All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for valve balls as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 28 valve ball manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked valve ball companies as of July, 2025: 1.Trans-Valve, 2.Engineering Laboratories, Inc., 3.Schubert & Salzer, Inc..
Table of Contents
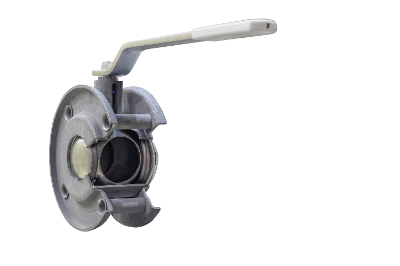 A Ball Valve is a valve with a ball-shaped plug. They are operated either fully open or fully closed. It is not suitable for flow adjustment by opening.
A Ball Valve is a valve with a ball-shaped plug. They are operated either fully open or fully closed. It is not suitable for flow adjustment by opening.
However, since the internal flow path is the same as the pipe diameter, there is almost no pressure loss. For this reason, the ball valve is often used in locations where there is no problem with only fully open or fully closed control.
Corrosion resistance can also be ensured by changing the material.
Ball valves are used in a wide range of applications, from consumer products to industrial applications.
For consumer products, ball valves are used for gas stove valves. They are also used in water supply valves.
In industrial applications, they are used in many situations due to their extremely low pressure drop and high shut-off performance. They are especially used in water and gas lines.
They are also used in lines conveying food solids and drainage lines containing sludge, since there are no obstructions in the flow path when fully open.
By applying a PFA coating to the inside or manufacturing with PVC or PTFE, it can also be used in chemical lines such as hydrochloric acid.
The structure of a ball valve is very simple. A ball-shaped valve piece with a cylindrical hole is contained inside, and the valve is opened and closed by rotating the valve ball 90°.
In general, the direction of the handle is fully closed when it is perpendicular to the flow path and fully open when it is parallel to the flow path. Since the direction of the handle is easy to distinguish, there is no need to worry about mishandling.
However, due to its structure, it is not suitable for flow control. PTFE is often used to seal the valve plug.
It is self-lubricating and can be used for many fluids, but cannot be used under high temperatures such as steam lines. Under high temperature and high pressure, heat-resistant materials or metal gaskets should be used.
Since the contact area between the gasket and the ball is large, the larger the bore size of the valve ball, the greater the opening and closing torque. 100 A or more will require a considerably large torque, making it difficult to open by hand.
There are several types of valves, such as Gate Valves, Check Valves, Globe Valves, and Ball Valves. Each type has different characteristics.
Gate valves and ball valves do not control flow rate. Globe valves can control the flow rate, but the pressure loss is higher. Each valve also has its own restrictions regarding the direction of flow.
Check valves are installed to prevent backflow, so they flow in one direction and not in the opposite direction. Globe valves are also basically one-directional. Depending on the structure, they may also be used in the reverse direction. Gate valves and ball valves basically have no restrictions on flow direction.
Valve ball valves operate by turning the handle 90° to stop the fluid. Because of its simple operation, it can open and close more rapidly than a gate valve. However, care must be taken to avoid water hammer.
In general, the handle is considered open when it is parallel to the piping.
There are two types of valve ball valves: reduced bore and full bore. Reduced bore valves have a valve plug opening smaller in diameter than the inside diameter of the piping. In the full bore, the valve plug opening is the same diameter as the pipe bore.
The pressure loss of a full bore is smaller than that of a reduced bore. Therefore, when designing piping, pressure loss calculations are performed to determine whether to use a reduced bore or a full bore. If there is a pressure drop problem due to a large pressure drop, a full bore will be used.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Swagelok Company was founded in 1947 in Cleveland, Ohio as a tube fitting manufacturer. The company serves numerous industries including the chemical, clean energy, food & beverage, industrial machinery, life sciences, and wastewater treatment industries. The copmany's product categories include hoses and flexible tubing, sample cylinders, welding systems, tubing and accessories, and measurement devices. The company's also offers engineering services including field engineering, onsite services, design and assembly services, training, and construction services.

Flomatic(R) Corporation, founded in Glens Falls, NY, in 1933 is a manufacturer of valves for the water and wastewater industry. The company's product portfolio includes Backflow Preventers, Break Off Plugs, Butterfly Valves, Check Valves and Constant Pressure Pump Control Valves. The company serves markets including Medical and Healthcare, Aerospace and Defense, Consumer Goods, Industrial Manufacturing and Construction and Building. The company also offers services including test and measuring the coating thickness of fusion bonded epoxy coat paint systems to ensure superior abrasion and corrosion resistance for longevity and verification organizations and labs to ensure safety.

