All Categories
History












This section provides an overview for press services as well as their applications and principles. Also, please take a look at the list of 13 press service companies and their company rankings. Here are the top-ranked press service companies as of March, 2026: 1.2G Energy, 2.Green Lotus Agency, 3.Press Release Network.
Table of Contents
Categories Related to Press Services

A press service is a process of deforming soft metals and other materials using a press machine.
A die is pressed against the material and strong pressure is applied by the press machine to deform it into the desired shape. The pressing mold is used by cutting and turning alloy steel such as pre-hardened steel and stainless steel.
A press service is characterized by the fact that the metal is deformed and formed in a single press by applying strong pressure. The greatest advantage is that a large number of pieces can be mass-produced at once in a short time because the processing time is extremely short.
Presses also require an initial investment and are recommended when products need to be mass-produced over a long period of time.
Press services are used for the mass production of a single part.
It is often used to form familiar metal products because it is a simple and easily mass-produced process. Many of the frames of automobiles and home appliances are made of metal, and most of the parts are press-formed because they can be processed to the same shape with high precision.
Generally, it takes 3 to 6 months to produce a single die, including fine adjustments to improve dimensional accuracy during processing. In order to accurately shape complex bends and curved surfaces, such as those found in the outer panels of automobiles, it is necessary to press a single sheet multiple times using multiple molds.
Press services are not suitable for parts used only in small quantities because of the time and cost required to prepare the dies.
The principle of press services is to cause plastic deformation of the metal to be formed by pressing a die against it while applying high pressure with a press machine.
When a load is applied to a metal, a force is generated that tries to return the metal to its original shape. This is called plastic deformation. By causing plastic deformation in a press machine all at once, large quantities can be produced in a short time with high accuracy.
There are three major types of press services:
These three processes may be combined to perform a series of processes on a single workpiece of metal.
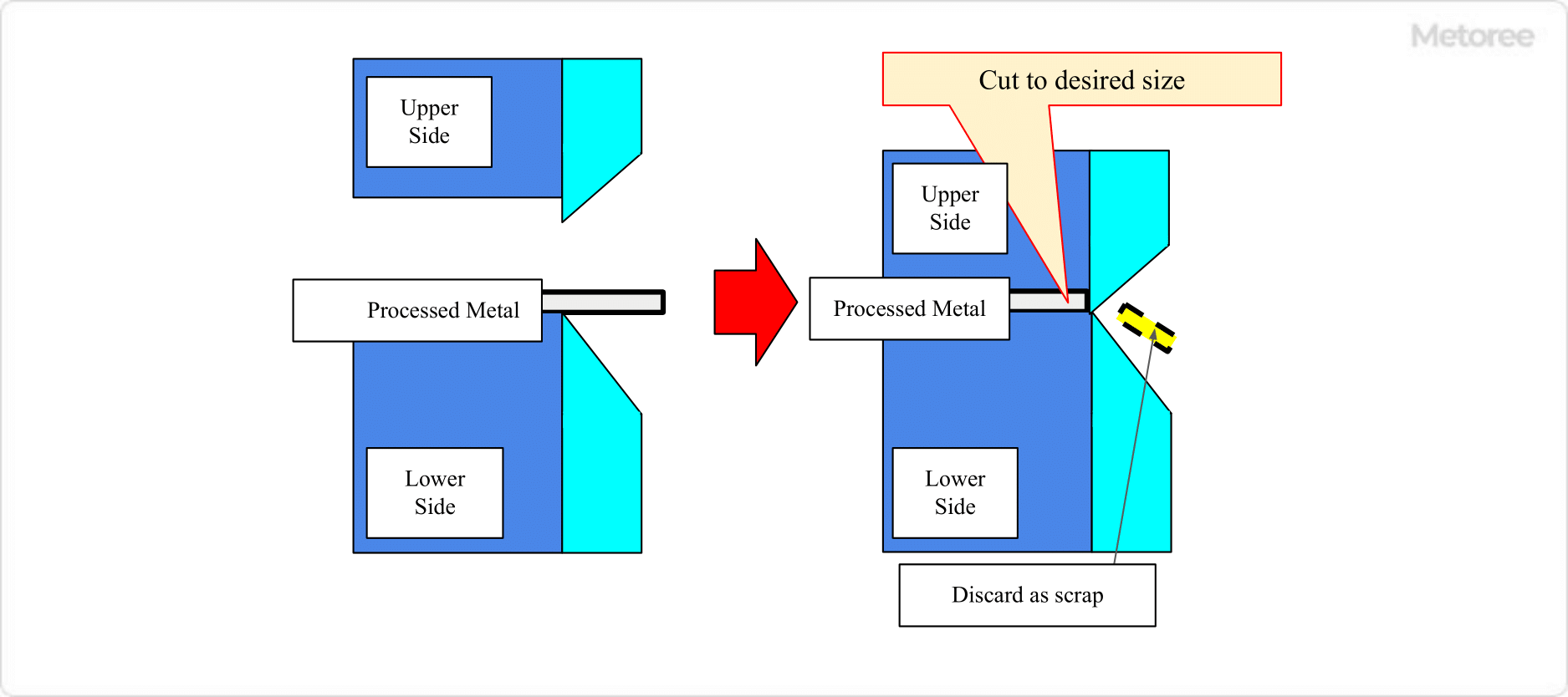
Figure 1. Shearing
