All Categories
History
This section provides an overview for mig weldings as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 1 mig welding companies and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked mig welding companies as of February, 2026: 1.ARCO Welding Supply Co..
Table of Contents
Categories Related to MIG Weldings
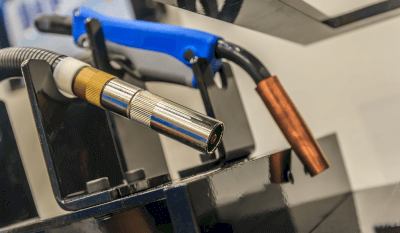
Metal inert gas (MIG) welding is a gas-shielded arc welding technique where an electric arc is created to weld metals. This process uses inert gases such as argon or helium as shield gases, which protect the welding area from atmospheric oxygen and prevent adverse reactions during the welding process.
Widely used in various industries, MIG welding is particularly effective for welding reactive metals like aluminum, copper, and stainless steel. Its ability to shield the weld area from air makes it ideal for welding non-ferrous metals. MIG welding is valued for its clean finish and fast welding speed, making it suitable for projects with many welding points or those requiring rapid completion. This method is efficient for large-scale welding operations.
In MIG welding, an arc discharge is generated between the electrode and the metal workpiece, creating temperatures of 5,000 to 20,000 degrees to melt various materials for welding. The use of inert gas ensures that no chemical reactions occur between the gas and the component, resulting in a clean weld finish. However, MIG welding typically has weaker joint strength compared to MAG welding due to the spread of the arc discharge, leading to shallower penetration.
The electrode in MIG welding melts during the process and is continuously supplied by an automatic feeding mechanism, obviating the need for manual electrode replacement. Different types of electrodes, including plated or flux-containing ones, are used depending on the specific welding requirements.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Ranking as of February 2026
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ARCO Welding Supply Co. |
100.0%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the mig welding page as of February 2026. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History