Schubert & Salzer, Inc. was founded and incorporated in 1999 in Concord, NC, and the company supplier of manufacturing expertise for all commercial and technical needs, a fully equipped workshop plus delivery from the regional warehouse if required within a day. The portfolio of the company includes On/Off Valves, Globe Valves, Sliding Gate Valves, Ball-Sector Valves, Segmented Disc Valves, and more. Today there are five direct regional offices besides the American headquarters located across the United States with representatives and distributors servicing all 50 states and over a dozen countries.

3M Company was founded in 1902 and is headquartered in St. Paul, Minnesota. 3M provides diversified technology services globally. 3M operates through four segments: Safety and Industrial, Transportation and Electronics, Health Care, and Consumer. The Safety and Industrial segment offerings include industrial abrasives, masking, and natural and color-coated mineral granules for shingles. The Transportation and Electronics segment offerings include ceramic solutions, light management films, and electronics assembly solutions. The Healthcare segment offerings include wound care, dentistry and orthodontia solutions, and filtration and purification systems. The Consumer segment offerings include consumer bandages, picture hanging, and stationery products.

Jarecki Manufactures, founded in 1982 and headquartered in Fairview, Pennsylvania, is a manufacturer and rebuilder of industrial valves. Specializing in a diverse range of valves, the company provides solutions for various sectors including aerospace, oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power. It offers features such as one source supplier, valve rebuilding, and unique seat design. The company’s products encompass metal seat ball valves, control valves, and check valves. It also conducts a hydrostatic test and a seat leakage test on every valve. The company’s adherence to international standards earned its ISO 9001 certification, ensuring its valves provide efficient fluid control and regulation.

Engineering Laboratories, Inc. is a manufacturer of solid precision plastic balls, beads, and shapes, founded in 1935 and headquartered in Oakland, New Jersey. Some of the products offered by the company include Cellulose Acetate plastic balls, Delrin plastic balls, Nylon plastic balls, Polypropylene plastic balls, as well as PVC plastic balls, Santoprene 40D plastic balls, Santoprene 87A plastic balls, and PTFE plastic balls. Its fully staffed in-house tool room can also perform the customization and experimentation required for the research and development of custom items.

Trans-Valve was established in 1996 in Alabama as a manufacturer of valves for industrial and commercial use. The company produces various valves, valve seats, and seals. There are also Stainless Steel balls, Transmitter Isolation Ball Valves, bubble-tight shut-off, knife gates, and tank valves available because these valves have stainless steel bodies and some are crafted to be placed safely in wetted parts. Fastener mounting kits for Transmitter Isolation Ball Valve or for replacing an existing Knife gate valve are also available.

CIC Ball Company, founded in 2002, is a supplier and manufacturer of industrial balls, headquartered in North Wales, Pennsylvania. The company offers a range of products including plastic balls, hollow plastic balls, polyurethane balls, rubber balls, as well as steel balls, and phenolic balls for various applications, including environmental, pollution control, chemical processing, mining, and metal treatment. Their products are designed to meet the requirements of these industries, providing solutions for buoyancy, liquid level sensing, separation, agitation, and other related applications.

Hartford Technologies was founded in 1926 in Hartford, Connecticut and is currently headquartered in the suburbs of Hartford in Rocky Hill. The ISO 9001 certified company is a manufacturer of custom bearings and assembly solutions for the automotive, agriculture, medical, and other industries. The company has four primary product categories: Custom Bearings & Components, Precision Balls, Bearing Parts, and Precision Pins, Shafts, and Rollers. The company’s manufacturing and service capabilities include prototype development, 3D modeling, technical support including inventor management, and quality control systems.

DK Machine Inc., established in 1985, and headquartered in Fort Edward, New York, is a manufacturer of precision valve balls and spherical grinding. The company's products are made in all types of materials including titanium, inconel, monel, zirconium, and stainless steel which are used in industries, such as military, mining, pulp and paper, and oil & gas. DK Machine complies with MIL-I-45208A standards, which ensures that the company's products meets quality standards.