Shearing is a process of cutting a workpiece to a desired size or shape by preparing two blades on the top and bottom of the workpiece and pressing them together at once. As a processing method that applies shearing processing, there is also a processing method called punching processing in which a target mold is punched like a cookie cutter to cut out the desired shape from a flat plate-shaped processing agent.
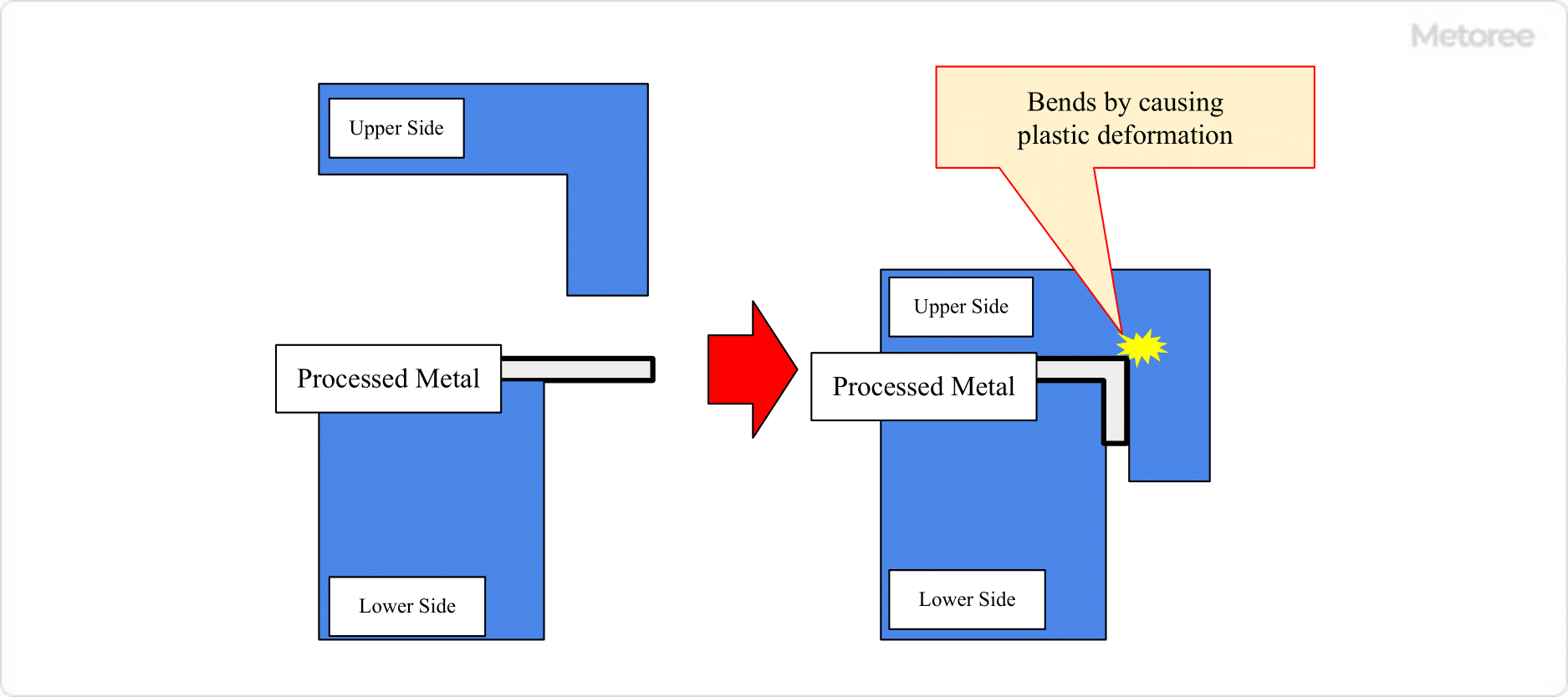
Figure 2. Bending process
Bending is a process for bending metal by pressing a V- or L-shaped bending die against the material to be processed using press services. Since many metals are hard and cannot be bent without strong pressure, it is important to bend them with a press machine that can apply strong pressure at once.
The use of press services allows the angle of bending to be set precisely, but there is a limit to the angle of bending that can be set because undercutting may occur, where the product cannot be pulled out of the die after processing.
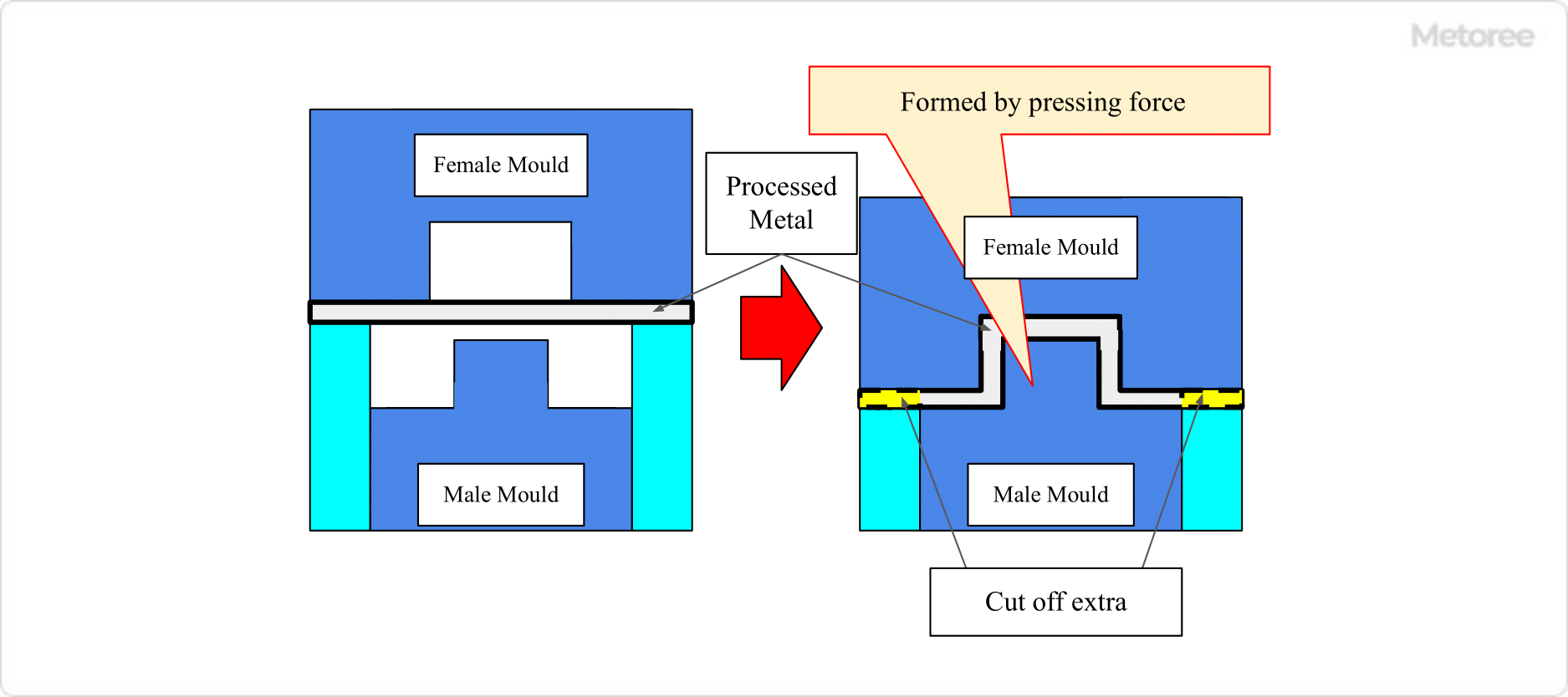
Figure 3. Drawing process
Drawing is a processing method in which a flat sheet of metal is deformed into a container shape by preparing a concave part of the desired shape on the receiving side of the press services and a convex part on the extruding side and applying it to the press machine.
