, and GaN. Furthermore, the optical communication components include devices like Photodetectors and Lasers. Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) and millimeter wave integrated circuits work for the wireless industries, and power devices for power electronics.

Seminex Corporation, founded in 2003 in Massachusetts, designs and manufactures infrared laser diodes and optical amplifiers used for automotive, military, medical, and industrial settings. The company produces the latest high-power lasers such as 1550 nm Triple Junction laser diodes for ToF LiDAR and Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (SOAs) for FMCW LiDAR in the chip, array, and surmount designs, with all diode laser products customizable in various powers and wavelengths to meet customer specifications.


U.S. Lasers, Inc., is an American privately held corporation that manufactures and produces a large range of laser diodes and modules. Established in 1992, the company offers a wide range of lasers and laser systems for industrial, medical, and scientific applications. They are used in various applications, including telecommunications, barcode readers, laser printers, and industrial machining. In addition, the company also offers technical support, training, and repair services to meet the specific needs of its customers.

Redfern Integrated Optics (RIO) established in, Australia in 2000, is a supplier engaged in single frequency narrow line width lasers and modules. Their product range include subsystems to the clean energy, security, oil and gas, and test and measurement markets. The company is entered the Silicon Valley in 2003 and backed by a consortium of venture capital funds to develop a commercially viable semi-conductor laser optimized for fiber sensing applications and they have an office in Santa Clara, California.

AeroDiode is a company founded in 2016. Headquartered in Carlsbad, California, USA, the company is a supplier of laser diodes and modules for various industries. AeroDiode offers a diverse range of laser products, including diodes, modules, and drivers. These products are widely used in applications such as industrial manufacturing, scientific research, and medical procedures. The company also provides technical support services, with comprehensive product information and customer services to meet the specific needs of its customers.

LuxNet Corporation is a Taiwanese manufacturer, established in 1999 is an optical semiconductor devices and packaged optical components for optical communication. The company products enable voice, video, and data communications for networking, storage, and cable TV applications. It has its own epi-layer design and fabrication process, as well as global manufacturing capability, and also offers wafer processing services and chip fabrications. They endeavor to provide products with high volume, high yield, and competitive prices. It has received various awards and rankings for its corporate governance and performance and serves customers in Taiwan, China, the US, and other countries.



SPI Lasers, founded in 1923, is a top manufacturer and supplier of advanced technology such as machines and systems, lasers, power electronics, power tools, smart factories, and software. Their primary goal is to develop and connect production technology, making it more efficient, precise, and future-proof for the benefit of manufacturing and its upstream and downstream processes. They offer cutting-edge software solutions to make the Smart Factory possible, enabling us to implement high-tech processes in industrial electronics.

Edinburgh Instruments was founded in 1971 and is a manufacturer of advanced molecular spectroscopy and gas detection products and is headquartered in Livingston, Scotland. The primary attention of Edinburgh Instruments lies in the design and production of customized spectroscopic systems catering to several spectroscopy markets such as Photoluminescence, Raman, UV-Vis, and Transient Absorption. The company engages in research, manufacturing, and commercializing a diverse array of goods catering to the scientific research and industrial sectors.

Located in Austria and Germany, Ams-Osram is a sensor design and manufacturing company that specializes in compact form factors, low power, high sensitivity, and multi-sensor applications. They were established in 1981 and were formerly known as austriamicrosystems AG. In 2012 it changed its name to ams AG. They have a technology portfolio for sensing, lighting, and visualization, ranging from light emitters and optical components to micro-modules, integrated circuits, and related software. Their work develops technology for use in the consumer, industrial, medical, and automotive sectors.

Laserline, established in 1997, and based in Mulheim-Karlich, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of lasers. The product portfolio includes a diverse range of lasers with additional components and different materials. The company offers high-quality industrial lasers with permanent optimization products and processes under technical standards and regulations. The products are used in various industries for development and environmental management. The company products are ISO certified with internal audits and regular certification periods.

Ushio Inc., established in 1964 in Tokyo, Japan, is a manufacturer and supplier of specialized light sources, with a particular interest in ultraviolet (UV) and visible light. The company boasts an extensive product portfolio that includes various lighting solutions, including laser diodes, UV lamps, visible lights, lamps designed for projectors, and halogen lamps. These diverse products cater to a wide array of industries and applications, including architecture and landscape illumination, disinfection and deodorizing, litho-patterning, optical systems, as well as curing and bonding processes.