United States Ball Corp., founded in 1996, and based La Mirada, CA, has been a manufacturer and supplier of precision balls and spherical components such as valve balls, modified balls, spherical grinding & lappings, and gage balls utilizing materials such as titanium, iron, nickel, stainless steel, and copper. The balls are used in the medical, military, aerospace, pharmaceutical, and food industries. The company is ISO 9001:2015 and AS9100D certified and offers drilling and tapping services for balls used in jewelry, decoration, protective ends, and contact elements.

Plast-O-Matic was formed in 1967 in New Jersey, now situated in Cedar Grove, New Jersey. Plast-O-Matic serves aquarium, chemical dosing, chemical processing, metal finishing, semiconductor, wastewater treatment, water purification, and government application industries. Product offerings include product data sheets, CAD downloads, installation & maintenance instructions, ball valves, check valves, gauge guards, pressure regulators, process cooling sticks, anti-siphon valves, shut-off and diverter valves, sight glass & level indicators, solenoid valves, venting valves, other process controls & pumps, and custom valves.

Assured Automation was founded in 1983 and is headquartered in Roselle, New Jersey. Assured Automation is an ISO 9001:2015 certified supplier of automation equipment serving manufacturing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries among others. Assured Automation offers products in 2 major product lines: valves and flow meters. Valves include compact on/off valves, actuated 2-way and 3-way ball valves, actuated butterfly valves, actuated plug valves, actuated globe valves, manual gate valves, manual valves, lead free brass valves, thermal and remote shutoff valves, valve actuators, and valve & actuator accessories. Flow meters include water meters, fuel meters, industrial flow meters, lube-oil meters, and others.

CORTEC is an ISO certified company established in 2004 and is based in Houma, Louisiana, United States. The company is a manufacturing, design, sales and service organization that specializes in valve applications for high temperature and pressure use. The company’s products consist of trunnion ball valves, check vales, poppet valves, choke relief valves as well as drilling diverter valves that can be used in both onshore and offshore facilities. The company also offers services such as field installations, training programs for customers and maintains long-term relationship with the customers.

Surplus Valves and Fittings is a company located in Houston, Texas, and is a supplier of valves and fittings of various brands including Swagelok, Parker, and Crawford that are used for liquid and gas pressure applications in building and manufacturing industries. The company stocks various valves such as ball valves, bleed valves, check valves, diaphragm-seal valves, gauge valves among others and fittings including adapters, filters, nipples, O-rings, ferrules as well as connectors, and supplies them to customers within and outside Texas at fraction of the cost of retailers.

M&C TechGroup Germany GmbH, established in 1985 and headquartered in Ratingen, Germany, is a manufacturer of gas sampling, gas conditioning, and process control solutions. The company offers a wide range of products such as gas sample probes, heated lines, pumps, coolers, and more. It also provides filters, analyzers, temperature controllers, and gas conditioning systems. Its gas sample probe SP10 can withstand temperatures of up to 180 °C [356 °F]. The company serves several industries such as glass industry, chemical industry, environmental technology, power plants, and more.

Highlight Tech. Corporation, established in Tainan City, in 1977 is a manufacturer engaged in vacuum valves, gate vales and vacuum components for ultra-high vacuum environment process engineers. The company's product range includes LED, Touch flat panel display, semiconductor, optoelectronics technology and film vacuum coating. The company has service locations in Taiwan, China and worldwide representatives in Europe, Asia, The USA and Australia. In 2022 the company entered the Chinese market by selling the equipment of Thin-film Photovoltaic, developed by HTC.

Effebi Spa is an Italian ISO 9001:2015 and DVGW-certified manufacturer of brass valves that was established in Bovezzo, Brescia in 1973. The company produces butterfly valves for air or liquids, ball valves for gas or steam, and diaphragm valves for abrasive or corrosive fluids. It also offers valves utilizing pneumatic or electric actuators, specialized valves for solar systems or irrigation, and related accessories such as fittings. The company’s products are commonly used in the agricultural, petrochemical, and solar energy industries, as well as in heating, cooling, and plumbing systems.

KEIHIN CO., LTD, founded in Japan, in 1953 is a manufacturer of industrial valves. The company's product portfolio includes ball valves, ate valves used for isolating and regulating the flow of liquids, gases, and slurry, Check Valves, Pressure Relief Valves, and diaphragm valves used for sterile and aseptic applications in the pharmaceutical and food industries.Their products are used in markets such as Automotive and Transportation, Telecommunications, Industrial Automation, Healthcare and Medical Devices and Aerospace and Defense.
Scientific and Production Enterprise Sibtechnocenter, established in 2003 and headquartered in Tyumen, Russia, is a manufacturer and developer of blowout preventive oil and gas equipment. The company's products include hydraulic blowout preventers, manual BOPs, and coiled tubing equipment. It also offers preventive products with nominal bores of 156, 160, and 180 mm and working pressures of 21 and 35 MPa. Its design department specializes in import-substituting equipment, including valves, sealing complexes, and manifolds. The company produces serial and experimental high-precision metalworking products with CNC lathes, grinding, and sharpening machines. Its testing services include ultrasonic flaw detection, axial load, and low-temperature tests.