Since the concavities and convexities are aligned to form the desired shape, right-angle bending cannot be handled, but a three-dimensional shape with a rounded edge can be formed. Compared to bending, it is necessary to hold down the outer circumference firmly because it is pressed against the mold, so the material is required to be one size larger, and the material cost tends to be higher.
These processing methods can be combined to create more complex shapes.
*Including some distributors, etc.
Sort by Features
Sort by Area




Pathlabs is an American digital media distributor and advertisement campaign promoter based in Missoula Montana, founded in 2021. The company provides its services to advertising agencies as a media execution partner, assisting in the design, implementation, and analytics of online advertising campaigns. Campaign promotion methods it utilizes include online video, digital audio, affiliate marketing, paid social media posts, and sponsored social network content. The company has worked with various websites and services including TikTok, SnapChat, Hulu, Facebook Marketing Partners, and Google Ads.

Advanex Inc, established in 1946 and headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is a manufacturer of precision springs and pressed components. The company's products include wire springs, flat springs, deep drawings, insert moldings and spring assemblies. It has a prototyping center equipped with five types of NC multi-forming machines that provides customers customization facilities. It provides Finite element analysis services to predict the effect of physical influences such as loads and vibrations on the product.and wire spring calculation program to calculate load or durability of a spring. The company is ISO 9001 certified and follows an inspection system with various equipment for quality checking.

2G Energy, founded in Germany in 1995, is a manufacturer of combined heat and power plants (CHP) for the decentralized provision of power and heat based on gas motors. The company's product portfolio includes plants with an electrical output of 20 to 2,000 kW. , and digital and control solutions. The company serves industries such as farming to municipalities, the housing industry, commercial enterprises, medium-sized industries and large industries to the energy sector.







Ranking as of March 2026
Derivation Method| Rank | Company | Click Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2G Energy |
19.0%
|
| 2 | Green Lotus Agency |
14.3%
|
| 3 | Press Release Network |
9.5%
|
| 4 | EIN Presswire |
9.5%
|
| 5 | The Really Useful Information Company |
9.5%
|
| 6 | The Cly-Del Manufacturing Company |
4.8%
|
| 7 | Pathlabs. |
4.8%
|
| 8 | 38 Digital Market |
4.8%
|
| 9 | SRV Media Pvt. Ltd |
4.8%
|
| 10 | FatJoe |
4.8%
|
Derivation Method
The ranking is calculated based on the click share within the press service page as of March 2026. Click share is defined as the total number of clicks for all companies during the period divided by the number of clicks for each company.Number of Employees
Newly Established Company
Company with a History
*Including some distributors, etc.
*Including some distributors, etc.
| Country | Number of Companies | Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
 United States of America
United States of America
|
4 | 44.4% |
 Japan
Japan
|
2 | 22.2% |
| Morocco | 1 | 11.1% |
 Canada
Canada
|
1 | 11.1% |
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
|
1 | 11.1% |