All Categories
History

This section provides an overview for plastic processings as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 1 plastic processing companies and their company rankings.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Plastic Processings
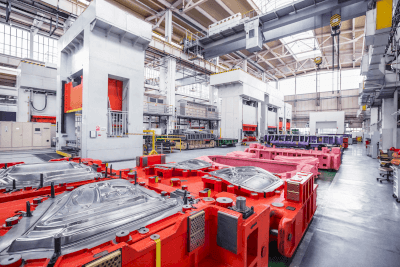
Plastic processing refers to a method of shaping materials through external force, causing permanent deformation. Common materials like aluminum, when subjected to sufficient force, maintain their deformed state and do not return to their original shape.
This process shapes materials into desired forms, utilizing the material’s plastic zone property, where it remains permanently deformed under force.
Plastic processing is widely used in metal material fabrication, including press processing, where metal is deformed into predefined shapes using mechanical press machines. This process is integral in creating products like automobile frames, where precision shaping is essential.
The process leverages the material’s transition from its elastic zone, where it can return to its original shape, to its plastic zone, where it remains permanently deformed. Brittle materials like glass, which crack under deformation, are unsuitable for plastic processing. This method also induces work hardening, enhancing the material's strength, and reduces residual stress after the external force is removed.
Forging shapes metal through striking with tools or molds, using forging hammers or presses.
Rolling stretches metal by passing it between rolls, commonly used in steel mills for sheet metal production.
Press processing includes shearing, bending, and squeezing methods, using mechanical, hydraulic, or hand press machines.
Extrusion involves pressing material through a die to create long shapes like wires and rods, using extrusion molding machines.
Drawing pulls material through a die to create bar materials, suitable for making thin wires or fine needles.
This method uses concave-convex molds pressed against a round bar to create bolts suitable for materials with certain elongation and strength properties.
Plastic processing enhances material quality through work hardening and stress reduction. It's a cost-effective method, as it doesn’t generate waste like cutting processing. However, mold costs can be high, and prototyping may use other methods like total cutting or 3D printing. When automated with molds, processing time reduces, making it ideal for mass production of metal parts in industries like automotive and appliance manufacturing.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area


Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 Japan
Japan
|
1 | 100.0% |
1 products found
1 products
HIKARI KOGYO
720+ people viewing
■What is the MF Technology Award? Sponsored by the Japan Forming Machinery Manufacturers Association, this is the world's highest award for presses...