Hamamatsu Photonics K.K., established in 1953 and headquartered in Hamamatsu, Japan, is a manufacturer of sensors and emitters for both visible and invisible light. It stocks products like LEDs, lamps, and photodiodes used in several industries, including consumer electronics, dental imaging, and environmental monitoring. The sensor and light source components are also available as modules and units that can be incorporated into systems the company develops, like optical measurement systems or imaging systems. The ISO 9001-certified company stocks over 15,000 devices, units, and systems that ship to over 100 destinations worldwide, and it has ten research and production bases.

NICHIA CORPORATION was established in 1956 and is located in Tokushima, Japan is a manufacturer of organometallic compounds and electronic materials. The company offers a diverse product catalog including cathode materials, laser diodes, and magnetic materials among others. These products have applications in LCD backlighting, electric vehicles, and energy storage. In 2023, the company received the 26th Optical Design Award for high-efficiency task lighting that can reduce light pollution thus promoting technological exchange.





Sacher Lasertechnik GmbH, founded in 1992 and headquartered in Marburg, Germany, is a manufacturer and supplier of high power tunable external cavity diode lasers. The company’s product portfolio includes tapered amplifier systems, pulsed diode lasers, and vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers. These products are applied in various sectors, including scientific research, as the lasers are widely used in laboratories and research institutions, industrial manufacturing, and metrology and instrumentation. The company has a global distribution network in various countries, including the United States, Japan, and Australia.

Appointech, Inc., established in 1998 and based in Hsinchu, Taiwan, is a manufacturer specializing in the production of light sources, power meters, and fiber optic testing equipment. The company boasts a comprehensive product line that includes handheld test instruments, LED modules, and fiber transceivers designed for precision and stability in optical testing and measurement. It holds ISO 9001 certification, and these instruments offer advantages such as absolute sensitivity, accuracy, and durability, making them ideal for applications in telecommunications, data centers, research and development, and network installation.

Ushio is a manufacturer of industrial light sources and is headquartered in the Netherlands since 1964. The company is known for its discharge and incandescent filament lamps, laser diodes, Excimers, and LED chips. The company makes additional devices like power supplies for chemical, medical, and scientific purposes, as well as lamp houses for radiation emissions. The company caters to various industries such as providing Projector Lamp Technology for cinemas, in the medical industry they aid in analysis and procedures like Endoscopy, other than that stage and studio lighting, sports venues, UV disinfecting, and general lighting all are applicable.

Quantel Laser established in, France in 1970, is a manufacturer engaged in solid-state lasers, dye lasers and laser diodes. Their product range include olid-state lasers, lumibird manufactures lasers for the industrial, scientific, defense, space and medical markets. The company's products are used for atom cooling, materials research, combustion analysis, end-pumping, photoacoustic imaging, satellite communications, and nuclear fusion. The company provised sales support and they have sales network all around the world.

Cutting Edge Optronics, Inc. is based in Saint Charles, Missouri, USA, and is a manufacturer of laser diode arrays and system hardware established in 1992 before becoming a subsidiary of Northrop Grumman in 2000. The company primarily produces application-specific laser diode arrays, including for the medical, military, and scientific research industries. It also offers laser system hardware products such as laser gain modules for unstable oscillator resonators, and laser diode drivers for delivering precise currents to diodes in a system. The company is ISO 9001:2015 certified, and mainly serves the military, aerospace, and medical industries.

Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation, founded in 2015 and headquartered in Atsugi, Japan, is a manufacturer of various semiconductor products and electric/electronic equipment, as well as other related businesses. Its range of products includes image sensors, microdisplays, board computers, and laser diodes used in several industries, such as logistics, manufacturing, security, agriculture, and transportation. The company conforms to the IATF 16949 standard and ISO 9001 and has 33 bases in 13 countries worldwide. It has received several awards, including the National Invention Award, Okochi Award, US Walter Kosonocky Award, and Manufacturing Japan Grand Award.

