All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for lan modules as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 23 lan module manufacturers and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked lan module companies as of July, 2025: 1.IPC2U Group, 2.Schmersal GmbH & Co. KG, 3.ATLAS GENTECH.
Table of Contents
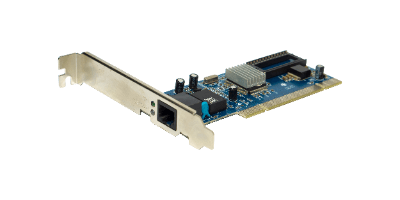
A LAN module is a critical component enabling devices to connect to a local area network (LAN), either through wired or wireless connections. These modules, which can be integrated into devices or connected via interfaces like USB or PCI, facilitate data exchange and communication over networks, supporting standards such as TCP/IP and encryption protocols for secure wireless communications.
LAN modules are integral to a wide array of devices, extending beyond PCs and smartphones to:
Their versatility makes them foundational to the connectivity of IoT devices devices, empowering almost any networked device.
LAN modules operate based on several core principles:
For wired LAN modules, the category of LAN cables used affects transmission speed, with categories ranging from CAT5e to CAT8, supporting speeds up to 40 Gbps. Selection of the appropriate cable category is crucial for maximizing network performance.
Modern LAN modules cater to the IoT's demands with compact sizes and low power consumption, ensuring they fit into various devices and maintain efficiency, especially in battery-powered scenarios.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area

Intel Corporation, an American company founded in 1968 and headquartered in Santa Clara, California, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in the design and production of semiconductor microprocessors. The company's product portfolio includes processors, graphics processing units, software, wireless products, and various other items. These products find applications in education, transportation, financial services, retail, and government. The company offers customer services including technical support, software development, cloud services, security services, and research and development collaboration. The company has manufacturing facilities, research and development centers, sales offices, and partnerships with businesses and organizations across various continents.

RTD Embedded Technologies, Inc. located in Pennsylvania, USA, founded in 1985, is a manufacturer and supplier specializing in rugged and modular computer boards and systems. The company’s products include digital signal processing, data acquisition and processing, video capture, UPS technologies among others. Its experience and knowledge base of computer technologies allows quick and efficient solutions to customer requirements. The company is AS9100 and ISO 9001 certified which prioritizes quality with a zero-defect approach, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement across various operational areas.

Zones, LLC, established in 1986, is an American supplier of information technology (IT) solutions and services, headquartered in Auburn, Washington. The company offers cloud and data center solutions, covering cloud implementation and migration, infrastructure management, and data protection. The EdgeConnect services, featuring the Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) solutions, are offered to optimize networking systems. The company also provides security assessment, implementation, and management services, along with digital workplace solutions. Complementing these services, the company offers a range of products from renowned brands such as Apple, Dell, HP, Intel, and Microsoft, including desktops and workstations, notebooks and tablets, servers, software, and memory.

Jansum Electronics Dongguan Co. Ltd., located in Changping Town, Dongguan City, is a manufacturer specializing in R&D and production of various magnetic components, catering to diverse industries and the global market. The company offes a wide range of products, including ethernet transformers, telecom transformers, inductors, power transformers, solar inverter inductors, and more. These products find various applications in routers, medical devices, smart meter applications, security equipments, among other electronic equipments that require magnetic components.

TDK Electronics, established in 1935 and headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is a developer, manufacturer of electronic components and systems. Its product portfolio spans capacitors, ferrites, and inductors, including piezo and protection devices. The company also offers sensors and sensor systems, covering temperature, pressure, magnetic, and MEMS sensors. Furthermore, TDK provides power supplies, energy devices, magnetic heads, and more, all branded under TDK, EPCOS, InvenSense, Micronas, Tronics, and TDK-Lambda, catering to diverse electronic needs. The company operates about 20 development and manufacturing sites, along with a network of design, manufacturing locations, and sales offices situated in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America.

Axiomtek Co., Ltd., established in 1990 and headquartered in Taipei City, Taiwan, is a manufacturer of industrial computer products. The product range includes industrial motherboards, single-board computers, embedded systems, ruggedized and fanless computers, and touch panel computers. These products are equipped with stability, durability, and optimal-performance capabilities, making them ideal for various industries such as industrial automation, transportation, gaming, healthcare, and digital signage to offer advanced solutions to meet the evolving needs of industrial computing solutions.