Bola-Tek Mfg. Co., Ltd., headquartered in Taichung, Taiwan, and founded in 1966, is a manufacturer of valve balls and stems. The company has expanded its product range to encompass several valve types, including ball valves, gate valves, globe valves, check valves, and butterfly valves. Its stainless steel and carbon steel products adhere to industry standards like ASTM, EN, JIS, and ANSI. It provides the API 607 fire-safe approved BT-V3WMH series, engineered for fire-safe performance. Additionally, it offers a 2-piece ball valve tailored for high-pressure applications, featuring a 6000psi rating.


OMAL S.p.A., established in 1981, is a manufacturer of quarter-turn pneumatic and electric actuators, along with ball, butterfly, and pneumatic valves, based in Rodengo Saiano, Brescia, Italy. The company's product line serves industries such as food, chemical, pharmaceutical, power as well as energy and naval sectors. With ISO 9001:2015 and AD2000 certifications, the company strategically invests in technical expertise and customization. It is a family-led business with over 100 employees across two locations in Italy.

Fitok Group, established in 1988 and located in Wuhan, Hubei, is a manufacturer that produces general instrumentation valves and fittings. The company offers a wide range of products, including instrumentation valves, fittings, manifolds, filters, and 2D/3D drawings. It also offers hoses, tubing, sampling systems, tooling, and subsea Products. Its product acts as a barrier, preventing active compounds from reacting with or adsorbing to the stainless steel. The company has received ISO 9001:2015, ISO 15848, and ASTM F1387 certification. It serves a wide range of industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, thermal power, nuclear power, and hydrogen applications.

HANSA-FLEX, been in business since 1962 and headquartered in Bremen, Germany, is a manufacturer of various types of hydraulic products and services. The company produces hoses, hose fittings, couplings, pipe fittings, and ball valves. It also fabricates hydraulic components, flanges, adapters, and pipes. The variants of its hoses, braided hoses, are oil, high-temperature, ozone, and weather-resistant. It has more than 80,000 parts relating to all aspects of hydraulics. It could also configure the customers’ hose lines based on their required specifications.

EM-Technik is a manufacturer and supplier of fittings and connectors fabricated from special plastics that was established in Maxforf, Germany, in 1965. The company’s products include couplings, fittings, and valves for controlling or regulating the flow of liquids in industrial processes. These are fabricated from chemical-resistant fluoropolymer plastics such as PEEK, PTFE, and PVDF. It also offers related accessories, including clamps, tubes, and seals. The company’s products are used mainly by its clients in petrochemical processing, power generation, and water and wastewater treatment.




Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Trans-Valve |
6.7%
|
| 2 | Engineering Laboratories, Inc. |
6.0%
|
| 3 | Schubert & Salzer, Inc. |
5.8%
|
| 4 | CORTEC |
5.6%
|
| 5 | CIC Ball Company |
5.6%
|
| 6 | Jarecki manufactures |
5.1%
|
| 7 | Flomatic(R) Corporation |
4.9%
|
| 8 | Hartford Technologies, Inc. |
4.4%
|
| 9 | Swagelok |
4.4%
|
| 10 | M&C TechGroup Germany GmbH |
4.2%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the valve ball page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
15 | 55.6% |
 Japan
Japan
|
4 | 14.8% |
 Germany
Germany
|
3 | 11.1% |
 Taiwan
Taiwan
|
2 | 7.4% |
 Italy
Italy
|
2 | 7.4% |
 Russia
Russia
|
1 | 3.7% |
216 products found
216 products
Wadatoku Co., Ltd.
170+ people viewing
Last viewed: 8 hours ago
Wadatoku Co., Ltd.
150+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Wadatoku Co., Ltd.
160+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Consus Co., Ltd.
270+ people viewing
Last viewed: 17 hours ago
■Features ・One-piece body, reduced port. - Lock handle (L handle) and butterfly handle (T handle) are available as options. - The wetted parts are...
Consus Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 20 hours ago
■Features - Three-piece body, full port structure, butt welding type. -Connection shape can be changed by replacing the end cap. -Standard lock han...
Consus Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Features ・Three-piece body, full port structure, socket welding type. -Standard lock handle ensures safety. -Connection shape can be changed by r...
Consus Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features ・Full port structure with low pressure loss. - A SUS handle is available as an option for the standard FC handle. ・The key can be locke...
Consus Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
■Features - A type with an integrated arm lock coupling adapter on the exit side. ・Full port structure with low pressure loss. - A SUS handle is a...
Consus Co., Ltd.
250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Features ・This is an air cylinder driven valve with an actuator for CSH-NW. ・The operating mode is single-acting or double-acting. - Solenoid va...
Consus Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
■Features - Threaded ball valve compatible with NPT (American tapered pipe thread standard). ・One-piece body, reduced port. - The wetted parts are...
Consus Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features ・This is an air cylinder driven valve with an actuator for CSH-PS. ・The operating mode is single-acting or double-acting. - Solenoid va...
Consus Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
■Features ・One-piece body, reduced port. ・One side has a tapered male thread (R) and the other side has a tapered female thread (Rc), simplifying...
Consus Co., Ltd.
250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 13 hours ago
■Features ・This is an air cylinder driven valve with an actuator for CSH-BS. ・The operating mode is single-acting or double-acting. - Solenoid va...
Consus Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 11 hours ago
■Features ・One-piece body, reduced port. - Tapered thread on the inlet side (Rc) and straight thread on the outlet side (G), making it ideal for p...
Consus Co., Ltd.
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 19 hours ago
■Features ・This is an air cylinder driven valve with an actuator for CSH-SS. ・The operating mode is single-acting or double-acting. - Solenoid va...
Consus Co., Ltd.
310+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features ・Two-piece body, full port. - The main body material is stainless steel 304 (handle cover green), which has excellent cost performance a...
Consus Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features ・CSJS's air cylinder driven valve with actuator. ・The operating mode is single-acting or double-acting. - Solenoid valves, limit switch...
Consus Co., Ltd.
250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
■Features ・Two-piece body, full port. - Lock handle (L handle) and butterfly handle (T handle) are available as options. - The main body material ...
Consus Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Features - Ball valve with electric actuator for NW flange connection for vacuum piping. ・Single phase AC 100V/200V 50HZ/60HZ DC 12/24V ・Waterpr...
Consus Co., Ltd.
220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
■Features ・Two-piece body, full port. - The main body material is stainless steel 316L (handle cover red) and the seat part is made of NEW PTFE, s...
Consus Co., Ltd.
250+ people viewing
Last viewed: 4 hours ago
■Features - Ball valve with screw connection electric actuator. ・Single phase AC 100V/200V 50HZ/60HZ DC 12/24V ・Waterproof/dustproof standard: IP...
Consus Co., Ltd.
210+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features - Threaded ball valve compatible with NPT (American tapered pipe thread standard). ・Two-piece body, full port. - The wetted parts are ma...
Consus Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 15 hours ago
■Features - Butt welding type ball valve with electric actuator. ・Single phase AC 100V/200V 50HZ/60HZ DC 12/24V ・Waterproof/dustproof standard: I...
Consus Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 23 hours ago
■Features ・Two-piece body, full port. ・The key can be locked at two points: fully closed and fully open. - Comes with a handle fixing function. -...
Consus Co., Ltd.
220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
■Features - Socket welding type ball valve with electric actuator. ・Single phase AC 100V/200V 50HZ/60HZ DC 12/24V ・Waterproof/dustproof standard:...
Consus Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
■Features - Three-piece body, full port structure. -Standard lock handle ensures safety. - Due to the bolt-tightening structure, it can be easily d...
Consus Co., Ltd.
220+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features - Three-piece body, full port structure, NW flange ball valve for vacuum piping. - Ideal for semiconductor-related and other equipment, v...
Consus Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 21 hours ago
■Features - Three-piece body, full port structure, NW flange ball valve for vacuum piping. - Ideal for semiconductor-related and other equipment, v...
Consus Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Features - Three-piece body, full port structure. -Standard lock handle ensures safety. -Connection shape can be changed by replacing the end cap....
Masaie Co., Ltd.
330+ people viewing
Last viewed: 26 minutes ago
■ Features ・ Latest Euro Normic EN331 compliant item ・ Full bore ・ Use: Cold water, compressed air, oil, fuel, non -corrosive chemicals, etc. ・...