Innolume, established in 2003 and headquartered in Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany, is a manufacturer that specializes in GaAs-, InAs- & and InP-based laser diodes. The company's product line includes diode laser-SM-12XX-TO-XXX 1130nm and Spatial single-mode laser diodes of any wavelength in the 780nm to 1340nm range. It also provides personal service to provide full support for its clients' projects. It offers laser diodes that can emit up to 1.2W of low-noise peak optical power. One of its products, the DFB laser, became a finalist in the Prism Awards in 2019. It serves various industries such as Datacom, Aviation, Chromatography, and more.

Imagine Optic, established in 1996 and based in Orsay, France, is a manufacturer of wavefront sensing and adaptive optics products. The company offers deformable mirrors for correcting wavefront distortions in optical systems, wavefront sensors for precise measurement applications, and adaptive optics components for improving the performance of existing optical systems. It also offers installation assistance and equipment recalibration services for customers requiring additional support. The company chiefly serves clients in the optoelectronic, consumer electronic, and computer science industries.

Daheng New Epoch Technology, Inc. is a Chinese manufacturer and supplier of optical components and systems that was established in Beijing in 1987 as a subsidiary of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The company produces optical modules such as fiber collimators, optical components such as beam splitters, and optical systems such as laser marking systems. It also offers optical subsystems such as optical coherence tomography systems, as well as design and engineering services for unique projects. The company’s products are commonly used in the biomedical, scientific research, and defense sectors.

Changchun New Industries Optoelectronics Tech. Co., Ltd. (CNI), established in 1996 and headquartered in Changchun, China, is a manufacturer and supplier of lasers and optical systems. The company's product range comprises Lasers, Spectrum Analyzers, Laser Application Systems, Laser Measurement Tools, and Laser Marking. These products are vital for various applications across research, industrial, and technological domains. They serve sectors such as electronics, photonics, research institutes, and industrial manufacturing. Besides producing hardware, it provides services such as optical measurement, laser processing, machine vision solutions, and photoelectric detection.

EBLANA PHOTONICS LTD, established in 2001 and based in Dublin, Ireland, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in laser diodes. The company's product portfolio includes narrow linewidth lasers, superluminescent diodes, and Fabry-Perot lasers. These products are used in various applications, including gas sensing in industries involved in the detection of gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), as well as in telecommunications and remote sensing. The company offers a range of post-fabrication services to complement its product offerings and cater to the needs of its customers, which include coating and volume chip testing.

Laser Components was founded in 1982 and is headquartered in Olching, Germany. The ISO 9001:2015 certified company also has locations and distributors across Europe and the United States. The company is a manufacturer and researcher for semiconductor technologies and dielectric coatings. Chemicals used include silicon, lithium tantalate, and deuterated L-alanine doped triglycene sulphate, known as DLATGS. The company’s product segments include IR Components, Photo Counters, Lasers, and Fiber Optics. The company’s services include repair, calibration, tool servicing, and job coatings.

Arrow Electronics, Inc. is a manufacturer and supplier of electronic components and enterprise software that was established in 1935 in New York City, New York, USA. The company primarily produces electronic components including interconnect cable assemblies, semiconductors, and fiber optics. It also offers enterprise computing software such as security suites, servers, and cloud hosts. The company is ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 45001-certified, and provides custom design as well as engineering services for its clients with unique projects.

Egismos Technology Corporation, established in 1995 and based in Burnaby, Canada, is a manufacturer and supplier of laser-based optoelectronics solutions. The company's product range includes Laser sensing, Laser module, Laser diode, Laser optics, and Laser driver IC. These products find applications in diverse areas, such as consumer electronics, medical devices, robotics, and various industrial projects. It serves markets ranging from the consumer industry to the medical fields and robotics. Its core services include customer satisfaction, embracing change, fostering partnerships and alliances, and ensuring transparent communication.

Jenoptik AG, established in 1992 and headquartered in Berlin, Germany, is an optical technology developer, manufacturer, and supplier. The company's products include imaging solutions, laser technologies, and custom LiDAR optical modules for 3D spatial applications. It also develops systems for optical testing and measurement solutions for manufacturers, custom optoelectronic reader devices, and customer-specific optoelectronic machine vision systems. On a larger scale, the company offers municipalities custom-designed intelligent camera solutions for public safety.