Nexcom was established in 1992 and is headquartered in Taipei, Taiwan developing and supplying innovative technologies, products, and services to empower businesses in The company offers a diverse range of products and solutions, including industrial-grade computers, embedded systems, IoT platforms, network appliances, and digital signage solutions. These offerings cater to applications such as factory automation, transportation, retail, healthcare, and smart cities. The company also deals with system integrators, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and end-users who require specialized computing solutions, so Nexcom produces tailored solutions that meet specific industry requirements.

IPC2U Group, established in 1990 and headquartered in Langenhagen, Germany, is an EN ISO 9001:2015-certified manufacturer of industrial computer systems for the commerical and industrial sectors. The company primarily produces industrial PCs for applications in the energy, transportation, and automation sectors. It also offers panel PC touchscreen interfaces for machine control, embeddable systems for industrial facilities, and digital signage for advertising or office usage. The company mainly serves clients in the energy, transportation, and industrial sectors.

Advantech Co., Ltd., established in 1981 in Neihu District, Taipei, is a pioneering manufacturer and designer of a range of products, solutions, and services. The company boasts an extensive product portfolio that includes system integration, customer-centric design services, cutting-edge embedded systems, automation products, and global logistics support. Its aim is to usher in an era of an intelligent planet through its automation and embedded computing products and solutions. These diverse products and services empower smarter ways of working and living to enhance the quality of life and productivity across various industries.

SMK Corporation, with its roots dating back to 1925 in Tokyo, Japan, has established itself as a manufacturer specializing in connectors, remote control systems, and electronic components. It boasts a diverse product portfolio that includes connectors, plugs, switches, remote control units, and touch panels. These quality components play pivotal roles in an array of applications and an assortment of industries, ranging from home electronics for the operation of devices like air conditioners, to the automotive sector in the rear-view mirrors. Furthermore, its solutions extend to the realm of mobile devices, wearable technology, such as smart glasses, and healthcare equipment.

Schmersal GmbH & Co. KG, founded in 1945, by Heinz and Philip Schmersal, is a name in safety technology, is a manufacturer of safety technology solutions, specializing in switchgear and control devices for various industries. With a diverse range of mechanical and electro-sensitive switching devices, they offer an extensive collection of safety switching systems and devices for safeguarding both humans and machinery. The company looks after three key domains: lift technology, automation technology, and safety technology. Their substantial approach position them as a global supplier of safety switching devices, catering to the safety and automation needs of various industries.

OnLogic, started in 2003 and headquartered in South Burlington, Vermont, is an ISO 9001-certified manufacturer of configurable small form factor computers. Its product portfolio includes rugged computers, panel PCs, and embedded computers, and it offers Cat 4 or Cat 6 variations for its extrovert 4G LTE modems, which are six months pre-certified and carrier-approved. Some of the company’s systems have been operating for over ten years. The company’s three locations across North America, Europe, and Asia can handle manufacturing runs of computers from 1 to over 10,000, and the company also offers OEM services like prototyping, branding, and lifecycle management.

Hunter Industries, established in 1981, and based in California, USA, is a manufacturer and supplier of residential and commercial irrigation. Their product portfolio includes rotors, AT systems, nozzles, spray bottles, hydras, controllers, sensors, remotes, valves, and accessories. The company offers a range of water-efficient, easy-to-use irrigation solutions for residential, commercial, and golf course applications. The products are used in various industries which include irrigation systems, landscape lighting, and custom molding industries.

Sony Professional, established in 1978 and headquartered in Basingstoke, United Kingdom, operates as a manufacturer and supplier specializing in professional audiovisual and broadcasting equipment. Their main product range encompasses quality cameras, camcorders, monitors, and audio solutions. Sony Professional plays a critical role in the media and entertainment industry, providing modern technology for content creation, broadcasting, and production. For its innovation and reliability, Sony's professional solutions backs significantly to capturing and delivering captivating visuals and audio experiences across a range of applications.