Ushio America, Inc., established in 1967 and headquartered in Cypress, California, is a manufacturer and distributor of photonics solutions. Its diverse product range includes xenon short arc, lasers, ultra-high-pressure UV, excimer, and metal halide lamps, serving various industries such as biotechnology, electronics, medical, and semiconductor. The company has obtained multiple certifications, including ENERGY STAR, DesignLights Consortium, and Underwriters Laboratories Inc. Its products are designed and manufactured in an ISO 13485-certified medical facility.

PhotonTec Berlin is a company that specializes in the development and production of fiber-coupled diode lasers and diode-pumped solid state lasers. With years of experience in product development and management in the laser and optics industry, PhotonTec Berlin works closely with its customers to ensure that its products and solutions meet their exact requirements. The available wavelength range covers ultraviolet 266nm to infrared 1550nm, with power levels ranging from milliwatts to hundreds of watts. This broad range of options enables them to offer solutions for a wide range of applications, including medical equipment, material processing, and scientific research.


TOPTICA EAGLEYARD is a global provider of high-power laser diodes based on GaAs(Gallium Arsenide). TE’s product portfolio features diodes with wavelengths from 630nm to 1120 nm catering to a range of high-end applications including gas detection, atomic clock, dental, illumination, spectroscopy, inter & intra satellite communication, dental, and LIDAR. TOPTICA EAGLEYARD serves various industries including industry, life science, space, defense, and research. TE operates independently under its own brand and sales organization while being part of the TOPTICA Photonics Group.

MPB Communications Inc., in Hymus Boulevard, Montreal, Quebec, was founded in 1976 and is a supplier of fiber laser and fiber amplifier subsystems for high-tech fields. The product categories are data center interconnects, fiber lasers, network-ready telecom solutions, gain modules, and test instruments such as erbium fiber amplifiers and broadband sources. The fiber lasers are continuous waves, pulsed, or single-frequency amplifiers. Whereas the network-ready telecom solutions include boosters, Raman pumps, wavelength converters, and translators used in telecommunication, holography, micromachining, atom cooling, and defense sectors. The company offers installation, after-sales support, a loaner program, custom design, and an extended warranty.
Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Frankfurt Laser Company |
10.4%
|
| 2 | OSI Laser Diode, Inc. |
5.1%
|
| 3 | ProPhotonix |
4.4%
|
| 4 | Aerodiode |
3.5%
|
| 5 | SemiNex Corporation |
3.4%
|
| 6 | RPMC Lasers, Inc. |
3.4%
|
| 7 | Sheaumann Laser, Inc. |
3.3%
|
| 8 | SPI Lasers |
3.0%
|
| 9 | U.S. Lasers |
3.0%
|
| 10 | Blue Sky Research |
2.9%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the laser diode page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
16 | 42.1% |
 Germany
Germany
|
6 | 15.8% |
 Japan
Japan
|
6 | 15.8% |
 Taiwan
Taiwan
|
2 | 5.3% |
 China
China
|
2 | 5.3% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 2.6% |
 Austria
Austria
|
1 | 2.6% |
 Netherlands
Netherlands
|
1 | 2.6% |
 France
France
|
1 | 2.6% |
 Ireland
Ireland
|
1 | 2.6% |
 Canada
Canada
|
1 | 2.6% |
123 products found
123 products
Takenaka Optonic Co., Ltd.
500+ people viewing
Last viewed: 14 hours ago
■Overview/Features ・With the knurling adjustment mechanism, you can adjust the distance from a minimum distance of 100 mm to a maximum distance of...
Takenaka Optonic Co., Ltd.
430+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Overview/Features ・60° fan angle, generates more than 3 times the output compared to conventional models, and reduces speckle noise. - Capable of...
QD Laser Co., Ltd.
1140+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Summary ・High peak output pulse drive is possible while maintaining laser class 1. ・Reliability data during nanosecond pulse drive can be provided.
6 models listed
QD Laser Co., Ltd.
550+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
■Summary ・High peak output pulse drive is possible while maintaining laser class 1. ・Reliability data during nanosecond pulse drive can be provided.
QD Laser Co., Ltd.
690+ people viewing
Last viewed: 10 hours ago
■Summary ・High peak output pulse drive is possible while maintaining laser class 1. ・Reliability data during nanosecond pulse drive can be provided.
2 models listed
QD Laser Co., Ltd.
510+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
■Summary ・High peak output pulse drive is possible while maintaining laser class 1. ・Reliability data during nanosecond pulse drive can be provided.
Seven Six Co., Ltd.
3410+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
Semiconductor laser diode fabric pellow laser. * There are other part numbers.
10 models listed
Seven Six Co., Ltd.
1190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
DFB laser of semiconductor laser diode.
4 models listed
Autex Co., Ltd.
300+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■Low-noise, high-speed modulation CW semiconductor laser module This is an extremely low-noise, easy-to-use CW laser that uses unique circuit techn...
Autex Co., Ltd.
420+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Low speckle semiconductor laser Since 2003, Pavilion, a semiconductor laser system manufacturer, has been leveraging its many years of experience ...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features A highly visible 515nm semiconductor laser light source. ・Since it is a semiconductor green laser, it can be used in a wide temperature ...
Yagyu Shokai Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 5 hours ago
■Features - By controlling the operating temperature, we aim to stabilize the output and oscillation wavelength and extend the life of the LD eleme...
Seven Six Co., Ltd.
930+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
Gain chip/gain module of semiconductor laser diode.
3 models listed
Nisshinbo Micro Devices Inc.
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 19 hours ago
■Frequency 9,300~9,500MHz ■Incoming power (peak) 100kW ■Recovery time 0.9μsec max. ■Others ・Isotope press ・RoHS compliant
Seven Six Co., Ltd.
760+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
■ Blue semiconductor laser / blue laser wavelength: 405 ~ 445nm Output: 160mW ~ 200W ・ Module type for embedded ・ Custom of fiber and connector i...
Nisshinbo Micro Devices Inc.
290+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Frequency 3,000~3,100MHz ■Incoming power (peak) 100kW ■Recovery time 2μsec max. ■Others ・Isotope press ・RoHS compliant
Nisshinbo Micro Devices Inc.
290+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
■Frequency 9,300~9,500MHz ■Incoming power (peak) 8kW ■Recovery time 0.5μsec max. ■Others ・Isotope press ・RoHS compliant
Nisshinbo Micro Devices Inc.
290+ people viewing
Last viewed: 10 hours ago
■Frequency 3,000~3,100MHz ■Incoming power (peak) 30kW ■Recovery time 0.5μsec max. ■Others ・RoHS compliant
Nisshinbo Micro Devices Inc.
300+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Frequency ・RF frequency: 9.345 ~ 9.475GHz ・IF frequency: 60 MHz typ ・LO frequency: Built-in VCO (Upper LO) ■Noise characteristics Noise Figure...
Tomita Co., Ltd.
450+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
■Wrap laser LAP LASER began developing laser products in 1984 in Lüneburg (about 40 km south of Hamburg). At first, there were only point and line ...
Autex Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 9 hours ago
■Complete backup system, long life, and high stability next-generation industrial CO₂ laser This is a sealed CO2 laser specialized for industrial u...
STC Co., Ltd.
520+ people viewing
Last viewed: 23 hours ago
You can choose from a rich lineup of over 40 types. We have visible light and near-infrared light laser diodes. We can handle low-priced, high-qual...
10 models listed
Time Technology Japan Co., Ltd.
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
Infrared camera for quick screening of human body temperature measurements. High cost performance/flexible combination of temperature measurement m...
Seven Six Co., Ltd.
820+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
VCSEL (surface laser) of semiconductor laser diode.
2 models listed
Tsukumo Engineering Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
■Summary ・Beam pocket (damper) is used to block laser light. -The inside has a structure that blocks and diffuses laser light by performing taper ...
Opttech Co., Ltd.
290+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
Laser diodes of various wavelengths are available. Typical wavelengths range from 375nm to around 2um. We can deliver the product in a package acco...
Optron Science Co., Ltd.
160+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Summary This product is a fiber pigtail module that connects a CAN package LD and fiber (single mode, polarization maintaining, multimode, large d...
Optron Science Co., Ltd.
90+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
■Summary ・Small and takes up little space, making it ideal for integration. ・A driver-exposed type without a housing is also available. ・Since i...
Japan Connect Industry Co., Ltd.
680+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
Nippon Connect Kogyo's power transistor sockets are available in a variety of TO packages and are compatible with high current (large current), hig...
10 models listed