Innodisk Corporation was established in 2005 and is a manufacturer and supplier of industrial embedded Flash and DRAM solutions based in Xizhi District, New Taipei City, Taiwan. The company manufactures various products such as embeeded disk card, industrial embedded DRAM memory modules, and server workstation memory. The products have been used in various industries such as server applications, embedded systems, and casino gaming. The company has certified in ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, and ISO 45001:2018.

Epson America, Inc. is a manufacturer and distributor of digital imaging products established in 1975 as a US subsidiary of Japan’s Seiko Epson Corporation. The company produces various digital imaging products for home and business use, including cameras, printers, home theater systems, and scanners, as well as printing accessories like ink and software. It also manufactures wearable devices, point-of-sale systems, and robots for industrial or factory automation, such as 6-axis and SCARA models. Epson America is headquartered in Los Alamitos, California, with regional offices, authorized resellers and service centers across North America including in Chicago, Atlanta, and Toronto.







B&H Foto & Electronics Corporation, founded in 1973 and based in Manhattan, New York City, is a retailer of photo, video, and other technological equipment. B&H is an authorized seller of Sony, Panasonic, Canon, Fuji, and more. The company serves photographers, musicians, and professionals with products related to film, music, photography, audio, art, and technology. The company's main products include photography gear, computers, televisions, drones, surveillance systems, and more. B&H store has nearly 500,000 items in stock for customers who need them.
Ranking as of July 2025
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IPC2U Group |
57.1%
|
| 2 | Schmersal GmbH & Co. KG |
4.9%
|
| 3 | ATLAS GENTECH |
4.3%
|
| 4 | RTD Embedded Technologies, Inc. |
4.3%
|
| 5 | B&H Foto and Electronics Corp. |
3.8%
|
| 6 | Zones, Inc. |
3.8%
|
| 7 | HUNTER INDUSTRIES |
3.8%
|
| 8 | OnLogic |
3.8%
|
| 9 | Electronic Security Sales |
3.3%
|
| 10 | Tritech Solutions |
2.7%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the lan module page as of July 2025. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
3 | 21.4% |
 China
China
|
3 | 21.4% |
 Taiwan
Taiwan
|
3 | 21.4% |
 Japan
Japan
|
2 | 14.3% |
 New Zealand
New Zealand
|
1 | 7.1% |
 Australia
Australia
|
1 | 7.1% |
 India
India
|
1 | 7.1% |
51 products found
51 products
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
500+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
■Summary This is an IEEE 802.11ah Wi-Fi HaLow™ wireless module that uses Morse Micro's MM6108 and supports SDIO/SPI host interface. This product o...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
390+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
Features ■Wi-Fi6 with stable communication, low power consumption, and high speed communication Wi-Fi6 is characterized by high-speed communication...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
350+ people viewing
Last viewed: 6 hours ago
■Summary This is an SDIO type wireless LAN combo module that supports IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac and Bluetooth® v5.0 BR/EDR/LE. This product is equipped...
Shinko Shoji Co., Ltd.
310+ people viewing
Last viewed: 17 hours ago
We offer a ``single board type'' that is equipped with major connectors such as USB and wired LAN, and a ``module type'' that can be freely expande...
Adbury System Co., Ltd.
290+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Add USB/LAN to Armadillo-IoT This is a dedicated add-on module that allows you to add USB and LAN ports to Armadillo-IoT Gateway G3/Armadillo-X1 (...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
310+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
■Summary This product is an SDIO type wireless LAN combo module that supports IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac and Bluetooth®. This product is equipped with Q...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
340+ people viewing
Last viewed: 15 hours ago
■Summary This product is an SDIO type wireless LAN combo module that supports IEEE 802.11ac/a/b/g/n and Bluetooth® v5.0 BR/EDR/LE. This product, wh...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
330+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 hour ago
■Summary SDIO SiP (System-in-Package) module equipped with Qualcomm's QCA9377 system-on-chip (SoC) and compatible with IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac and Bl...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
330+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
■Summary This product is a wireless LAN device driver exclusively for the SDIO wireless LAN module SX-SDMAC series and SX-SDPAC equipped with the Q...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
320+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
Overview SX-PCEAX-AP is an embedded wireless LAN module dedicated to Wi-Fi6 compatible access points equipped with Qualcomm's QCN9072 chipset. Even...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
280+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
Overview SX-PCEAX-AP6E is a built-in wireless LAN module dedicated to access points that supports Wi-Fi6E and uses Qualcomm's QCN9072 chipset. Desi...
Silex Technology Co., Ltd.
240+ people viewing
Last viewed: 21 hours ago
■Summary For those who want to equip their devices with the latest wireless LAN standard, IEEE 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), and the new frequency, the 6GHz ...
Optar Co., Ltd.
260+ people viewing
Last viewed: 16 hours ago
The LAN control power supply (abbreviation: LAN power supply) is an LED power supply that complies with the Ethernet standard. Insert a LAN cable i...
Cybernetech Co., Ltd.
530+ people viewing
■Features We offer seven different types of media converter line cards as 1Gb/10Gb card-type medicoms installed in collective medicon racks. These ...
6 models listed
SANYO DENKI CO., LTD.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 22 hours ago
Features ■High-speed communication Equipped with 1 Gigabit Ethernet. It can be used in the latest network environments such as virtualized systems ...
SANYO DENKI CO., LTD.
200+ people viewing
Last viewed: 12 hours ago
Features ■This is an interface card installed in our UPS to output external transfer signals from the UPS using voltage-free contacts. A contact or...
SANYO DENKI CO., LTD.
150+ people viewing
Features ■Contributing to the adoption of IoT devices By connecting the motion controller to a wireless LAN, you can wirelessly monitor equipment. ...
Airia Co., Ltd.
190+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Add two gigabit LANs This product is a PCI Express board that allows you to add two Gigabit LANs. ■Spare network line By adding two LANs, you can...
Airia Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
■This product adds a gigabit transfer LAN port to your computer. By connecting this product to the PCI Express slot on your computer's motherboard,...
Airia Co., Ltd.
200+ people viewing
■2.5Gbps (Gigabit) high-speed communication Mr.JACK is capable of 2.5Gbps (gigabit) transfer, which is 25 times faster than the commonly used 100Mb...
FXC Co., Ltd.
580+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Summary ・FXC optical modules are available in a lineup that supports QSFP28/QSFP+/SFP28/SFP+/SFP. ・There are also models that support communicat...
DWIN Technology
400+ people viewing
■Features ・Main chip ESP8266+4MB Flash ・Supports 802.11 (2.4GHz), frequency range 2.4G~2.5G (2,400M~2,483.5M) ・Antenna types include PCB onboard...
FXC Co., Ltd.
540+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Summary ・FXC optical modules are available in a lineup that supports QSFP28/QSFP+/SFP28/SFP+/SFP. ・There are also models that support communicat...
Codec Co., Ltd.
380+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
■Product features PC cards can be used with the latest desktop PCs. ・Compared to PCI boards and PCIe boards, you have a wider choice of wireless L...
L&F Co., Ltd.
230+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
Equipped with Asix AX88796BLF+ RJ45 connector with built-in transformer. A small universal board equipped with a 10/100 BASE-TX interface LAN contr...
L&F Co., Ltd.
170+ people viewing
Equipped with Asix AX88796BLF+ RJ45 connector with built-in transformer. This product is equipped with a 10/100 BASE-TX interface LAN controller AX...
Compass Lab Co., Ltd.
140+ people viewing
Last viewed: 37 minutes ago
NetCom Devices is a serial device server on the net. Serial devices connected to RS232, RS422, RS485, etc. are connected via LAN, and data communic...
Compass Lab Co., Ltd.
120+ people viewing
Last viewed: 2 hours ago
NetCom Devices is a serial device server on the net. Serial devices connected to RS232, RS422, RS485, etc. are connected via LAN, and data communic...
FXC Co., Ltd.
510+ people viewing
Last viewed: 3 hours ago
■Summary ・FXC optical modules are available in a lineup that supports QSFP28/QSFP+/SFP28/SFP+/SFP. ・There are also models that support communicat...
FXC Co., Ltd.
1000+ people viewing
Last viewed: 1 day ago
■Summary ・FXC optical modules are available in a lineup that supports QSFP28/QSFP+/SFP28/SFP+/SFP. ・There are also models that support communicat...